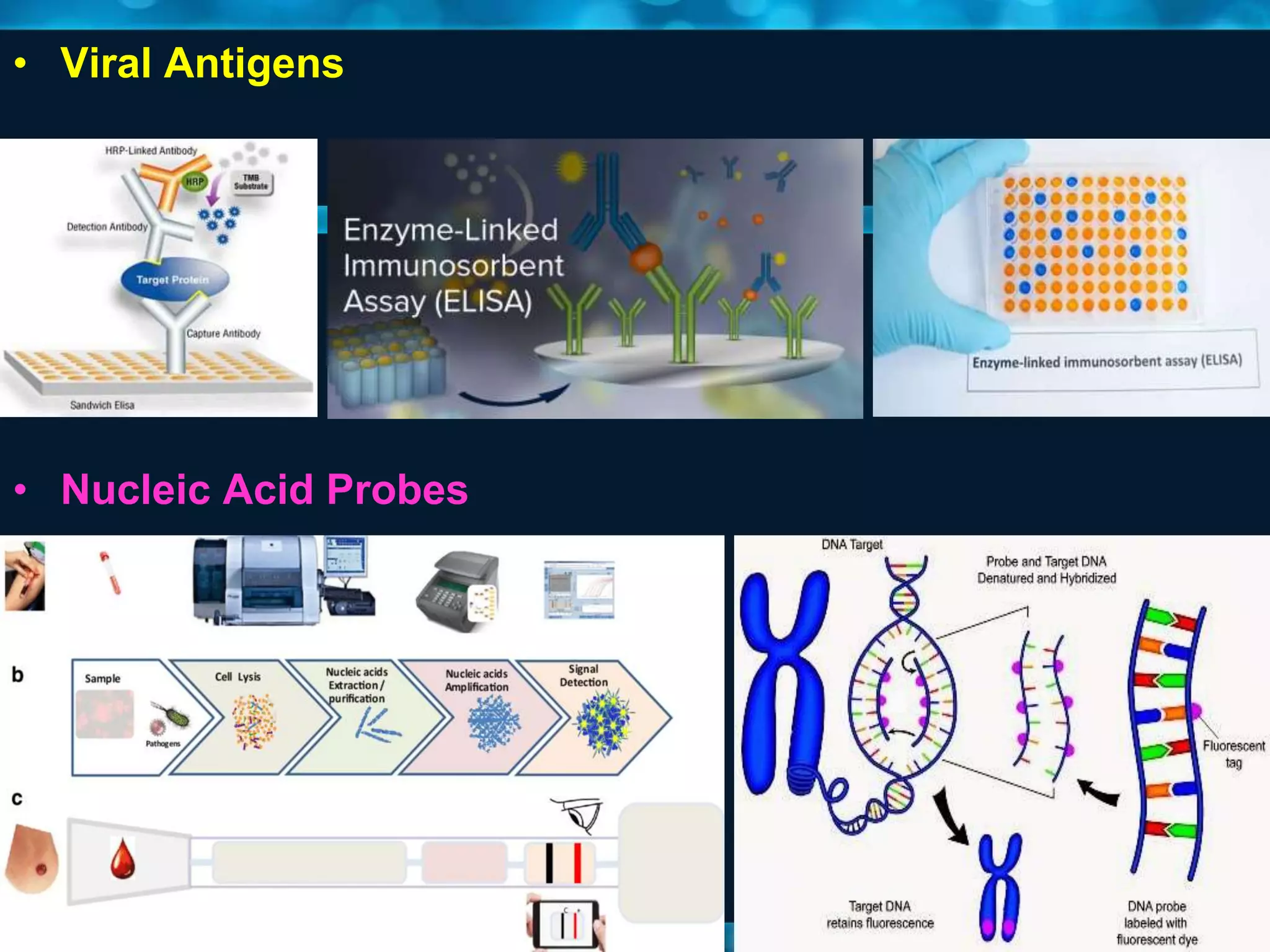
