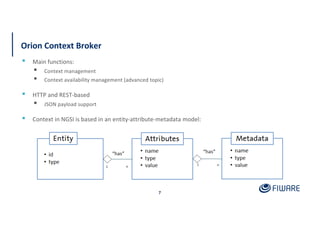
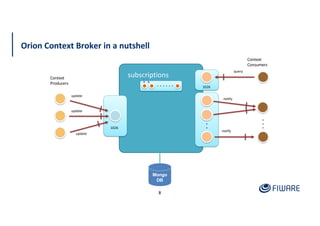
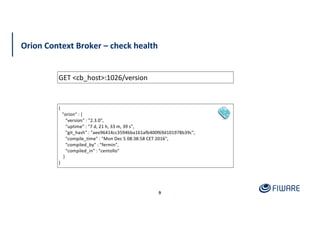
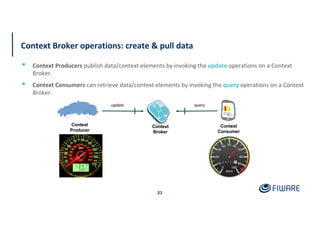
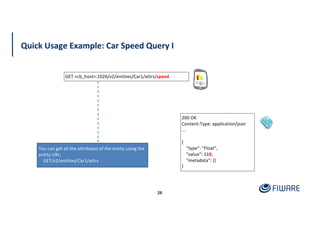
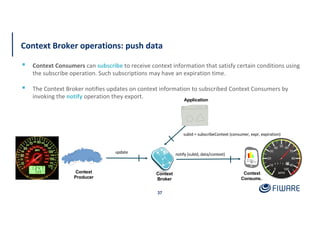
The document provides an overview of the Orion Context Broker architecture and its functionalities, including context management, data handling, and subscription notifications using the NGSI v2 API. It outlines the structure of entities, attributes, and metadata, along with various operations for creating, updating, and querying context data. Additionally, the document highlights advanced features such as batch operations and pushing data to improve efficiency in managing context information.










![Entity Examples in NGSIv2
13
{
“id”: “Traffic-Incidence-9876”,
“type”: “gsmadata:TrafficIncidence”,
“category”: “Vehicle Fault”,
“severity”: “Yellow”,
“vehicleType”: “Truck”,
“startDate”: "2015-07-17T09:31:11.112Z”
“roadName”: “N-122”,
“description”: “A truck is stopped on road”
}
{
“id”: “r786543”,
“type”: “Room”,
“name”: “Chrisantemum”,
“temperature”: 22,
“seatNumber”: 10,
“location”: {
“type”: “Point”,
“coordinates”: [31.2222200, 121.4580600]
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session3-corecontextmanagement-191127083615/85/Core-Context-Management-14-320.jpg)






![Simple Operations: Query payload examples
20
[
{
“id”: “123-456-789”,
“type”: “Vehicle”,
“model”: “C200”,
“brand”: “Mercedes Benz”,
“buildYear”: “2010”
},
{
“id”: “000-987-654”,
“type”: “Vehicle”,
“model”: “Astra”,
“brand”: “Opel”,
“buildYear”: “2003”
}
]
[
{
“id”: “123890-22222”,
“type”: “VehicleFault”,
“location”: {
“type”: “point”,
“coordinates”: [40.41, -3.70]
}
“startDate”: 2015-07-17T11:12:42.540Z”
}
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session3-corecontextmanagement-191127083615/85/Core-Context-Management-21-320.jpg)
![Simple Operations: Query Operations III
21
GET /v2/entities/r786543/attrs/temperature/value
▪ Tell me the temperature at the Chrisantemum room
▪ Only Value is returned → The most abbreviated response
GET /v2/entities?type=CarBrand&attrs=name&options=values
▪ Tell me the known car brands
23.5
[“Ford”, “Mercedes Benz”, “Hyundai”]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session3-corecontextmanagement-191127083615/85/Core-Context-Management-22-320.jpg)










![Quick Usage Example: Filters I
34
200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
...
[
{
"id": "Room2",
"pressure": 730,
"temperature": 29,
"type": "Room"
}
]
GET <cb_host>:1026/v2/entities?options=keyValues&q=temperature>28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session3-corecontextmanagement-191127083615/85/Core-Context-Management-35-320.jpg)
![Quick Usage Example: Filters II
35
200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
...
[
{
"id": "Room1",
"pressure": 720,
"temperature": 25,
"type": "Room"
}
]
GET <cb_host>:1026/v2/entities?options=keyValues&q=pressure==715..725
The full description of the Simple
Query Language for filtering can be
found in the NGSIv2 Specification
document](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session3-corecontextmanagement-191127083615/85/Core-Context-Management-36-320.jpg)

![Quick Usage Example: Subscription
38
POST <cb_host>:1026/v2/subscriptions
Content-Type: application/json
…
{
"subject": {
"entities": [
{
"id": "Room1",
"type": "Room"
}
],
"condition": {
"attrs": [ "temperature" ]
}
},
"notification": {
"http": {
"url": "http://<host>:<port>/publish"
},
"attrs": [ "temperature" ]
},
"expires": "2026-04-05T14:00:00.00Z"
}
201 Created
Location: /v2/subscriptions/51c0ac9ed714fb3b37d7d5a8
...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session3-corecontextmanagement-191127083615/85/Core-Context-Management-39-320.jpg)
![Quick Usage Example: Notification
39
POST /publish HTTP/1.1
Content-type: application/json; charset=utf-8
Ngsiv2-AttrsFormat: normalized
…
{
"subscriptionId": "574d720dbef222abb860534a",
"data": [
{
"id": "Room1",
"type": "Room",
"temperature": {
"type": "Float",
"value": 17.8,
"metadata": {}
}
}
]
}
27.9
17.8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session3-corecontextmanagement-191127083615/85/Core-Context-Management-40-320.jpg)
![List existing subscriptions
40
200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
…
[{
"id": " 51c0ac9ed714fb3b37d7d5a8 ",
"expires": "2026-04-05T14:00:00.00Z",
"status": "active",
"subject": {
"entities": [{
"id": "Room1",
"type": "Room"
}],
"condition": {
"attrs": ["temperature"]
}
},
"notification": {
"timesSent": 3,
"lastNotification": "2016-05-31T11:19:32.00Z",
"lastSuccess": "2016-05-31T11:19:32.00Z",
"attrs": ["temperature"],
"attrsFormat": "normalized",
"http": {
"url": "http://localhost:1028/publish"
}
}
}]
The full description of the
subscription object (including all its
fields) can be found in the NGSIv2
Specification
GET <cb_host>:1026/v2/subscriptions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session3-corecontextmanagement-191127083615/85/Core-Context-Management-41-320.jpg)



![Batch Operation Example: Create Several Rooms
44
201 Created
...
POST <cb_host>:1026/v2/op/update
Conten-Type: application/json
...
{
"actionType": "APPEND",
"entities": [
{
"type": "Room",
"id": "Room3",
"temperature": {
"value": 21.2,
"type": "Float"
},
"pressure": {
"value": 722,
"type": "Integer"
}
},
…
…
{
"type": "Room",
"id": "Room4",
"temperature": {
"value": 31.8,
"type": "Float"
},
"pressure": {
"value": 712,
"type": "Integer"
}
}
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session3-corecontextmanagement-191127083615/85/Core-Context-Management-45-320.jpg)