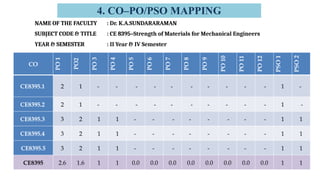
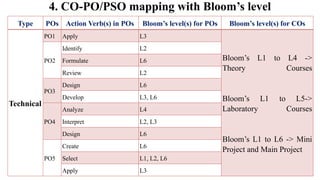
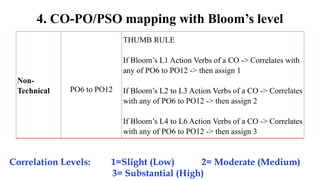
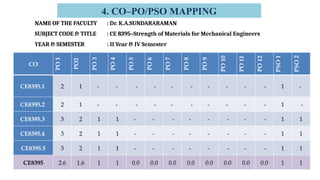
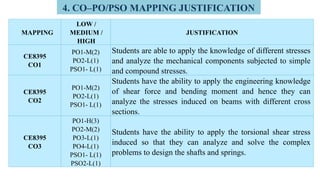
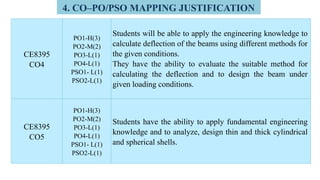
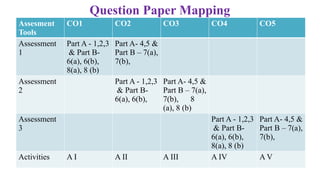
The document outlines Bloom's Taxonomy as a hierarchical framework for categorizing learning objectives in education, ranging from basic knowledge to advanced creation. It details program outcomes and specific course outcomes for a mechanical engineering course, including a mapping of these outcomes to Bloom's levels. Additionally, it provides justification for the correlation between course and program outcomes, indicating levels of understanding and application of engineering principles among students.