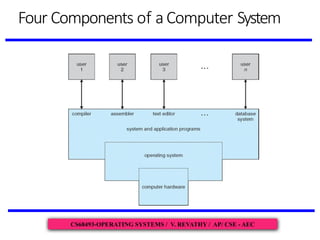
The document outlines the syllabus for the Operating Systems course at Arasu Engineering College, focusing on fundamental concepts such as the role and components of operating systems, their objectives, and how they manage computer resources. It introduces the organization of a computer system, the interplay between hardware, software, and users, and emphasizes the importance of efficiency and user convenience in operating system design. Additionally, it touches on the boot process and the distinction between system programs and application programs.