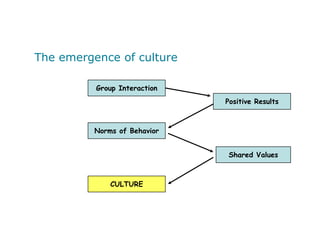
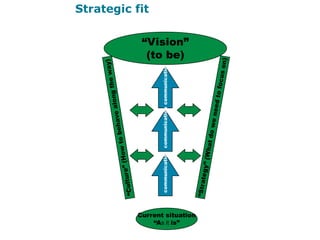
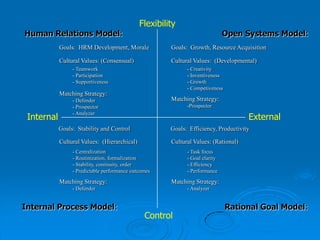
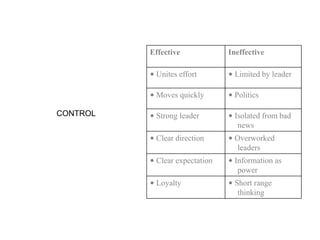
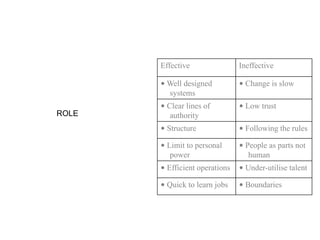
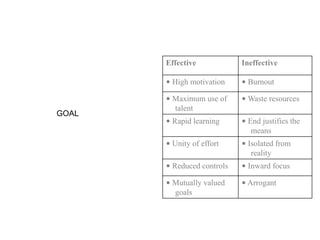
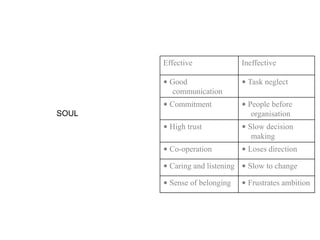
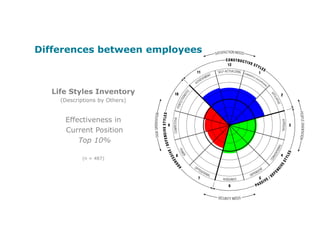
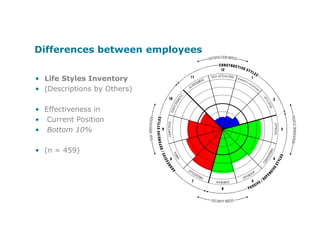
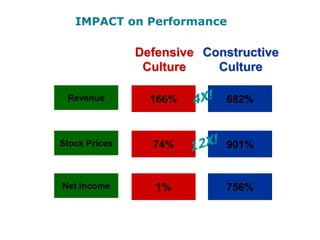
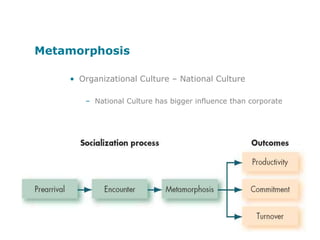
Corporate culture is defined as the set of key behaviors, beliefs and understandings shared by members of an organization. It establishes basic values and communicates the proper way to think and act. There are different models of corporate culture, including flexibility, control, roles, goals and soul-based models. Cultural fit is important as it engages employees and leads to better performance outcomes when present. Culture is created through symbols, stories, rituals and shared interpretations, and exploring it through interviews can provide insight. Constructive cultures tend to be more effective by promoting exchange and contributions from members.