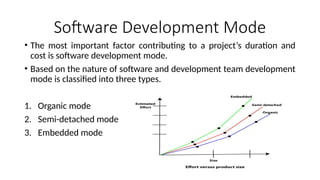
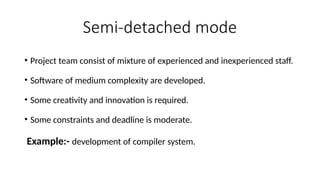
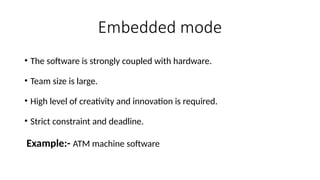
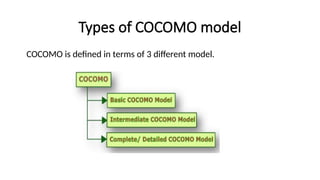
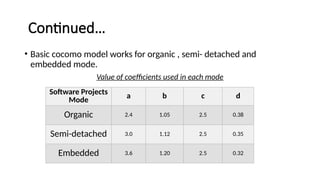
The Constructive Cost Model (COCOMO) is a widely used software cost estimation model proposed by Barry Boehm in 1981, which predicts project parameters such as effort, cost, and team size based on lines of code and various cost drivers. It categorizes software development modes into organic, semi-detached, and embedded, each with distinct characteristics affecting duration and cost. COCOMO consists of three models: basic, intermediate, and detailed, each offering varying degrees of accuracy in estimating project effort and cost, but it has disadvantages such as reliance on assumptions and averaging.