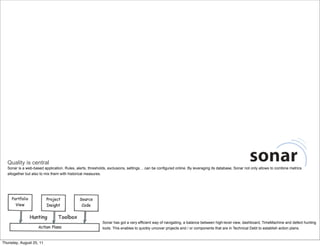
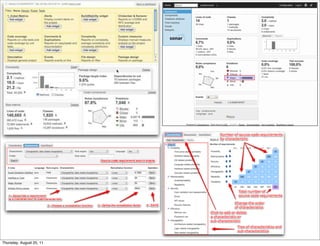
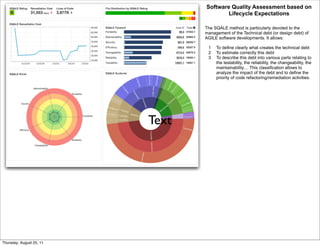
Code coverage is a measure of how much of the source code of a program is tested by a test suite. It helps ensure quality by enabling early detection of flaws. Common types of code coverage include statement, function, path, condition, and branch coverage. Tools like Cobertura, Clover, and Emma can help measure and analyze code coverage. Aim for 70-80% test coverage but 100% is not always cost effective or possible. Code coverage should be implemented from the start of development.