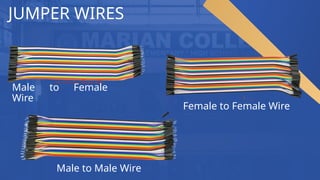
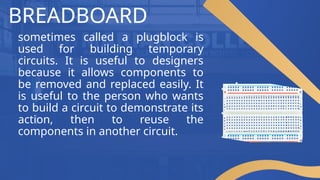
The document discusses breadboards, tools essential for building and testing temporary electronic circuits, highlighting their history, functionality, and components. It explains how modern breadboards, originating from wooden cutting boards, allow for the easy assembly and modification of circuits without soldering, and introduces key components like power supplies and jumper wires. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of understanding breadboarding for IT students in hardware prototyping, collaboration with engineers, and the integration of hardware and software.