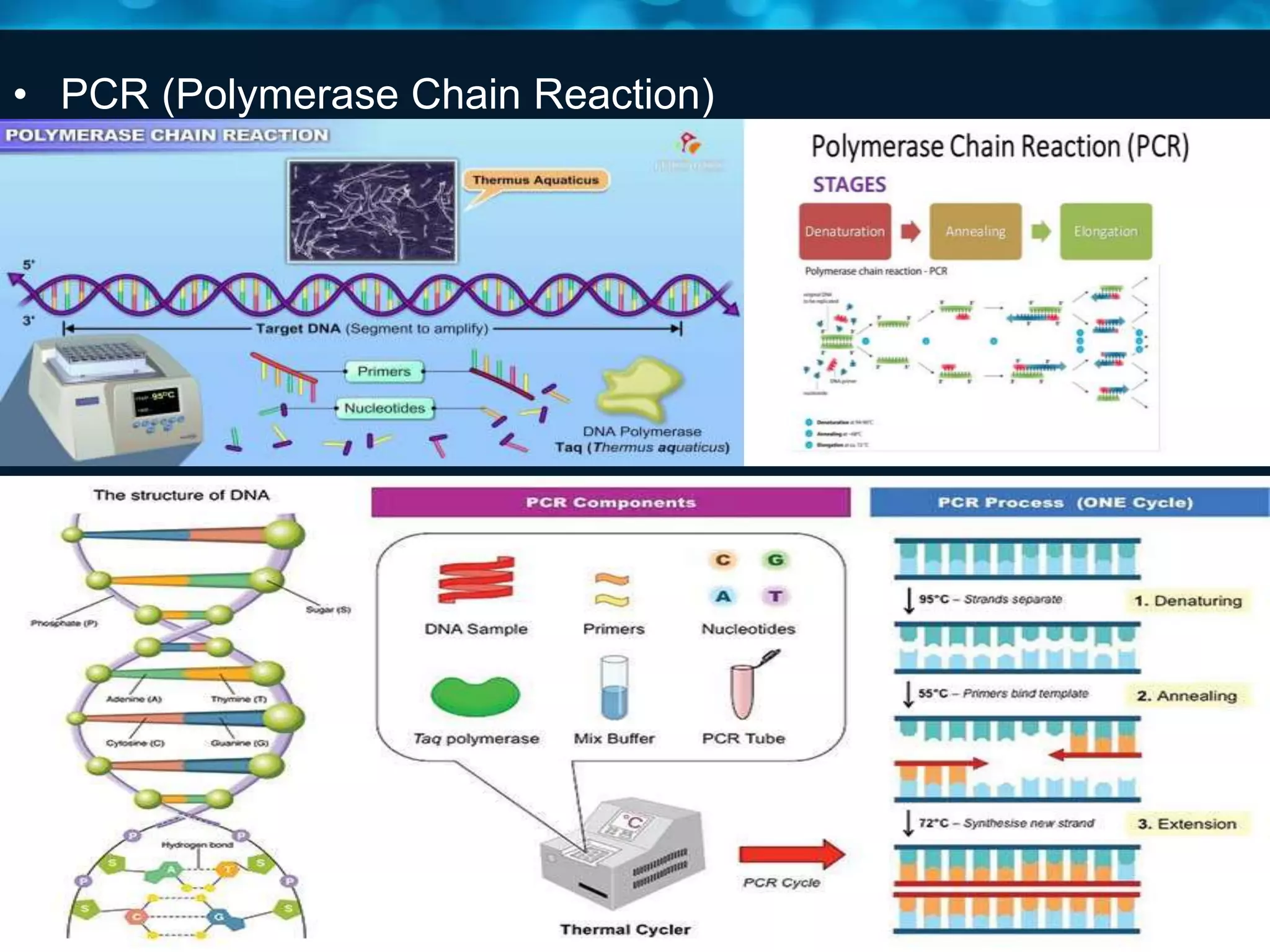
