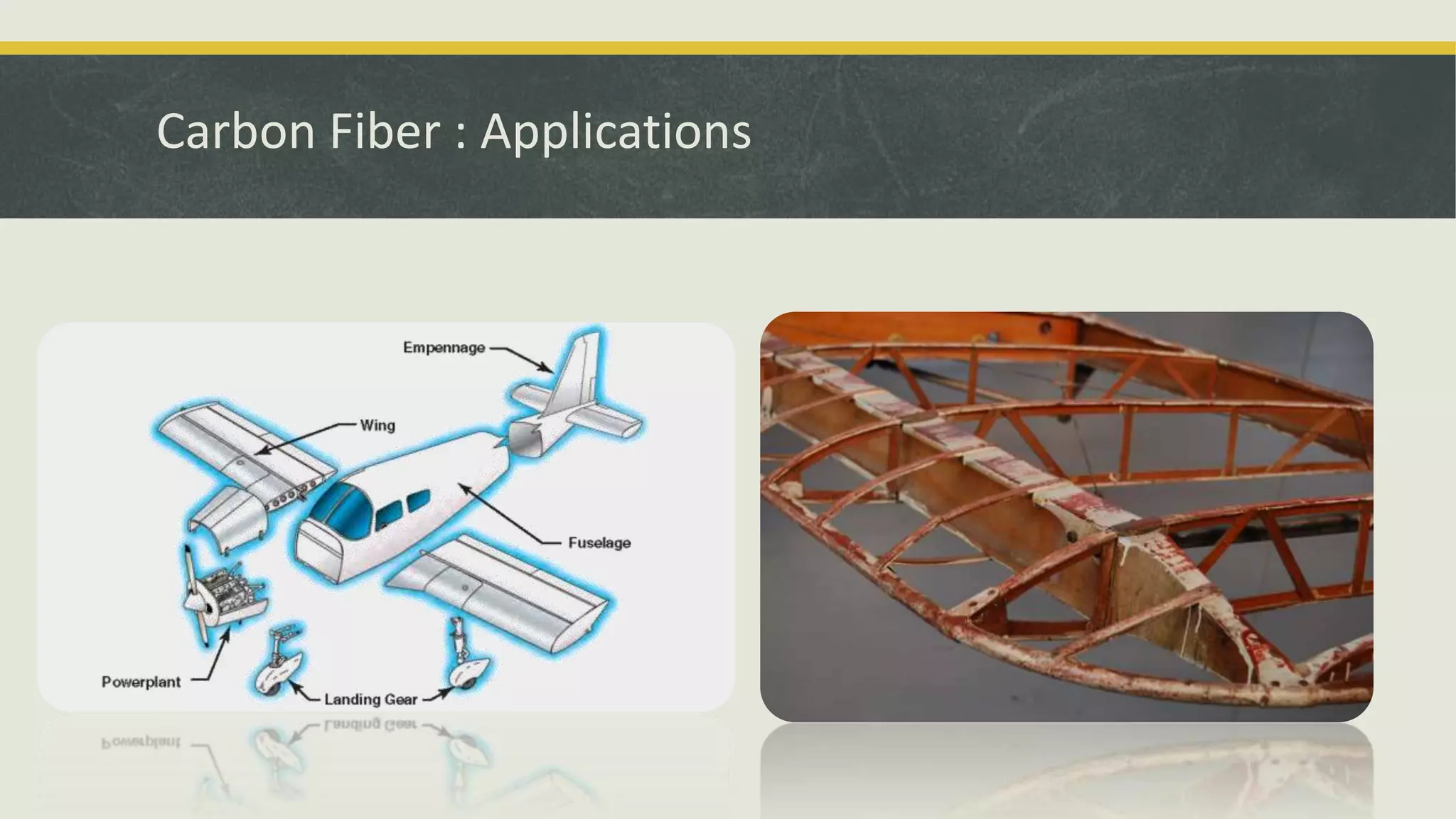
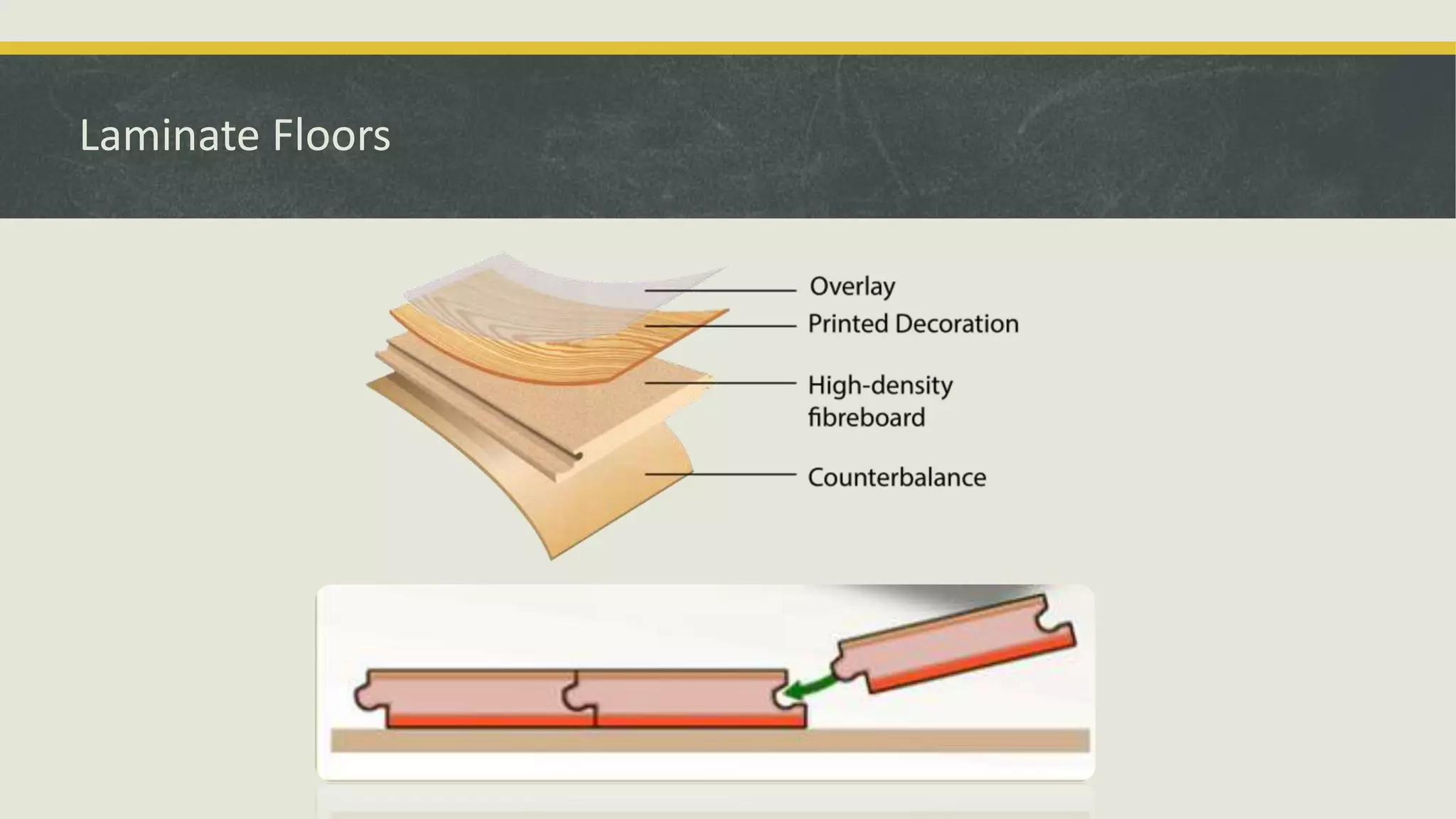
