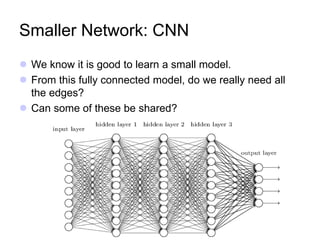
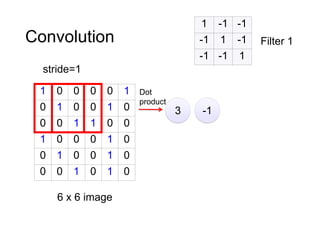
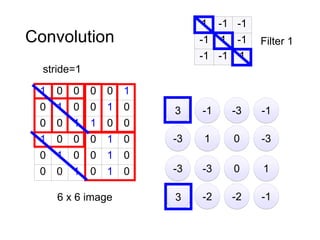
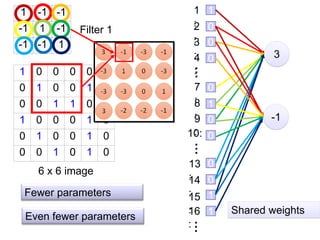
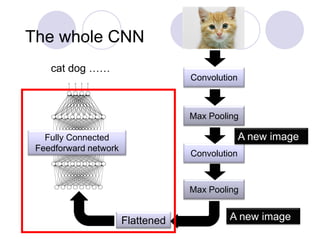
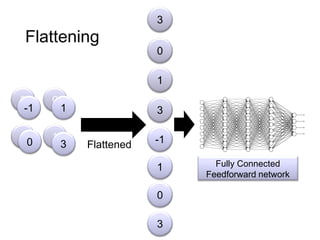
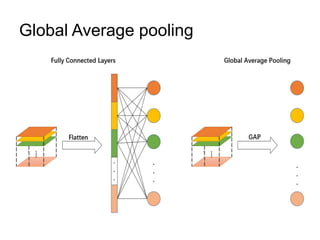
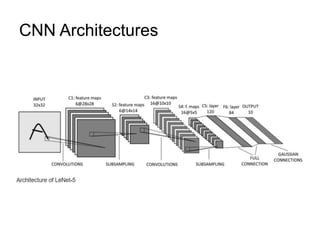
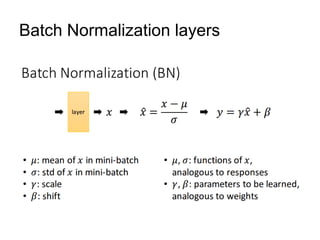
The document discusses Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and how they work. CNNs apply convolutional filters to images to extract features. The filters are smaller than the input images and are applied across the images. This allows the filters to detect local patterns and share weights, reducing the number of parameters compared to fully connected networks. CNNs use convolutional and pooling layers to further reduce parameters and complexity. The extracted features are then flattened and passed to fully connected layers for classification.