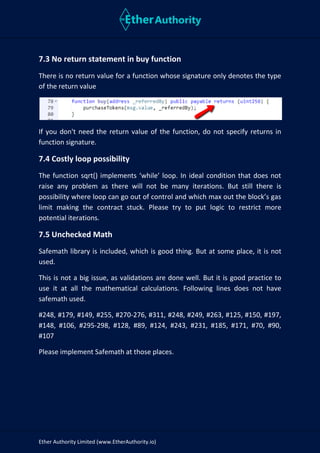
Crypto mining token is a platform built for short term mining profit accumulation. Our service works as exchange walt for securing your mining assets in form of decentralized fully automated (CMT) token. Token is built to function without any 2nd or 3rd party control.
According to the standard audit assessment, the Customer`s solidity smart contracts are “Secured”.
We used various tools like Slither, Solhint and Remix IDE. At the same time this finding is based on critical analysis of the manual audit.