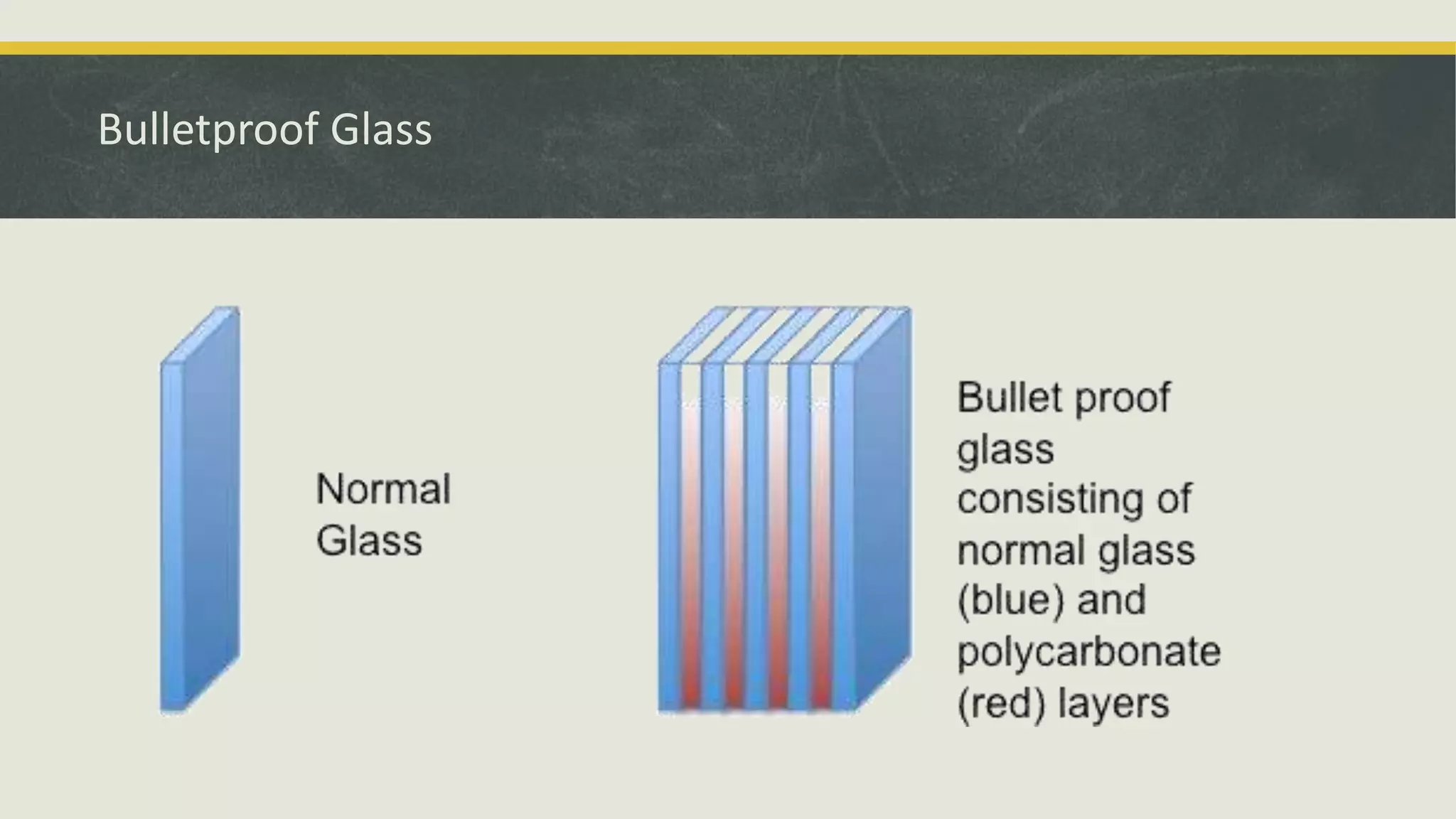
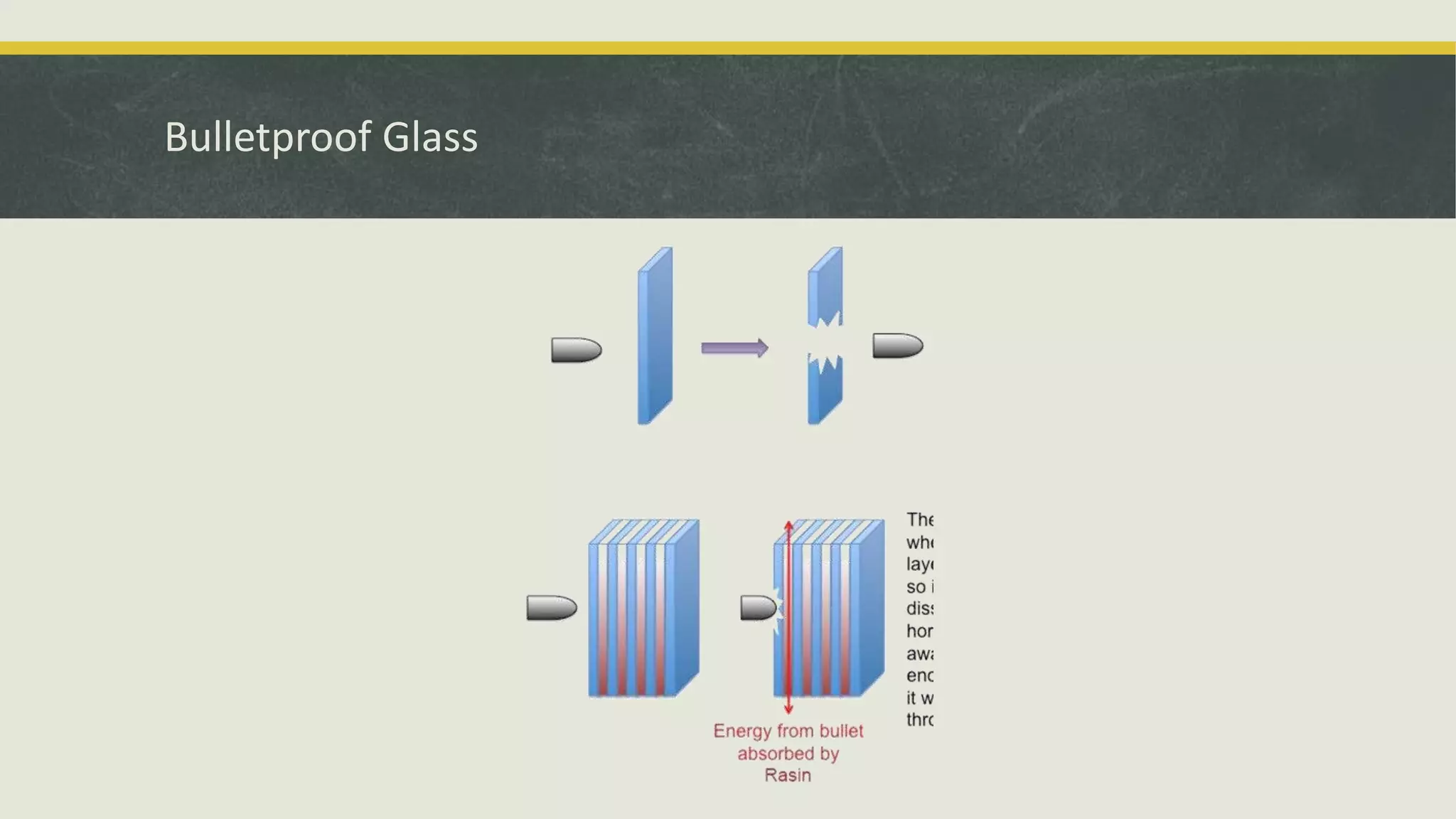
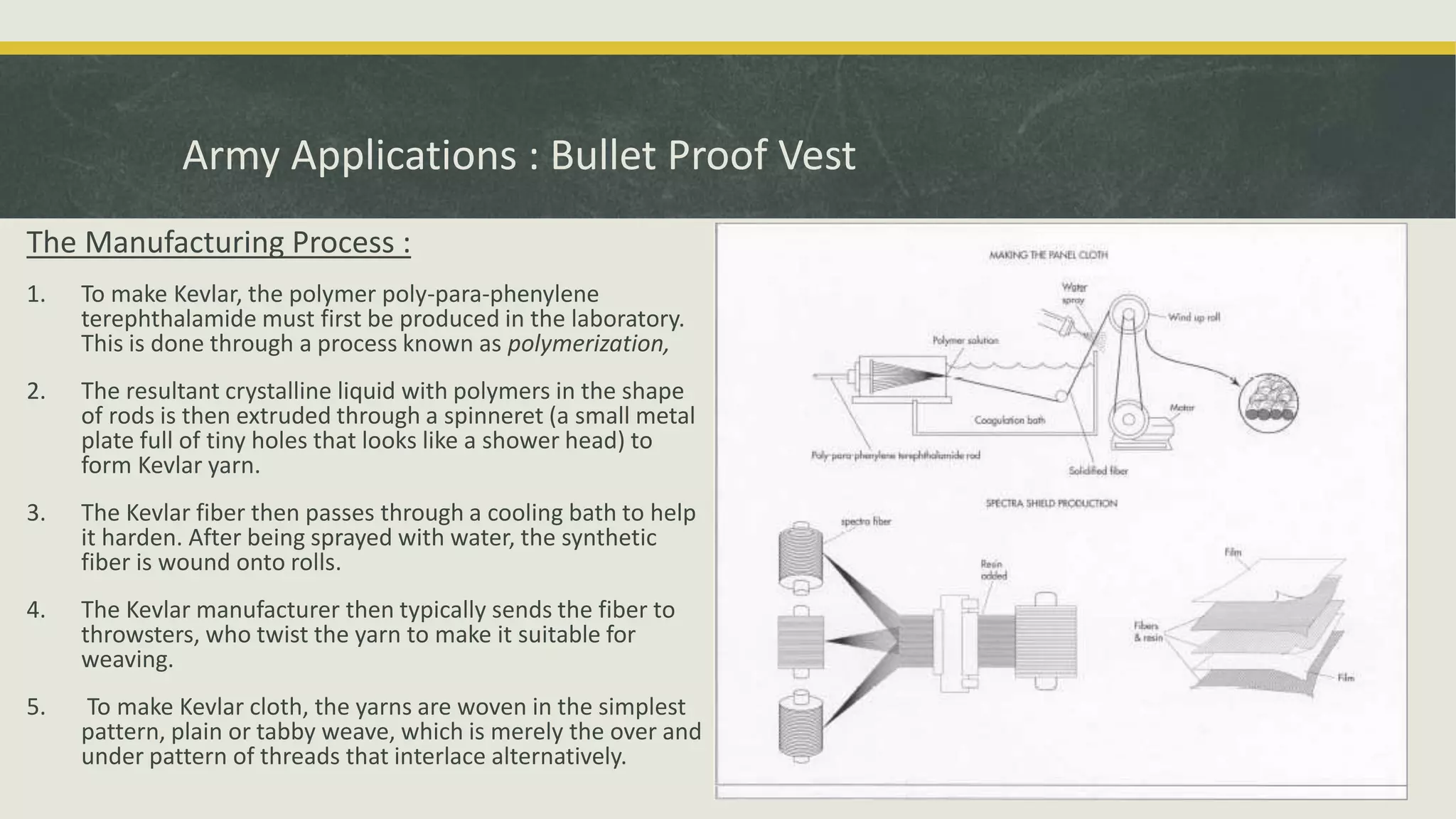
