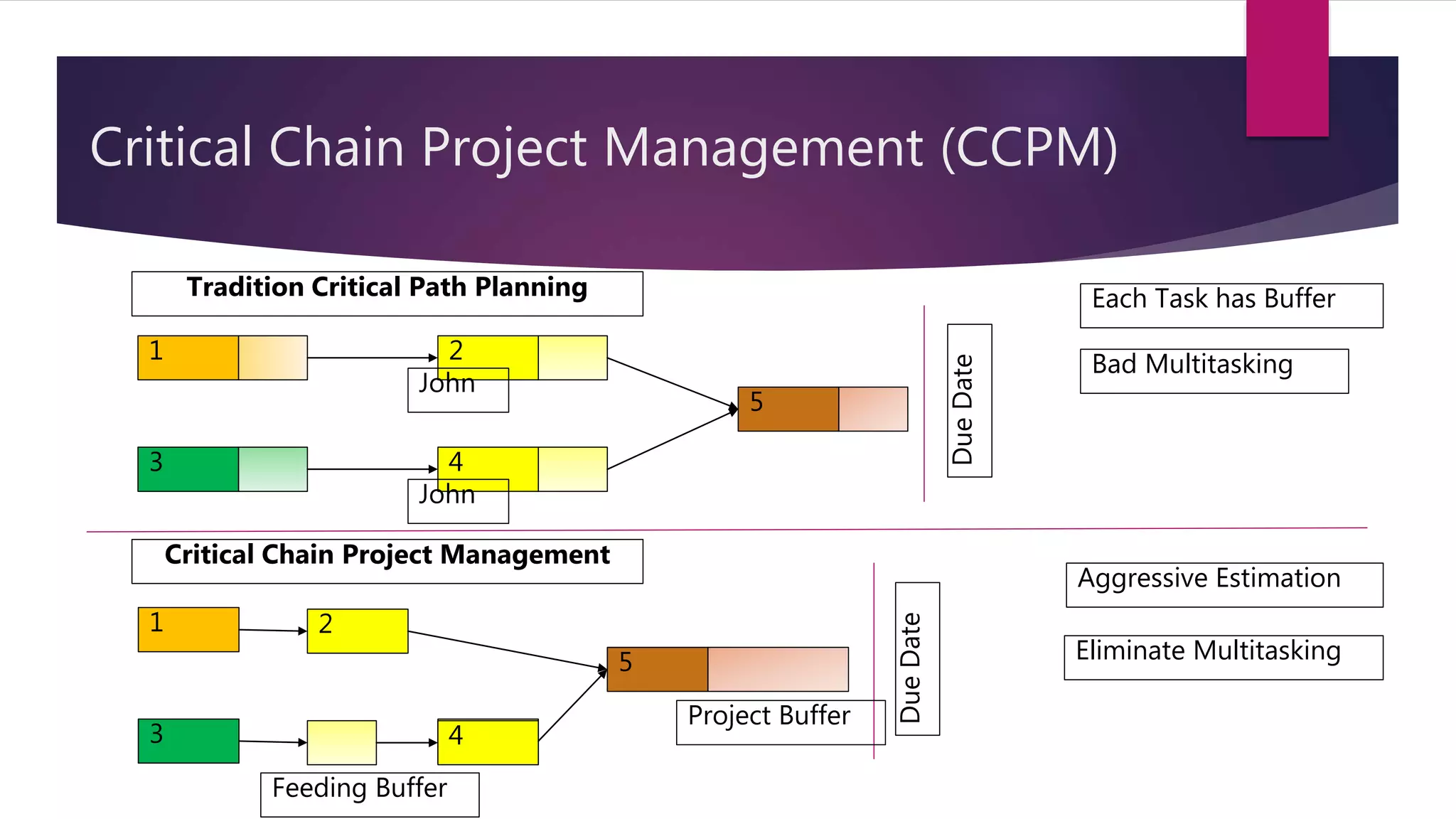
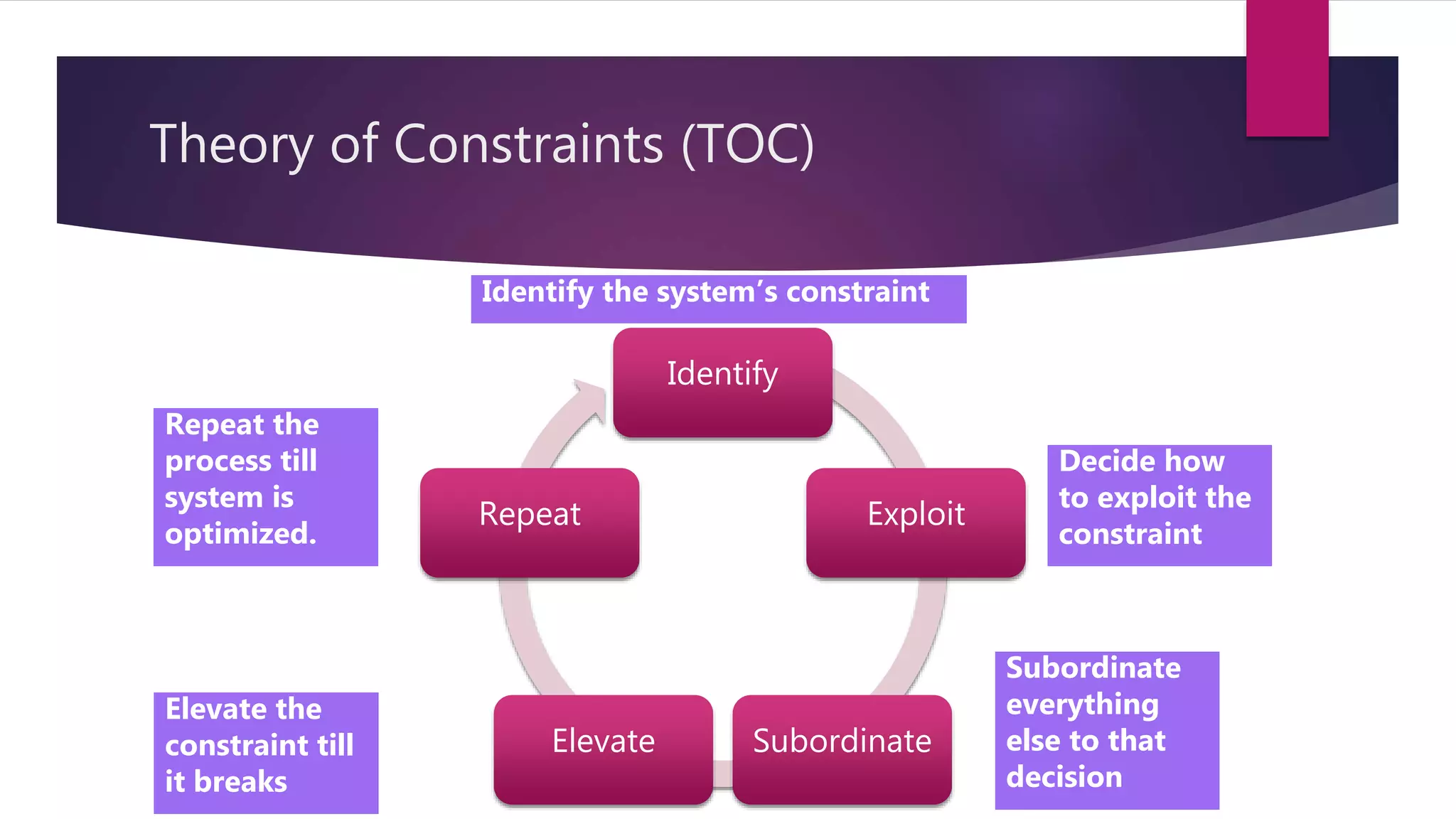
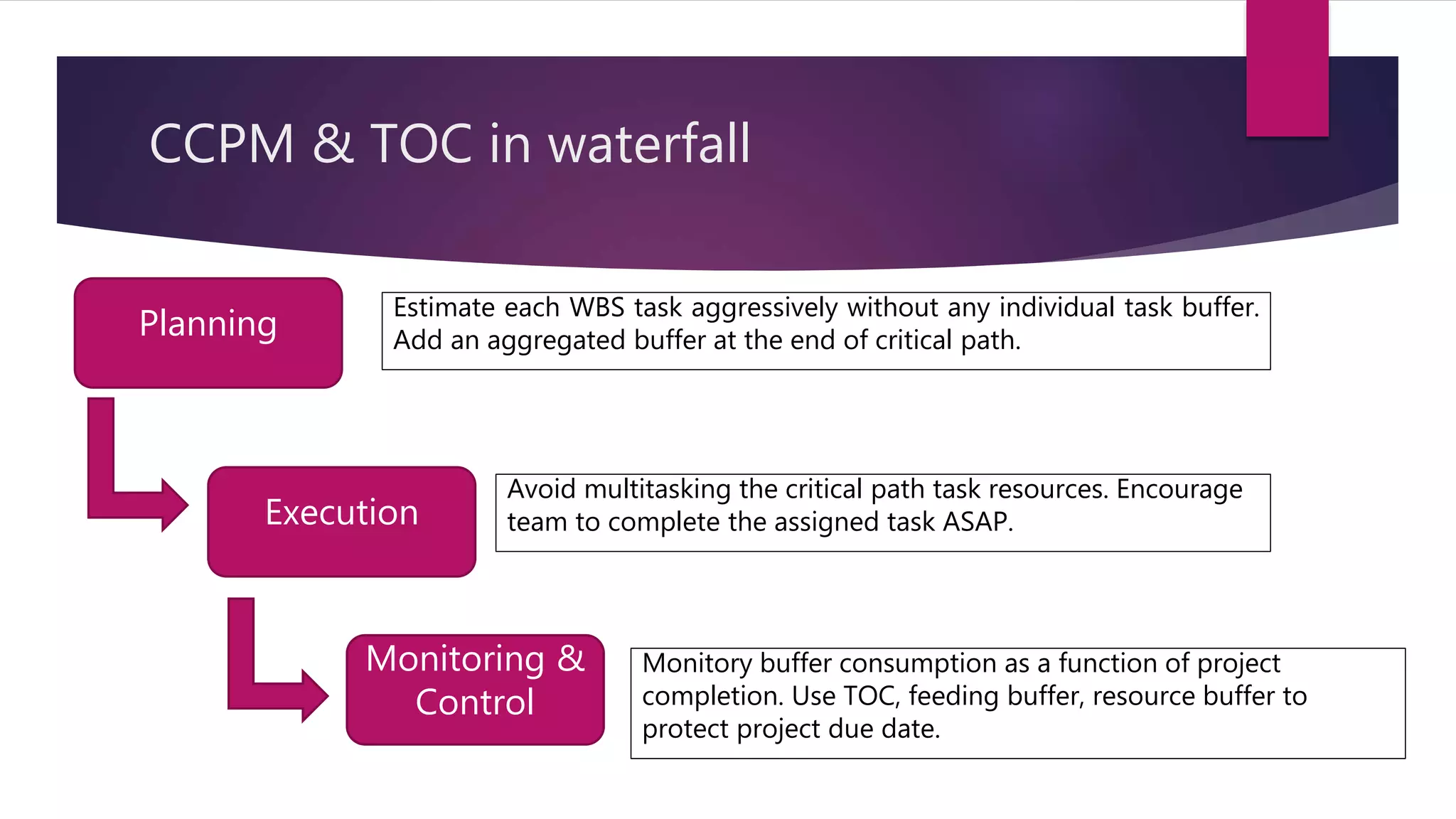
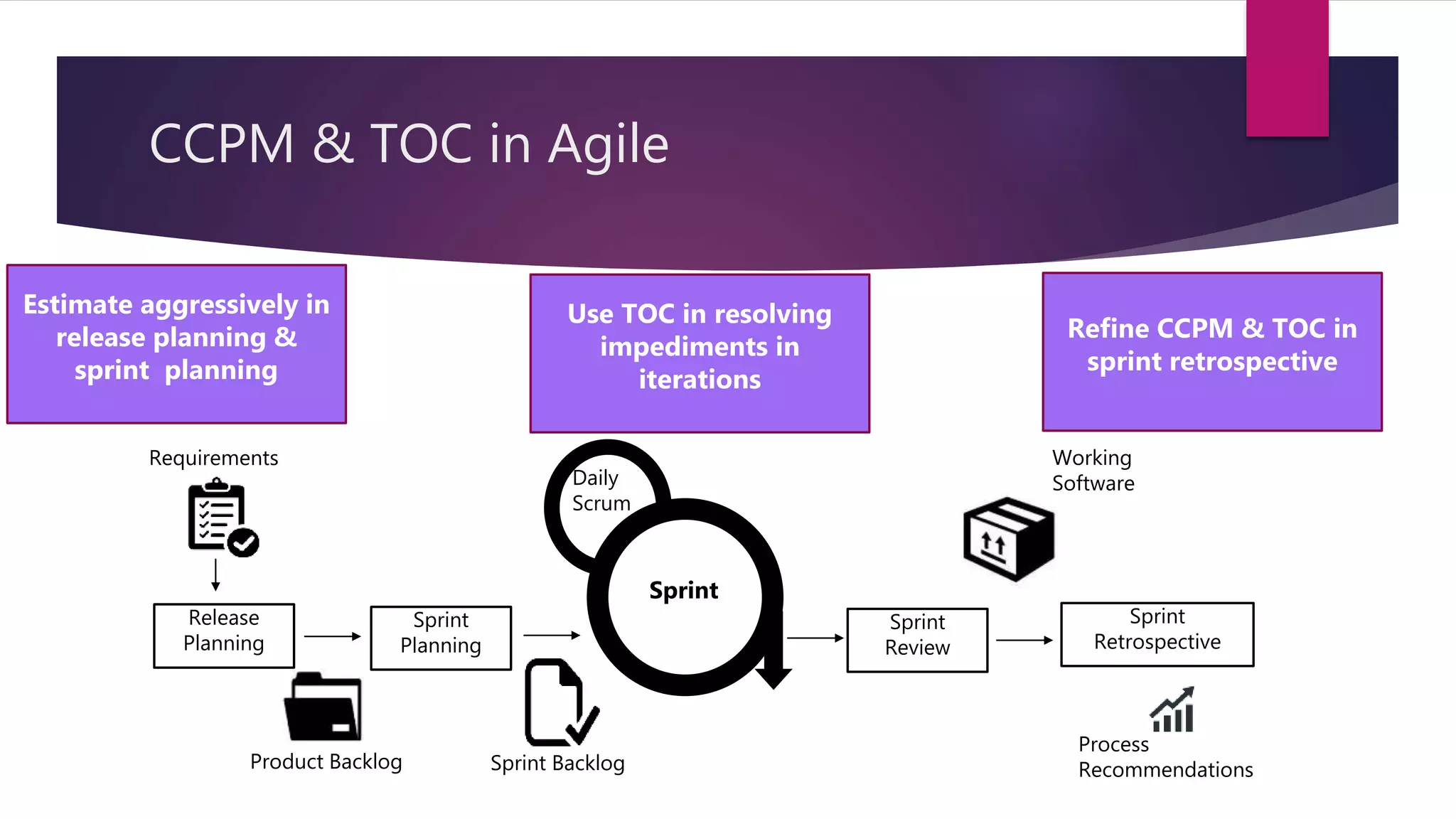
Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM) uses aggressive task estimates and buffers to eliminate wasted time from practices like multitasking, student syndrome, and Parkinson's law. It identifies the critical path and adds a project buffer at the end to protect the deadline. CCPM is based on the Theory of Constraints (TOC), which involves identifying, exploiting, subordinating, and elevating constraints. CCPM and TOC are applied in both waterfall and agile projects by aggressively estimating tasks, avoiding multitasking on the critical path, monitoring buffer consumption, and using TOC to resolve impediments.