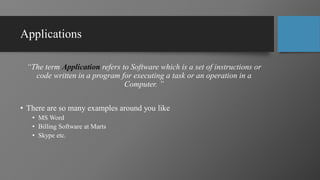
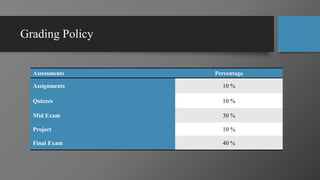
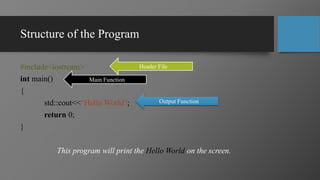
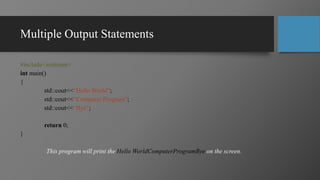
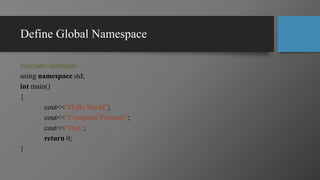
This document provides an overview of computer programming and applications. It defines key terms like data, programs, and information. It explains that a computer accepts user input (data), processes it under programs to produce output (information). Programming is defined as writing instructions for a computer to operate. Popular programming languages and applications are discussed. The document outlines the learning objectives, recommended books, and grading policy for a course on computer programming and applications. It provides an example of a simple "Hello World" program in C++ with explanations of the main components - header file, main function, and output function.