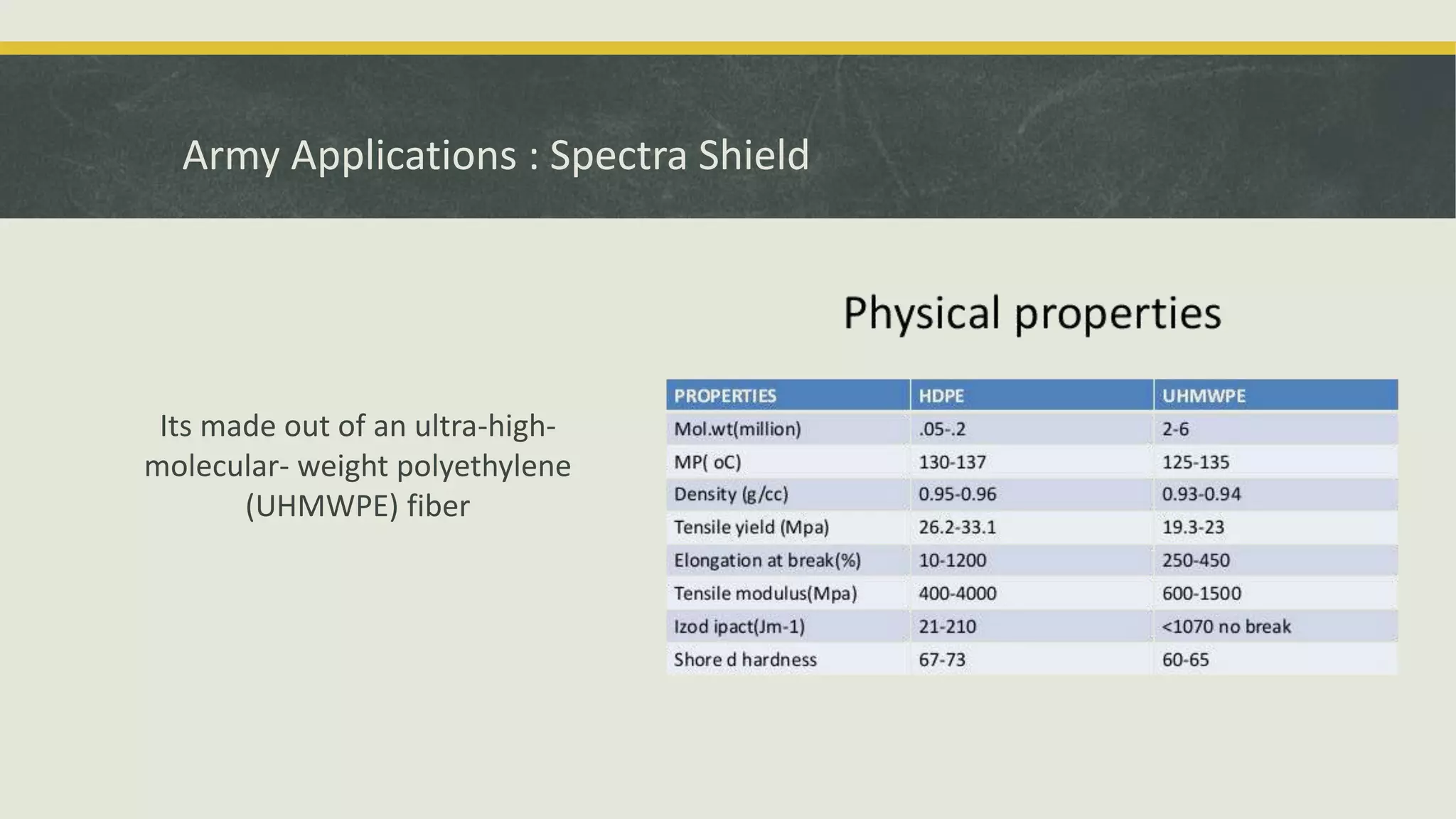
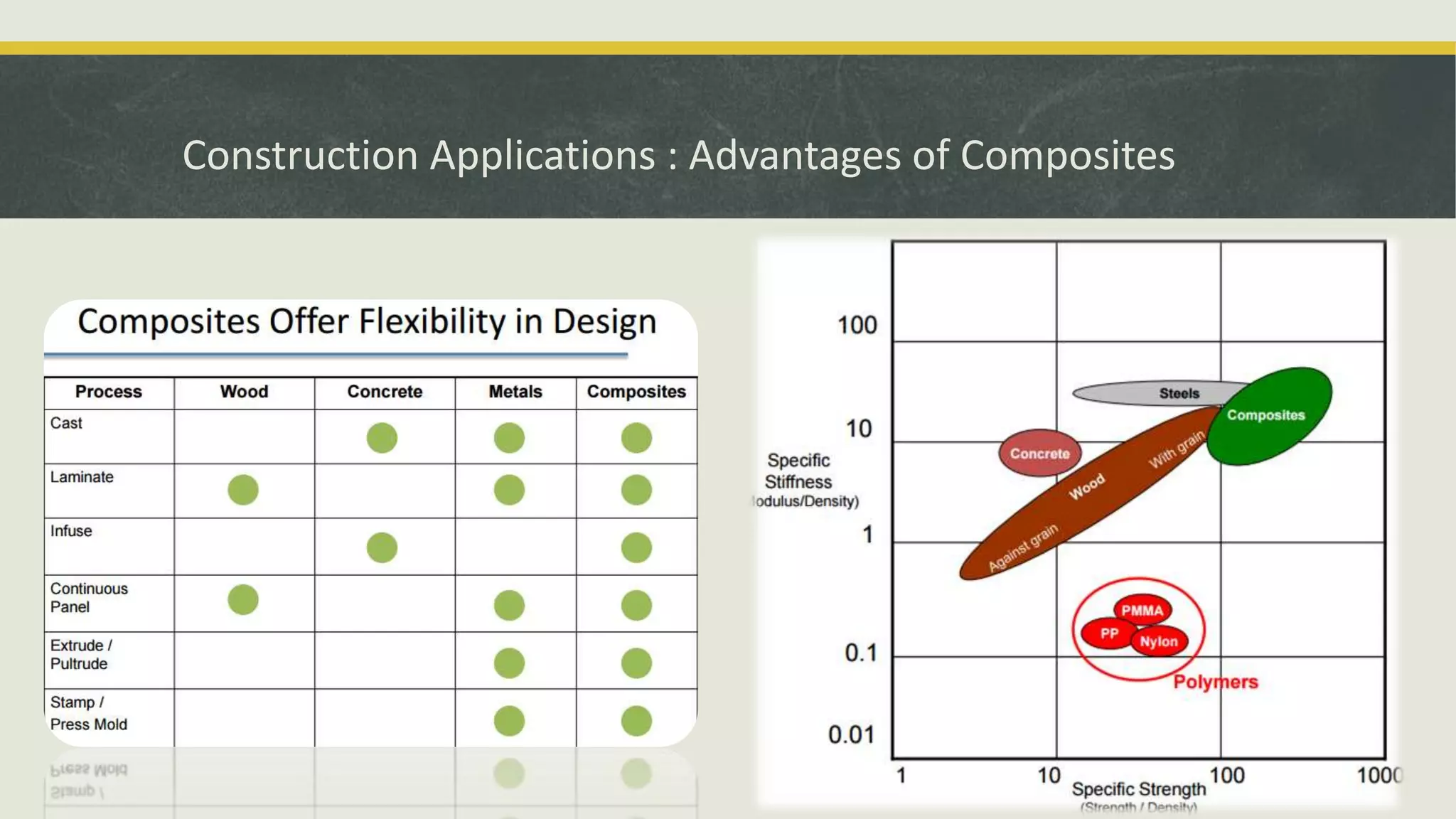
The document discusses various applications and properties of composite materials, including carbon fiber, fiberglass, bulletproof glass, and fiber reinforced concrete (FRC). It details the composition, manufacturing processes, and advantages of these materials in aerospace, construction, and military uses. Key properties include high strength-to-weight ratios, corrosion resistance, and design flexibility.