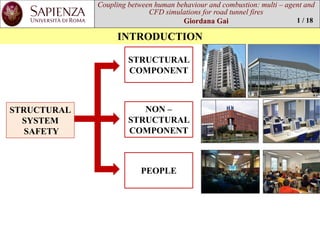
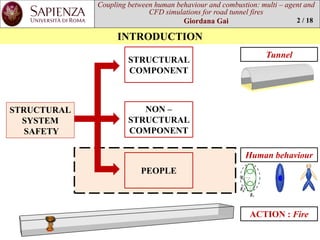
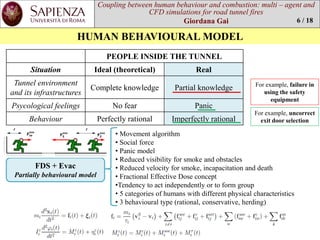
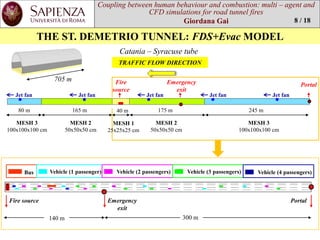
This document is a thesis that examines using multi-agent and CFD simulations to model human behavior and combustion in road tunnel fire scenarios. It presents a case study of the St. Demetrio tunnel in Italy, where FDS+Evac software is used to simulate egress times and conditions under different fire and ventilation scenarios. The results show that for a 6 MW car fire scenario, evacuation is completed within 15-20 minutes without issues with visibility or intoxication, though backlayering did occur for a bus fire scenario when one jet fan was off.


![Coupling between human behaviourand combustion: multi –agent and CFD simulations for road tunnel fires
Giordana Gai
Spatialaspects
1D -aspects
Temporalaspects
Codeand computationalcost
RANS
ReynoldsAverageNavierStokes
ANSYS FLUENT
20 cm –mesh
8 hoursofsimulation
LES
LargeEddy Simulation
FDS
20 cm –mesh
1hourofsimulation
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
0
200
400
Y [m]
Temperature [°C]
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
0
200
400
Y [m]
Temperature [°C]
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
0
5
10
15
20
Temperature [°C]
Time [s]
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
0
5
10
15
20
Temperature [°C]
Time [s]
+ Evac
COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS
4 / 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/couplingbetweenhumanbehaviourandcombustion-141103091113-conversion-gate01/85/Coupling-between-human-behaviour-and-combustion-5-320.jpg)


