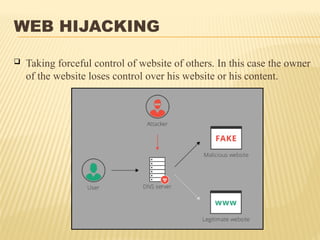
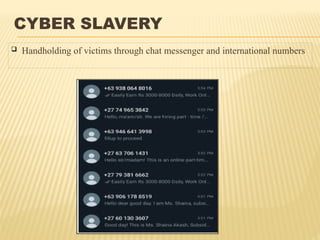
The virtual world has taken over the real one, E-business and E-commerce, which are the new mantras and electronic transactions dominate the overall business paradigm.
In this rapidly evolving e-world that depends on free flowing information, security is the major problem to be considered. We should know the types of cyber crime and also the how to prevent cyber crime. We should have knowledge about cyber security and steps for reporting cyber crime.