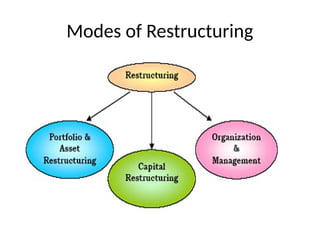
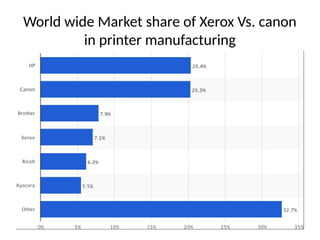
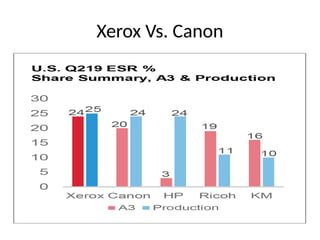
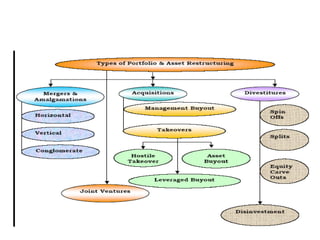
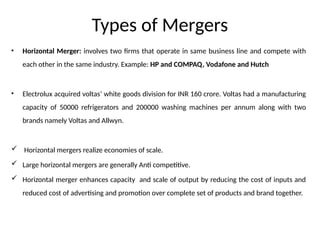
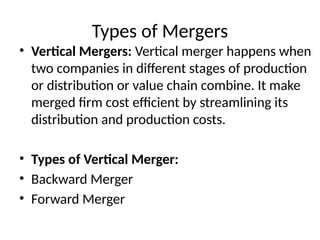
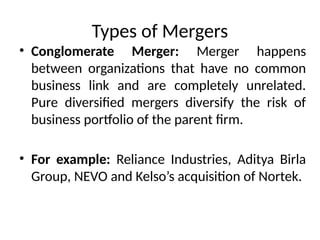
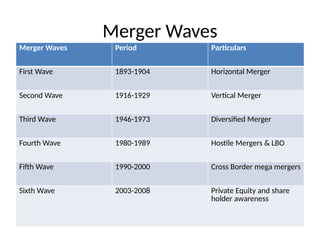
The document discusses corporate restructuring, outlining its importance in enhancing productivity and shareholder wealth, with several modes including organizational, financial, and portfolio restructuring. It includes case studies on Xerox and Harley-Davidson that highlight methods of regaining market share through restructuring initiatives. Additionally, it examines trends and motives behind mergers and acquisitions, emphasizing the need for strategy adaptation in response to market changes.