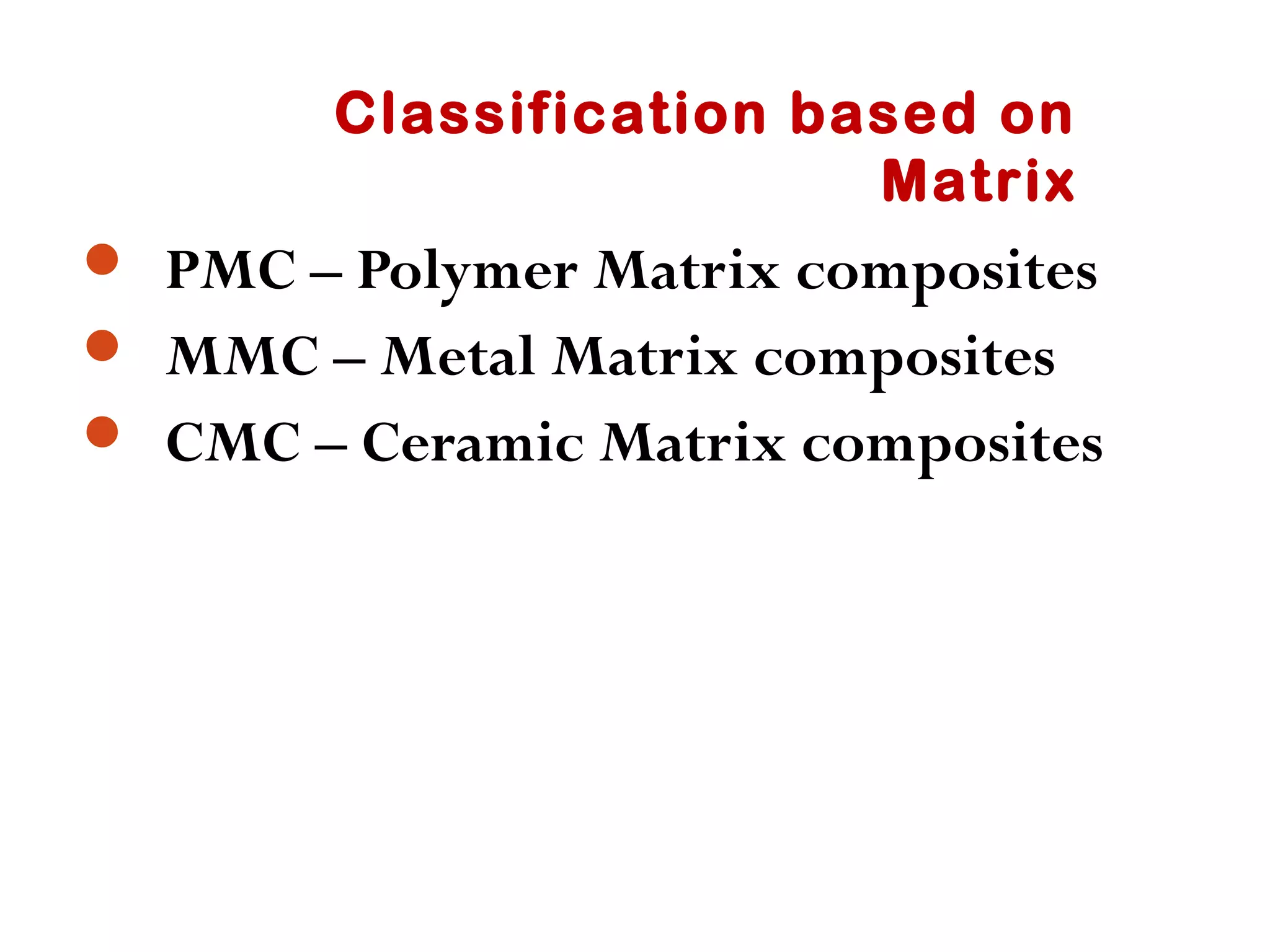
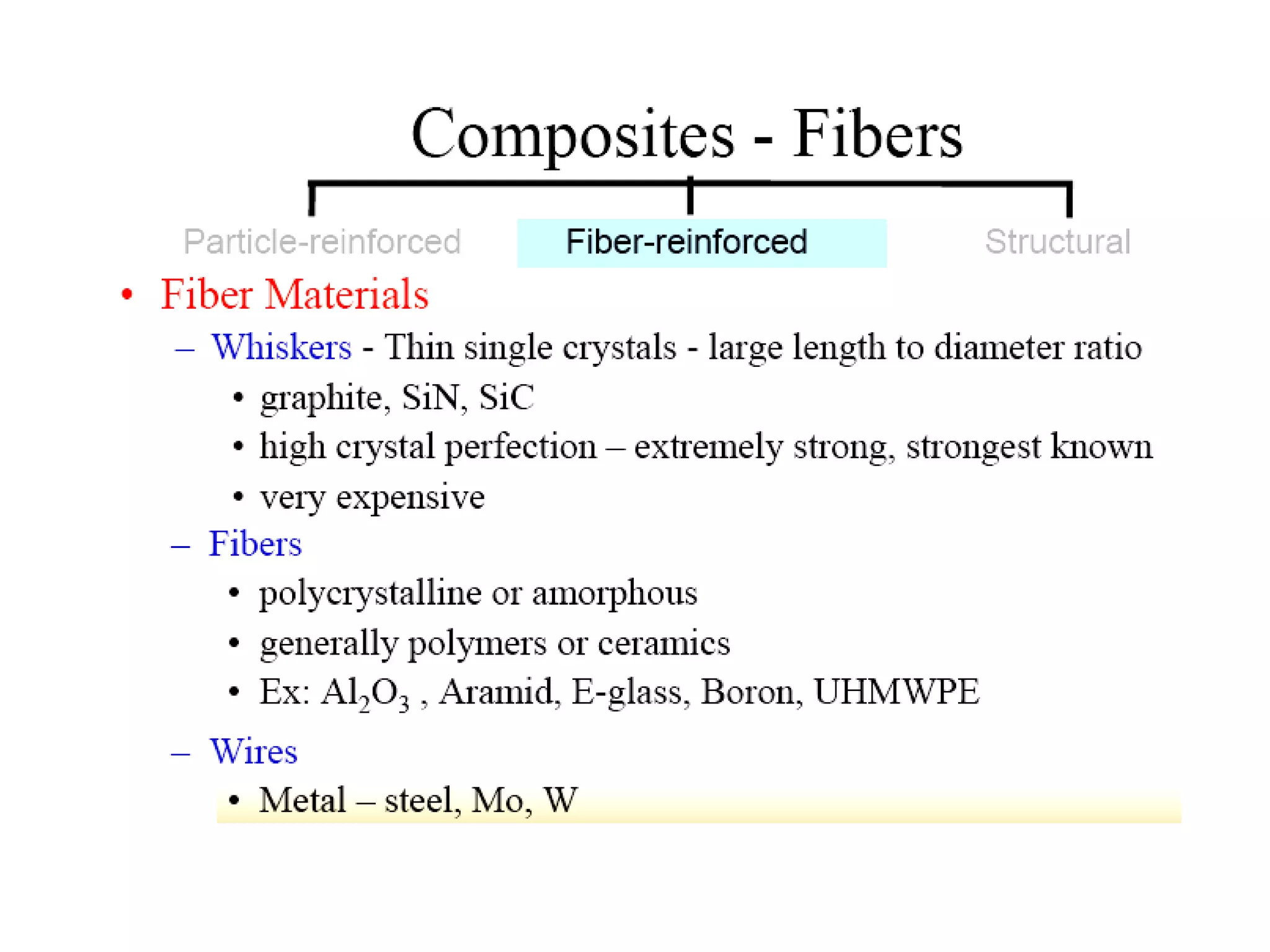
Composite materials are composed of two or more physically distinct phases that produce properties different from the individual components. Composites can be very strong yet light weight. Examples include fiberglass, carbon fiber reinforced plastics, and cemented carbides. Composites find applications in aerospace, automotive, sports equipment due to their high strength to weight ratio and other advantageous properties. They are classified based on matrix material (polymer, metal, ceramic) and type of reinforcement (particles, fibers).