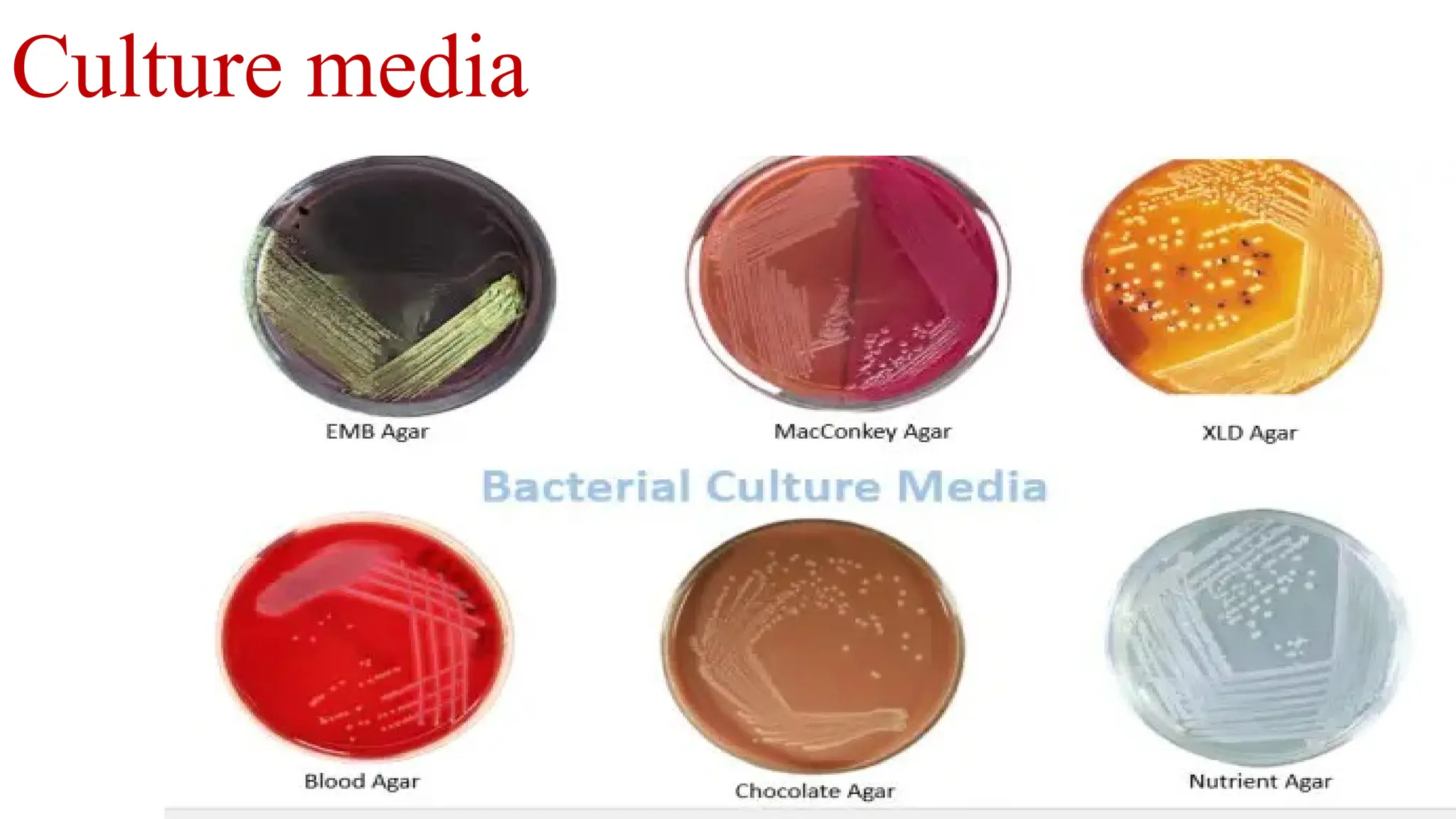
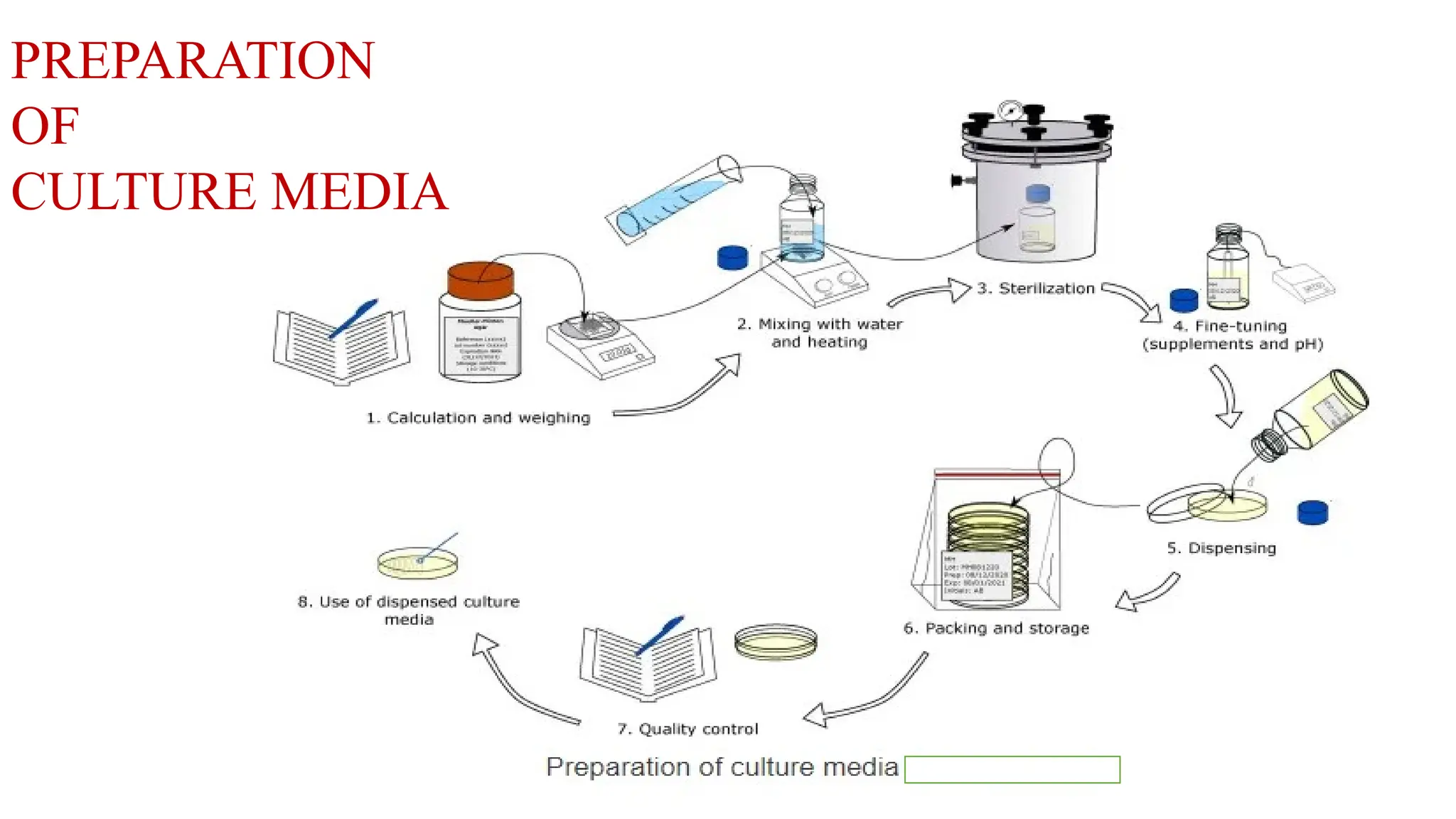
Culture media are essential for the growth of microorganisms in laboratories, typically based on meat extract or broth with additional nutrients. There are various types of culture media including simple, enriched, selective, differential, and enrichment media, each serving specific purposes in isolating and promoting bacterial growth. Solid media is created using gelatin or agar, while enriched media may include substances like blood or serum to support pathogenic bacteria's growth.