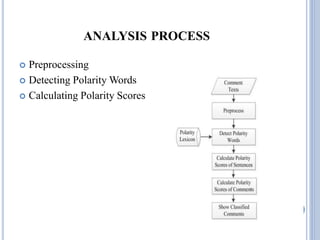
This document discusses techniques for rating cooking recipes based on user reviews, including sentiment analysis and text mining. Sentiment analysis involves classifying the polarity of reviews as positive or negative using techniques like preprocessing text, detecting polarity words, and calculating sentiment scores. Text mining is used to extract and analyze useful information from the large amounts of unstructured text data about recipes from sources like reviews. The analysis of reviews using these techniques helps users find the best recipes and provides feedback to recipe authors.






![ Sentiment Analysis is classified as:-
a. Machine learning approach
b. Lexicon- based approach
In accordance to Latent Aspect Rating Analysis [LARA]
Model, the words from reviews are given some weights.
For example:
“I loved the recipe. Tomato in the recipe made it
more delicious.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cooking-180922183430/85/Cooking-9-320.jpg)