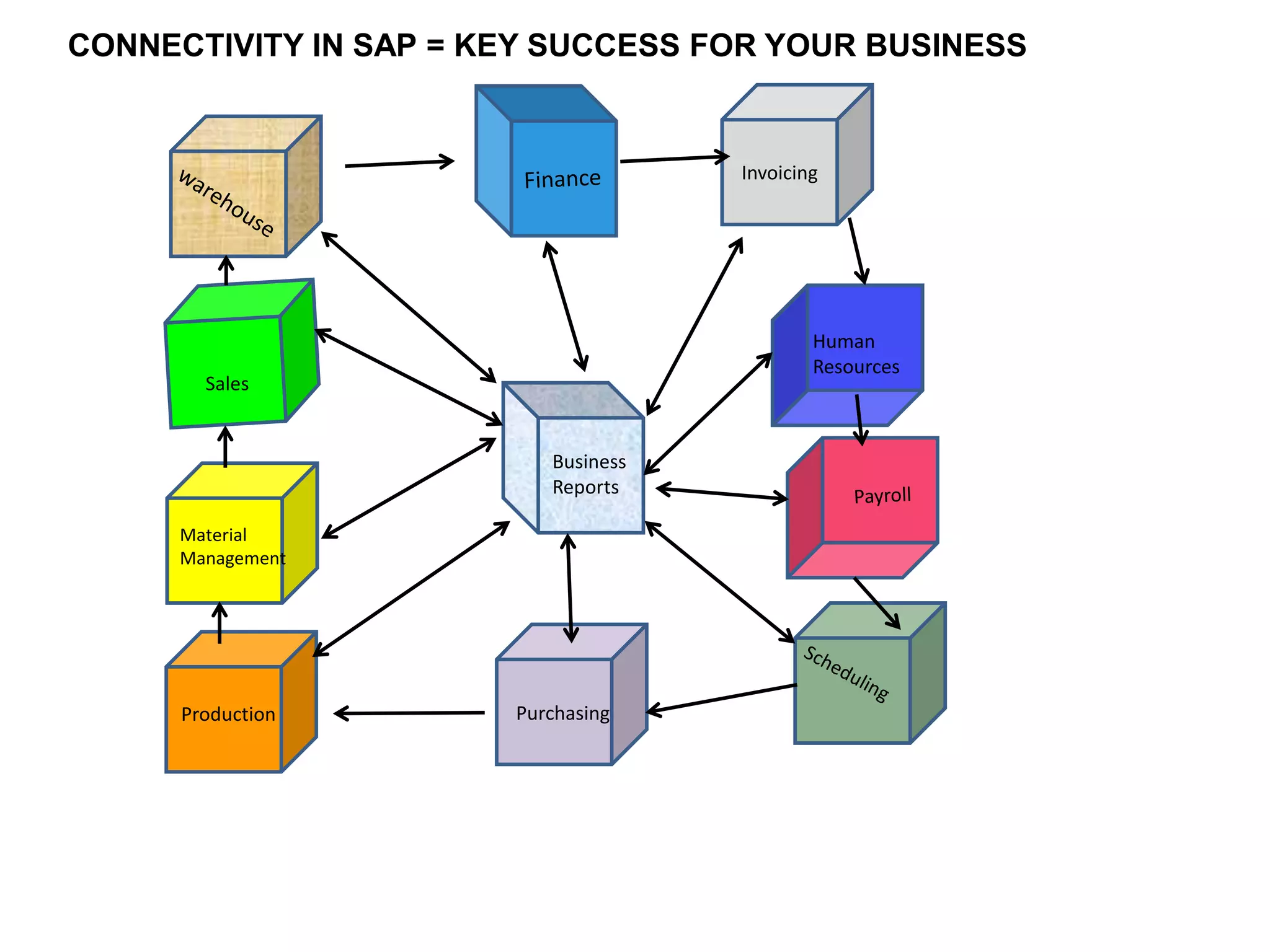
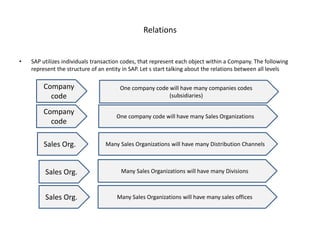
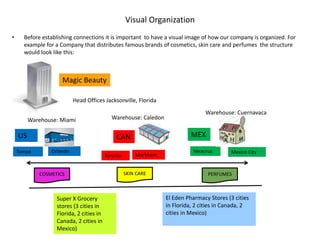
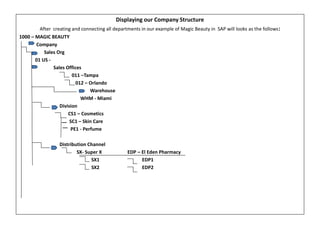
The document outlines the importance of SAP in managing business operations and the necessity of interconnecting all departments for efficiency. It provides definitions of key organizational codes within SAP, details on creating a client structure, and emphasizes the need for proper connectivity to access essential master data. A visual representation of a company's organization is also presented as an example to illustrate the connectivity process.