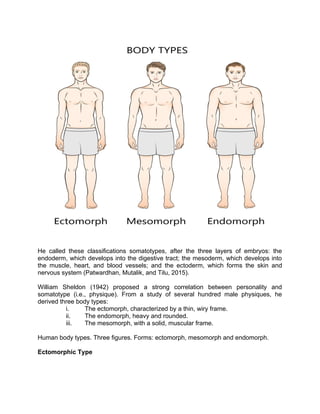
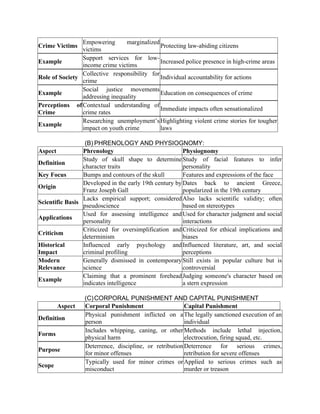
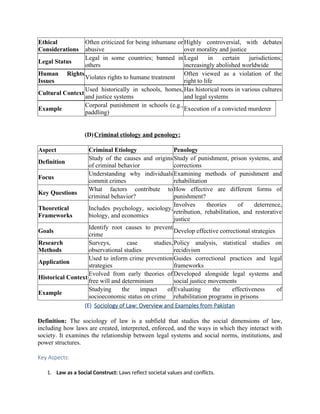
The document outlines major schools of thought in criminology, including supernatural, classical, positivist, Chicago, critical, and feminist criminology, detailing their proponents, assumptions, and key concepts. It discusses the psychological, social, and environmental differences between criminals and non-criminals, emphasizing factors such as impulsivity, family background, and socialization. Additionally, it covers Edwin Sutherland’s differential association theory, which posits that criminal behavior is learned through interactions with others, and the theory of social alienation, which connects feelings of disconnection from society to increased likelihood of criminal behavior.