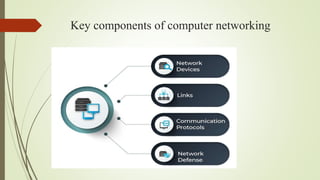
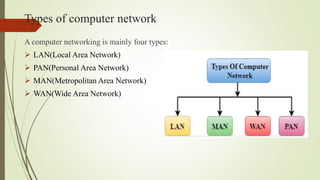
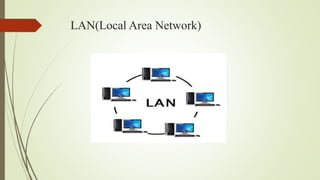
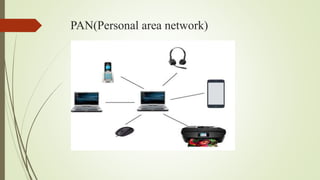
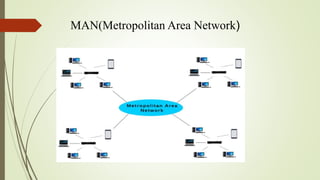
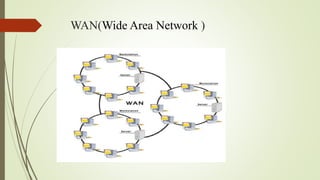
The document provides an overview of computer networking, defining it as a system that connects computing devices for information sharing. It discusses four main types of networks: LAN (Local Area Network), PAN (Personal Area Network), MAN (Metropolitan Area Network), and WAN (Wide Area Network), detailing their characteristics and uses. Key components include network devices, transmission media like wired and wireless links, and the broader implications of these networks in various sectors.