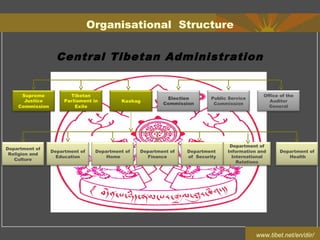
The document summarizes the organizational structure and background of the Central Tibetan Administration (CTA). It describes the executive, legislative, and judicial branches of the CTA including the Sikyong (President), Tibetan Parliament, Supreme Justice Commission, and various departments. It provides context that the CTA was established in 1959 in India after the Dalai Lama and thousands of Tibetans fled Chinese occupation of Tibet. The CTA aims to govern and provide services for Tibetans in exile until they can return to a free Tibet.