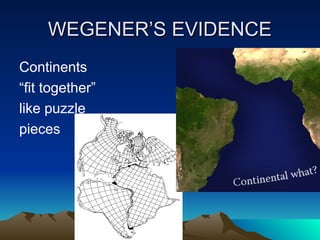
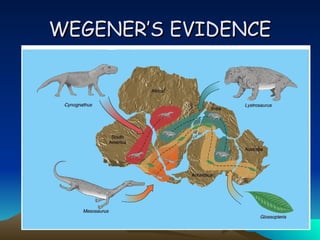
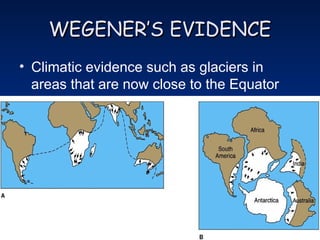
The theory of continental drift, proposed by Alfred Wegener, suggests that continents were once part of a single landmass called Pangaea, which broke apart and moved to their current positions. Wegener's evidence includes the distribution of similar fossils across continents, matching mountain ranges, and climatic indicators. Advances in satellite technology have allowed for the measurement of continental movement over time.