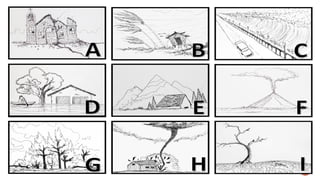
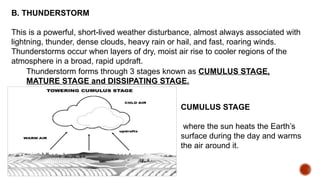
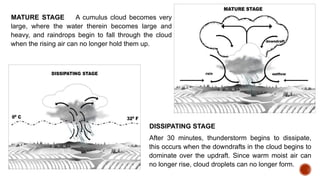
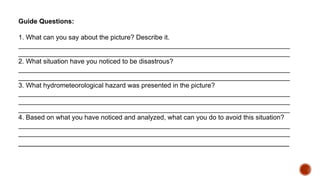
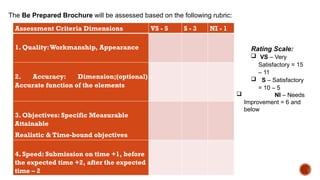
The document outlines educational content on disaster readiness and risk reduction, focusing on various hydrometeorological hazards such as typhoons, floods, and droughts. It includes objectives for learners to understand these hazards, develop emergency preparedness plans, and improve creativity through activities like brochure-making. The Philippines is highlighted as particularly vulnerable to natural disasters due to its geographic location, and various activities and quizzes are provided to engage students in the topic.