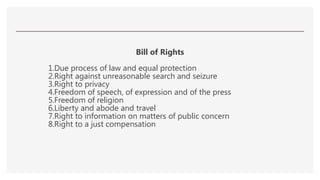
The document outlines the concept of community citizenship as defined by three dimensions: legal, political, and identity, emphasizing a citizen's rights and responsibilities. It references the 1987 Constitution of the Philippines, highlighting core Filipino values such as being godly, humane, nationalistic, and environmentally conscious. Furthermore, it lists key rights enshrined in the Bill of Rights, including due process, freedom of speech, and privacy rights.