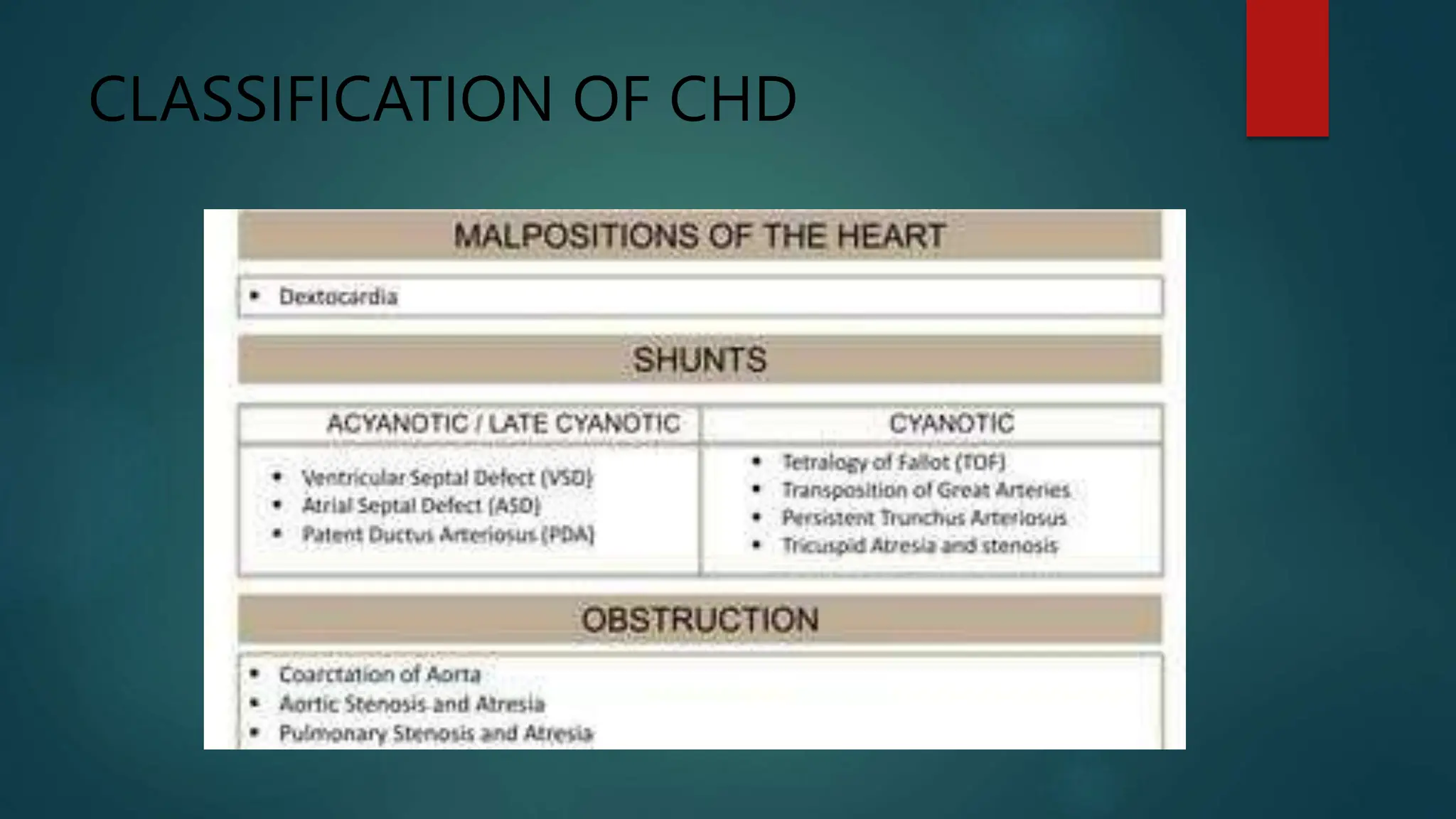
An atrial septal defect (ASD) is an abnormal opening in the wall separating the left and right atria of the heart. There are several types of ASDs which allow oxygenated and deoxygenated blood to mix. While many cases are asymptomatic, signs and symptoms may include a heart murmur, dysrhythmia, fatigue, infections, and breathlessness. Diagnosis is made through tests like echocardiogram and treatment often involves surgical closure of the defect. Complications can include arrhythmias, pulmonary hypertension, and heart failure if left untreated.