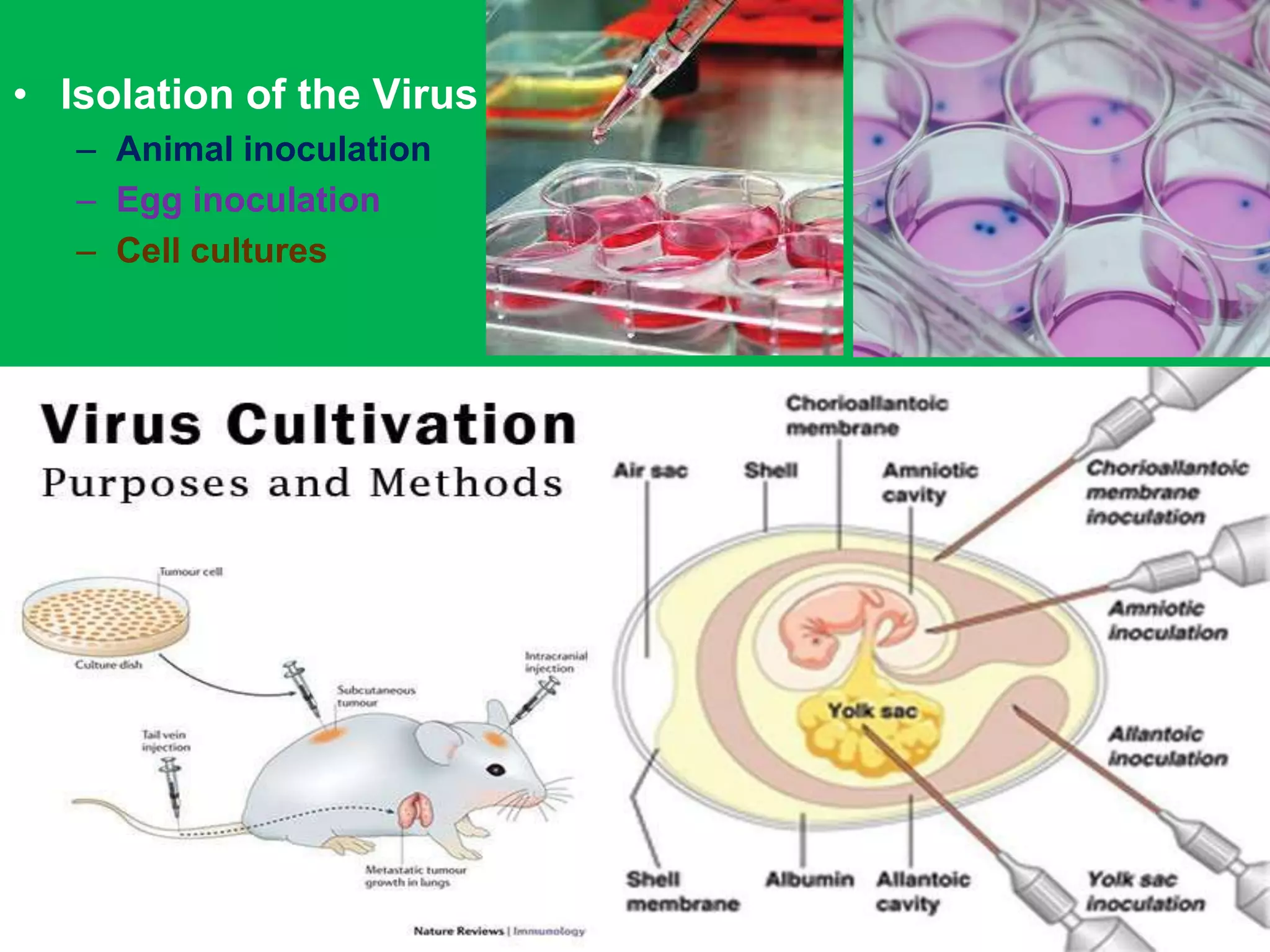
