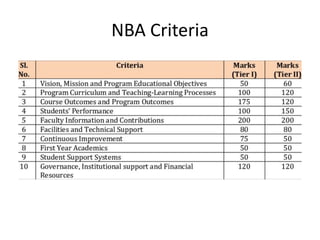
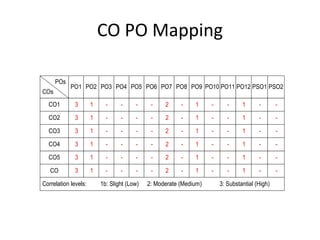
The document provides information about the vision, mission, and criteria for NBA accreditation of engineering programs. It discusses Bloom's Taxonomy, which is a framework for classifying educational objectives. It then lists the 12 Program Outcomes defined by NBA for engineering graduates. An example course on Engineering Chemistry is described with its 5 Course Outcomes. A table maps the Course Outcomes to the Program Outcomes to show correlation between the two. It also provides brief definitions of Program Educational Objectives and Program Specific Outcomes.