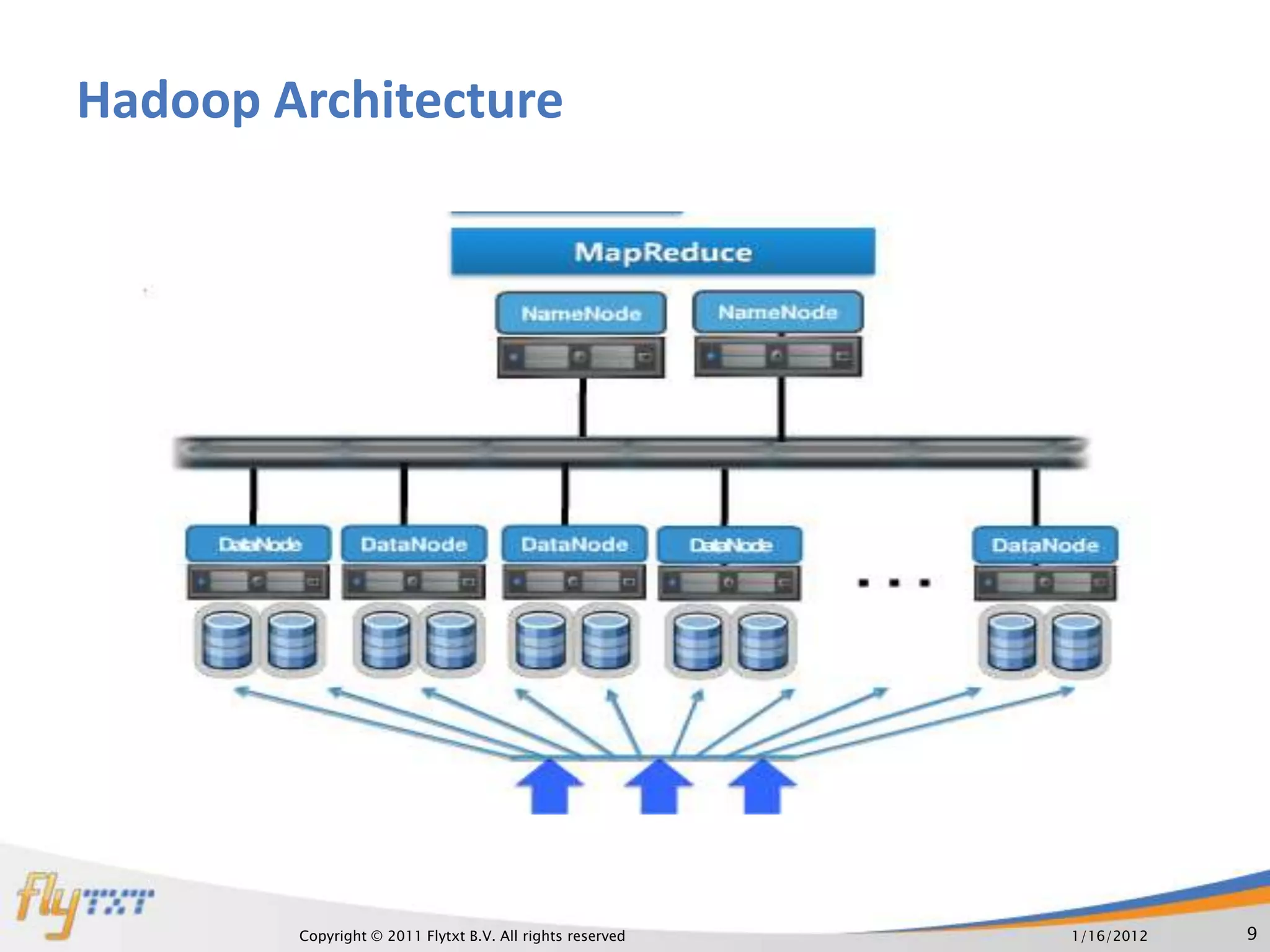
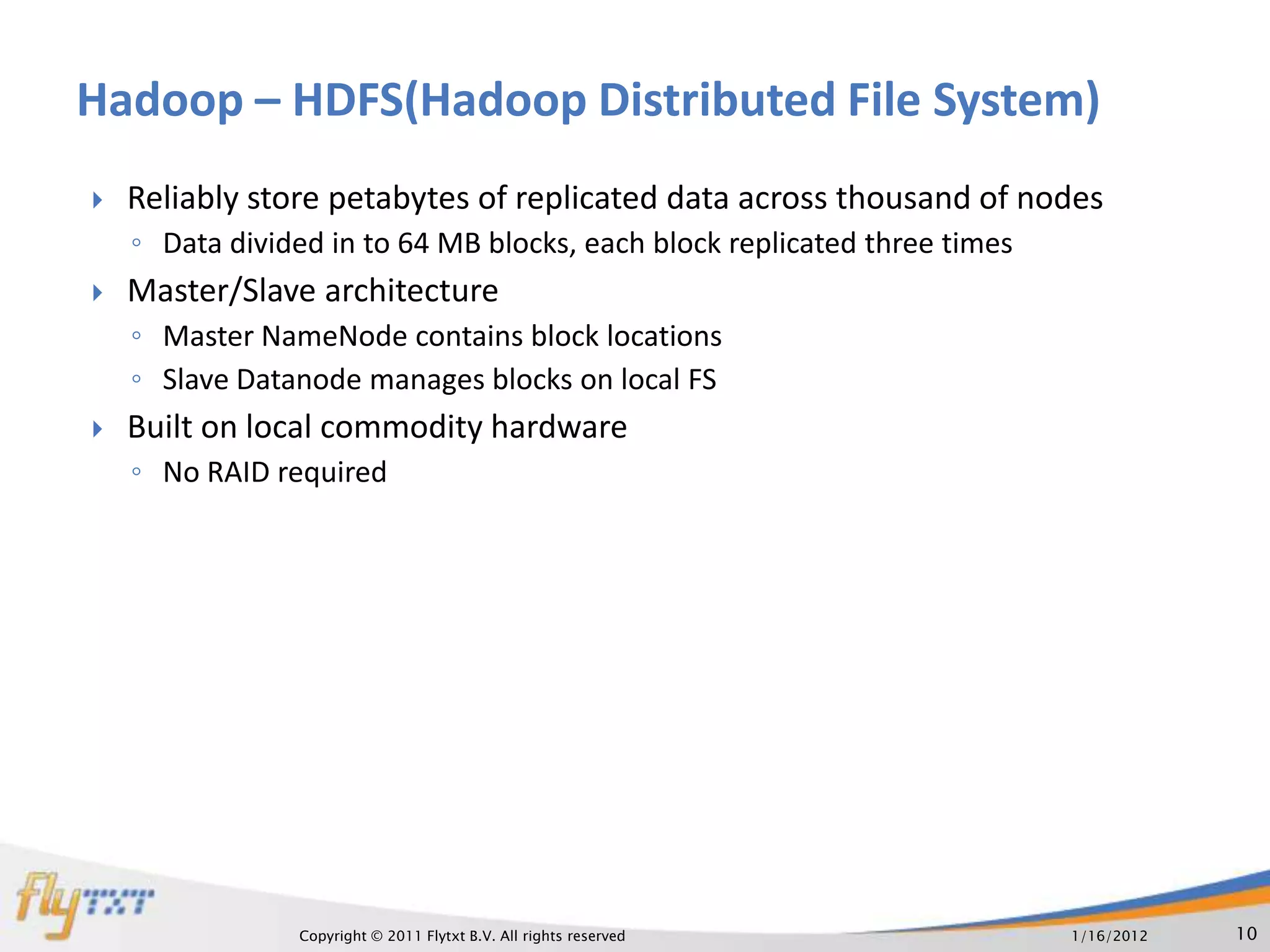
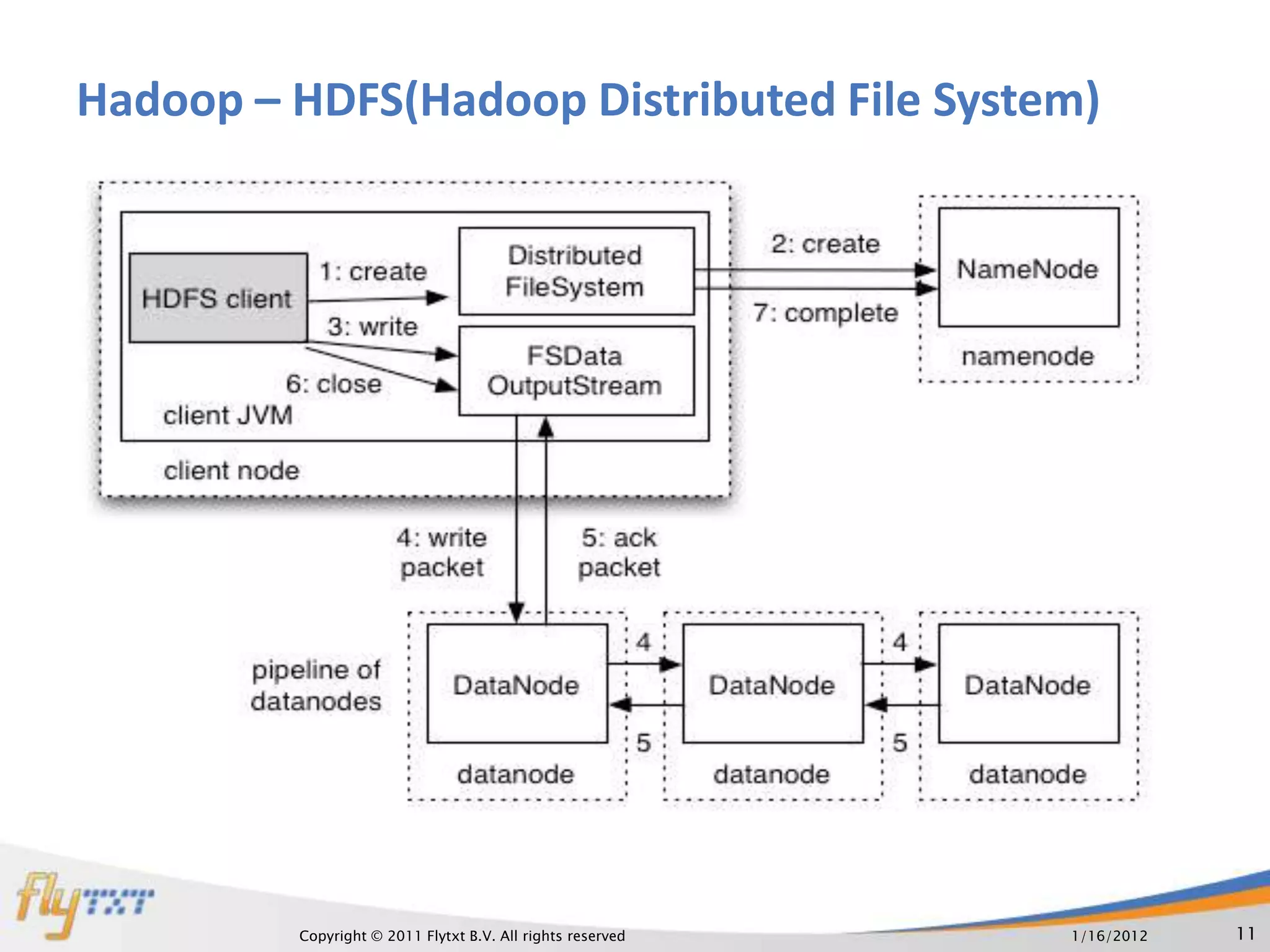
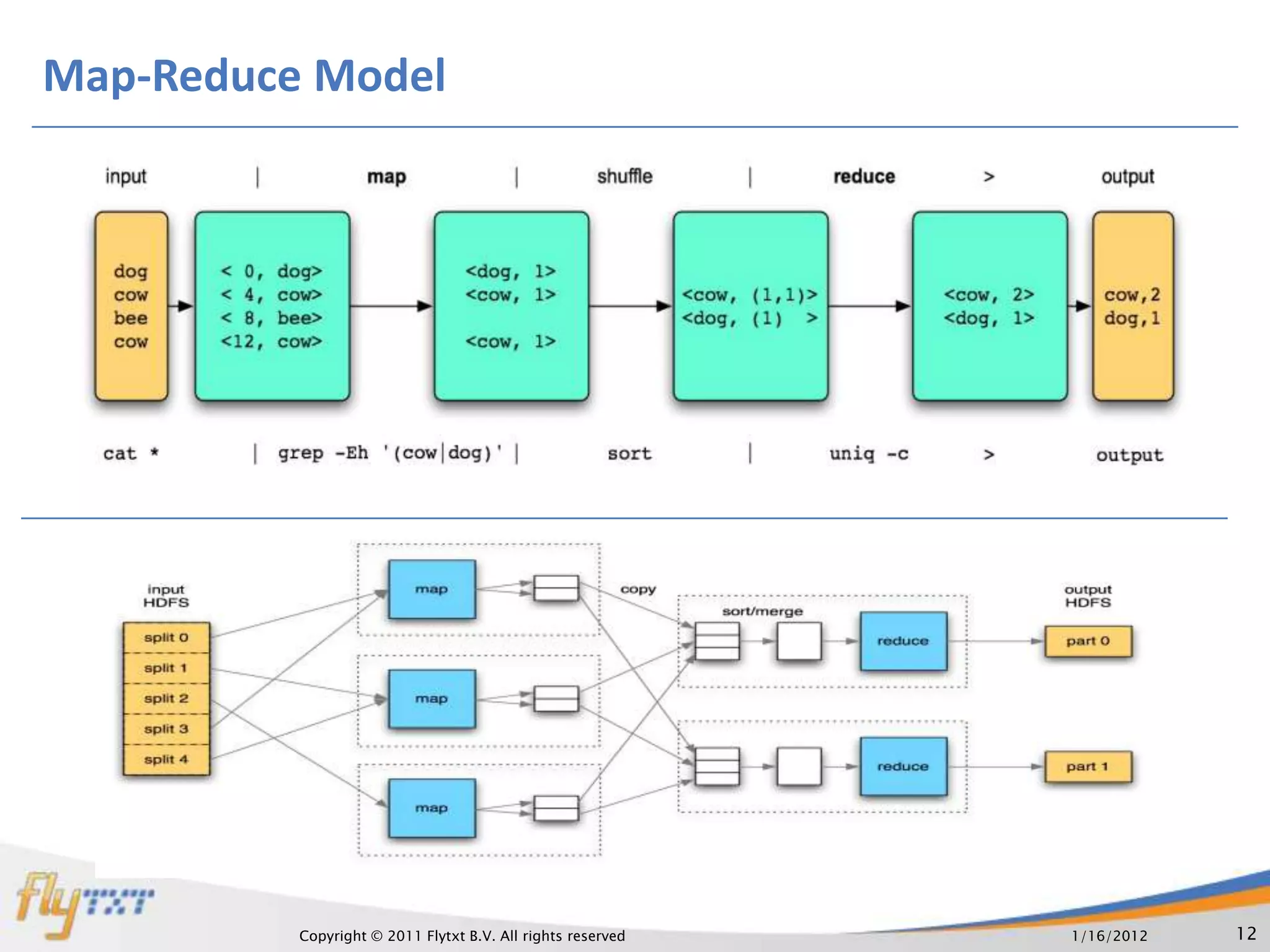