![Coupling between human behaviourand combustion: multi –agent and CFD simulations for road tunnel fires
Giordana Gai
0
20
40
CAR 2 LL - CAR 1 RL
CAR 4 LL - CAR 3 RL
CAR 6 LL - CAR 5 RL
CAR 8 LL - BUS RL
CAR 10 LL - CAR 7 RL
CAR 13 LL - CAR 9 RL
CAR 15 LL - CAR 11 RL
CAR 16 LL - CAR 12 RL
CAR 18 LL - CAR 14 RL
CAR 22 LL - CAR 19 RL
CAR 20 RL
CAR 21 RL
Time [s]
Formationofthe queueinside the tunnel
Left lane (LL)
Right lane (RL)
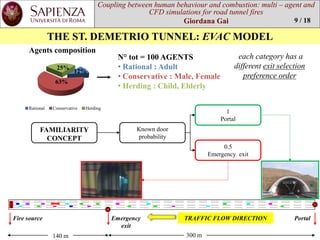
THE ST. DEMETRIO TUNNEL: EVACMODEL
0
0.005
0.01
0.015
0.02
0.025
0.03
0.035
0.04
0.045
250
275
300
325
350
Probability distribution
Time [s]
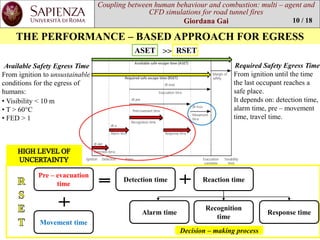
Pre -evacuation time distribution
Normal distribution
Truncated normaldistribution
ANAS ReferenceTime
ProbabilisticApproach
DeterministicApproach
11 / 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/couplingbetweenhumanbehaviourandcombustion-141103091113-conversion-gate01/85/Coupling-between-human-behaviour-and-combustion-12-320.jpg)
![Coupling between human behaviourand combustion: multi –agent and CFD simulations for road tunnel fires
Giordana Gai
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
0
1000
2000
3000
Time [s]
HRR [MW]
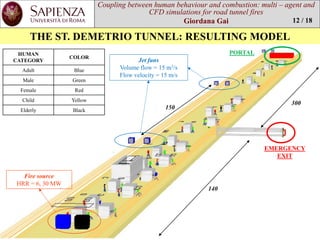
SCENARIOS
13 / 18
Jet fans
1 Jet fan
Emergencyexit
Emergencyexit
BUS FIRE
(30 MW)
2 –CARS FIRE
(6 MW)
•Idealbehaviour
•Realbehaviour
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
0
1000
2000
3000
Time [s]
HRR [MW]
Emergencyexit
Emergencyexit
•Realbehaviour](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/couplingbetweenhumanbehaviourandcombustion-141103091113-conversion-gate01/85/Coupling-between-human-behaviour-and-combustion-14-320.jpg)
![Coupling between human behaviourand combustion: multi –agent and CFD simulations for road tunnel fires
Giordana Gai
RESULTS (6 MW –fire)
14 / 18
0
20
40
60
80
100
0
500
1000
N°agents
Time [s]
Ideal egress
Emergency exit
Portal
Total evacuated agents
0
20
40
60
80
100
0
500
1000
N°agents
Time [s]
Real Egress
Emergency exit
Portal
Total evacuated agentsRATIONAL BEHAVIOUR
PANIC
Ideal egress
Real egress
0
20
40
60
80
100
Emergency exit
Portal
90
10
51
49
Number of agents
Ideal egress
Real egress
0
20
40
60
80
100
0
200
400
600
800
1000
Number of evacuated agents
Time [s]
Ideal
Real](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/couplingbetweenhumanbehaviourandcombustion-141103091113-conversion-gate01/85/Coupling-between-human-behaviour-and-combustion-15-320.jpg)
![Coupling between human behaviourand combustion: multi –agent and CFD simulations for road tunnel fires
Giordana Gai
RESULTS (6 MW –fire)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
Number of evacuated agents
Time [s]
15 / 18
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1,011.0
939.0
1,120.0
1,125.0
RSET[s]
Yes Jet Fan - Yes Em. Exit
No Jet Fan - Yes Em. Exit
Yes Jet Fan - No Em. Exit
No Jet Fan - No Em. Exit
Jet Fans
1 Jet Fan
EmergencyExit
EmergencyExit
2 –CARS FIRE
(6 MW)
Jet Fans
Em. Exit
1 Jet Fan
Em. Exit
Jet Fans
Em. Exit
1 Jet Fan
Em. Exit
EmergencyExit
EmergencyExit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/couplingbetweenhumanbehaviourandcombustion-141103091113-conversion-gate01/85/Coupling-between-human-behaviour-and-combustion-16-320.jpg)
![Coupling between human behaviourand combustion: multi –agent and CFD simulations for road tunnel fires
Giordana Gai
Human _ speed [m/s]*10-4
STREAKS
t = 593 s
t = 390 s
Portal
Emergency exit
RESULTS (6 MW –fire)
16 / 18
Thisisnotageneralresult: FDS+EvacshouldberunusingMonteCarlomethod(repeatedsamplingtodeterminethepropertiesofthephenomenon).
ThisisonlyonesamplingoftheMonteCarlosimulation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/couplingbetweenhumanbehaviourandcombustion-141103091113-conversion-gate01/85/Coupling-between-human-behaviour-and-combustion-17-320.jpg)
![Coupling between human behaviourand combustion: multi –agent and CFD simulations for road tunnel fires
Giordana Gai
RESULTS (6 MW –fire)
17 / 18
•Visibility _ soot [m] at z = 1.6 m
high visibility upstream the fire source during the egress time
ASET >> RSET considered scenario
•Humans FED 10-5
very low value, even for those scenarios with 1 jet fan off (emergency ventilation is so strong that there are no problems of intoxication)
•Temperature slice [°C]
low value (< 60°C) next to the emergency exit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/couplingbetweenhumanbehaviourandcombustion-141103091113-conversion-gate01/85/Coupling-between-human-behaviour-and-combustion-18-320.jpg)

![THE END
V –velocity field
0
20
40
60
80
100
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
Number of evacuated agents
Time [s]
Egress_ 6 MW fire
Ideal and Rational
Yes Jet Fan - Yes Em. Exit
No Jet Fan - Yes Em. Exit
Yes Jen Fan - No Em. Exit
No Jet Fan - No Em. Exit
12%
63%
25%
Agents composition
Rational
Conservative
Herding
Coupling between human behaviourand combustion: multi –agent and CFD simulations for road tunnel fires
Giordana Gai](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/couplingbetweenhumanbehaviourandcombustion-141103091113-conversion-gate01/85/Coupling-between-human-behaviour-and-combustion-20-320.jpg)

![Coupling between human behaviourand combustion: multi –agent and CFD simulations for road tunnel firesGiordana Gai
Human _ force total [N/m]
t = 300 s
t = 360 s
t = 327 s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/couplingbetweenhumanbehaviourandcombustion-141103091113-conversion-gate01/85/Coupling-between-human-behaviour-and-combustion-22-320.jpg)
![Coupling between human behaviourand combustion: multi –agent and CFD simulations for road tunnel firesGiordana Gai
RESULTS (6 MW –fire)
Human _ force total [N/m]
Block in the bus](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/couplingbetweenhumanbehaviourandcombustion-141103091113-conversion-gate01/85/Coupling-between-human-behaviour-and-combustion-23-320.jpg)