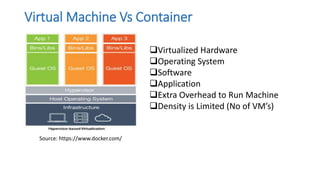
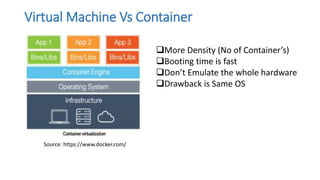
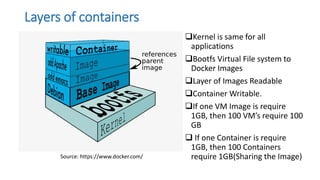
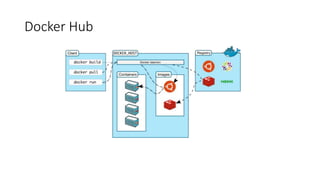
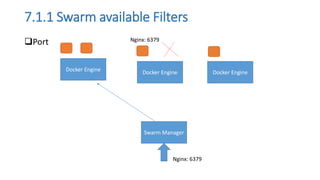
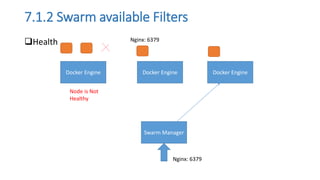
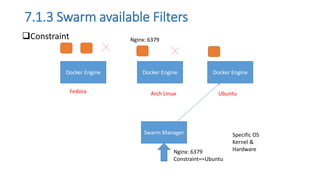
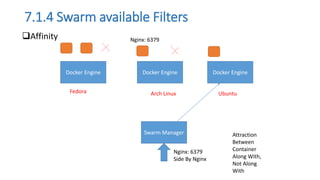
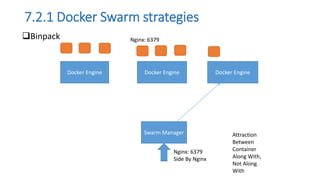
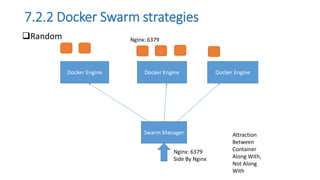
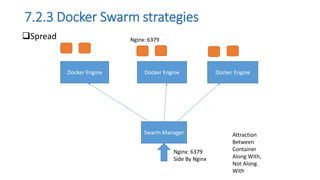
The document discusses the advantages of containerization over traditional hypervisor-based virtualization in cloud datacenters, highlighting the efficiency and resource allocation benefits of containers like Docker. It details how major tech companies have adopted containers, including features of Docker and Docker Swarm for managing container clusters and scheduling. Additionally, it outlines the differences between virtual machines and containers, emphasizing faster boot times and lower resource overhead with container usage.
![Introduction
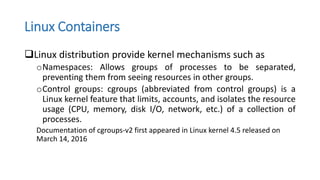
Most of cloud datacenters use virtualization which is implemented by
hypervisors such as Xen, KVM or Vsphere.
Container as a good alternative to hypervisor
Most of major IT vendors such as Google, Amazon, and Microsoft and
academic researchers have been interested in containerization of cloud
datacenters to overcome drawbacks of traditional hypervisor based
virtualization[02].
Google: 'EVERYTHING at Google runs in a container‘; Two billion containers a
week
Docker Container, Linux Container(LxC), Warden Container, Open Vz Container.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit6containerization1-231016053625-b3d602f8/75/Containerization-1-2048.jpg)