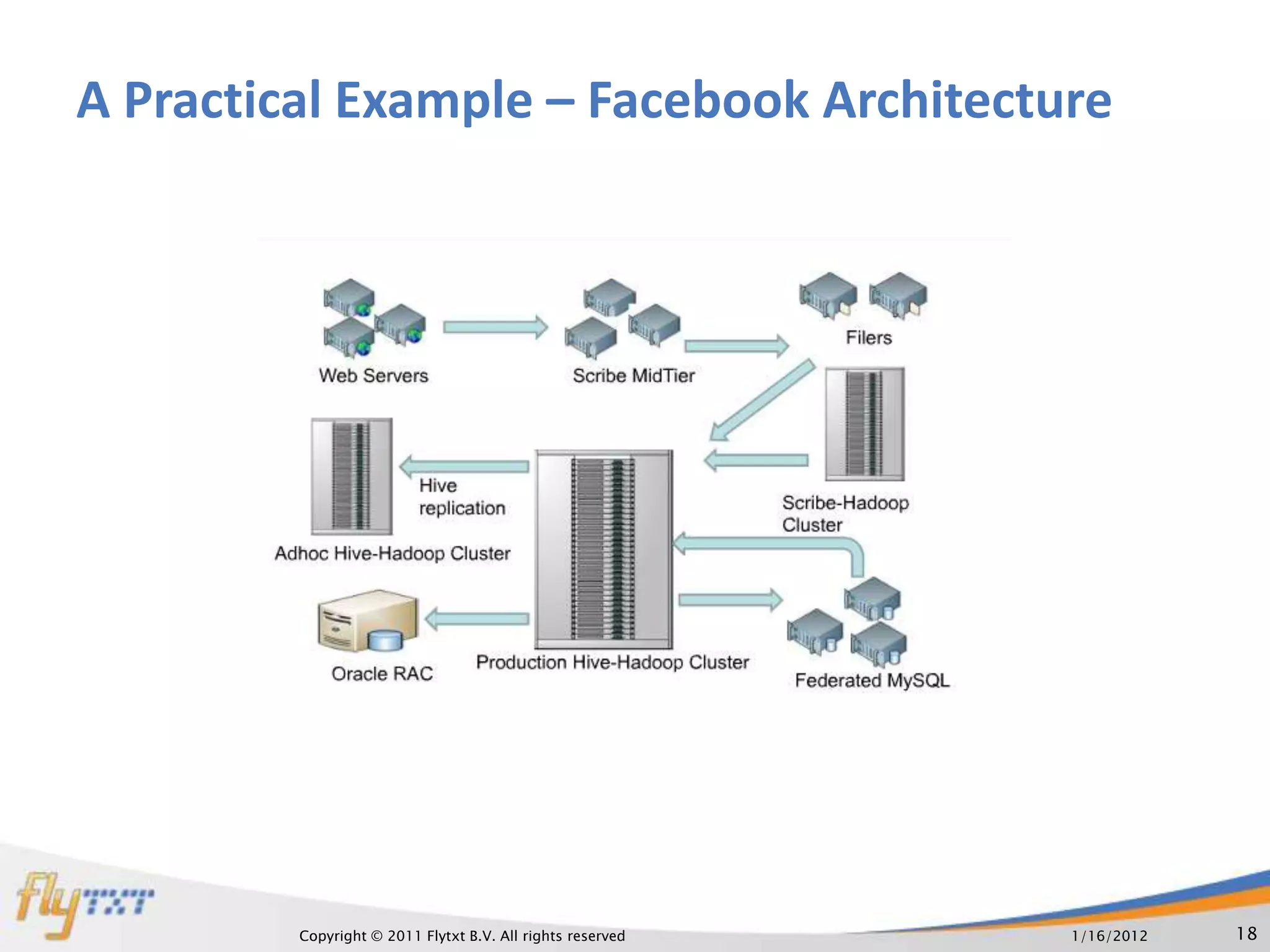
The document discusses RDBMS and Hadoop, comparing their uses and discussing how they can co-exist. It provides an overview of RDBMS concepts like normalization and ACID properties. Hadoop and MapReduce are introduced as using a distributed file system and parallel processing of large datasets. A practical example is given of a master website using RDBMS for user profiles and transactions, and Hadoop for analytics on continuous data streams. The document argues that both systems can co-exist, with each suited to different data and usage types.