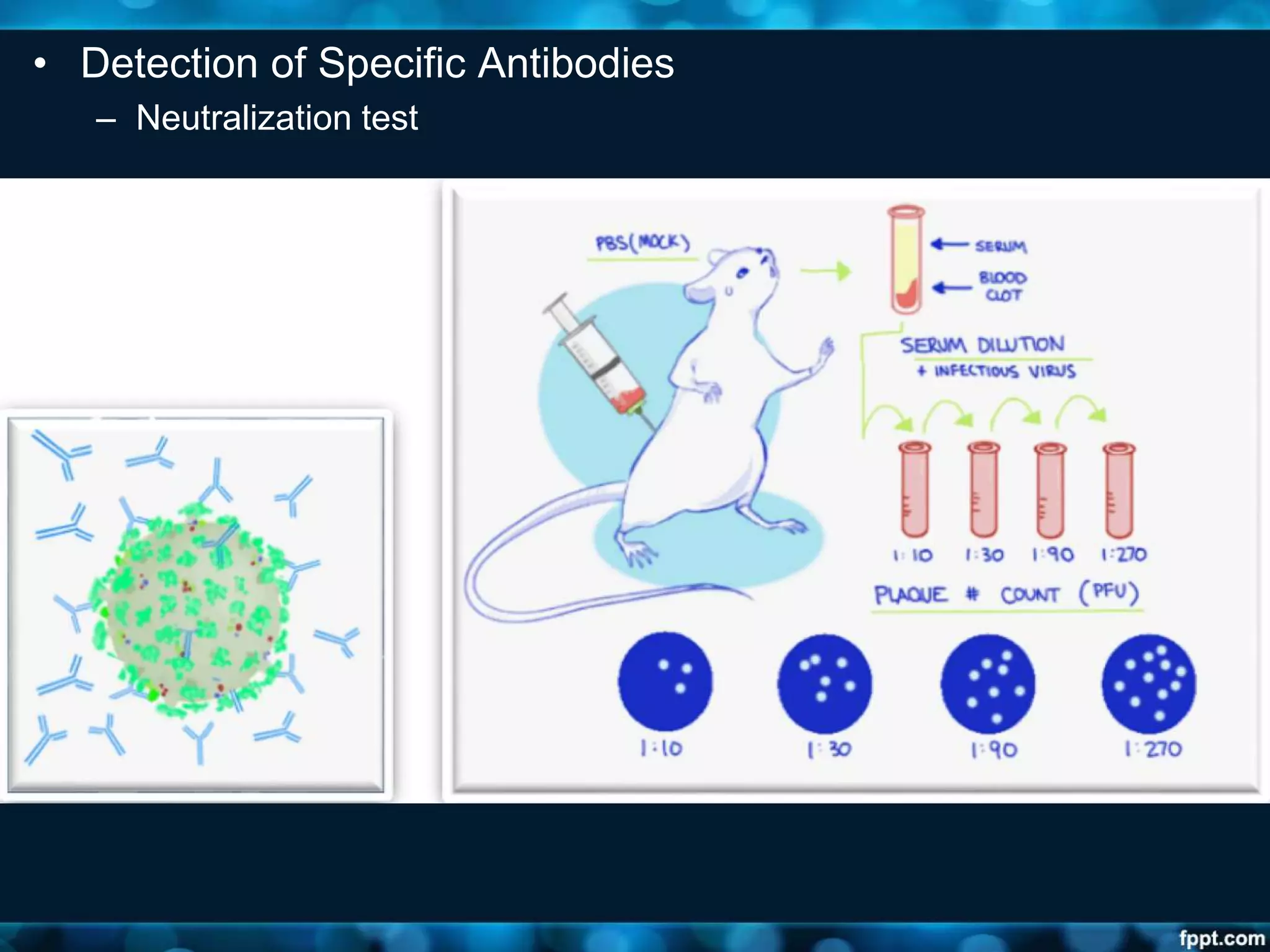
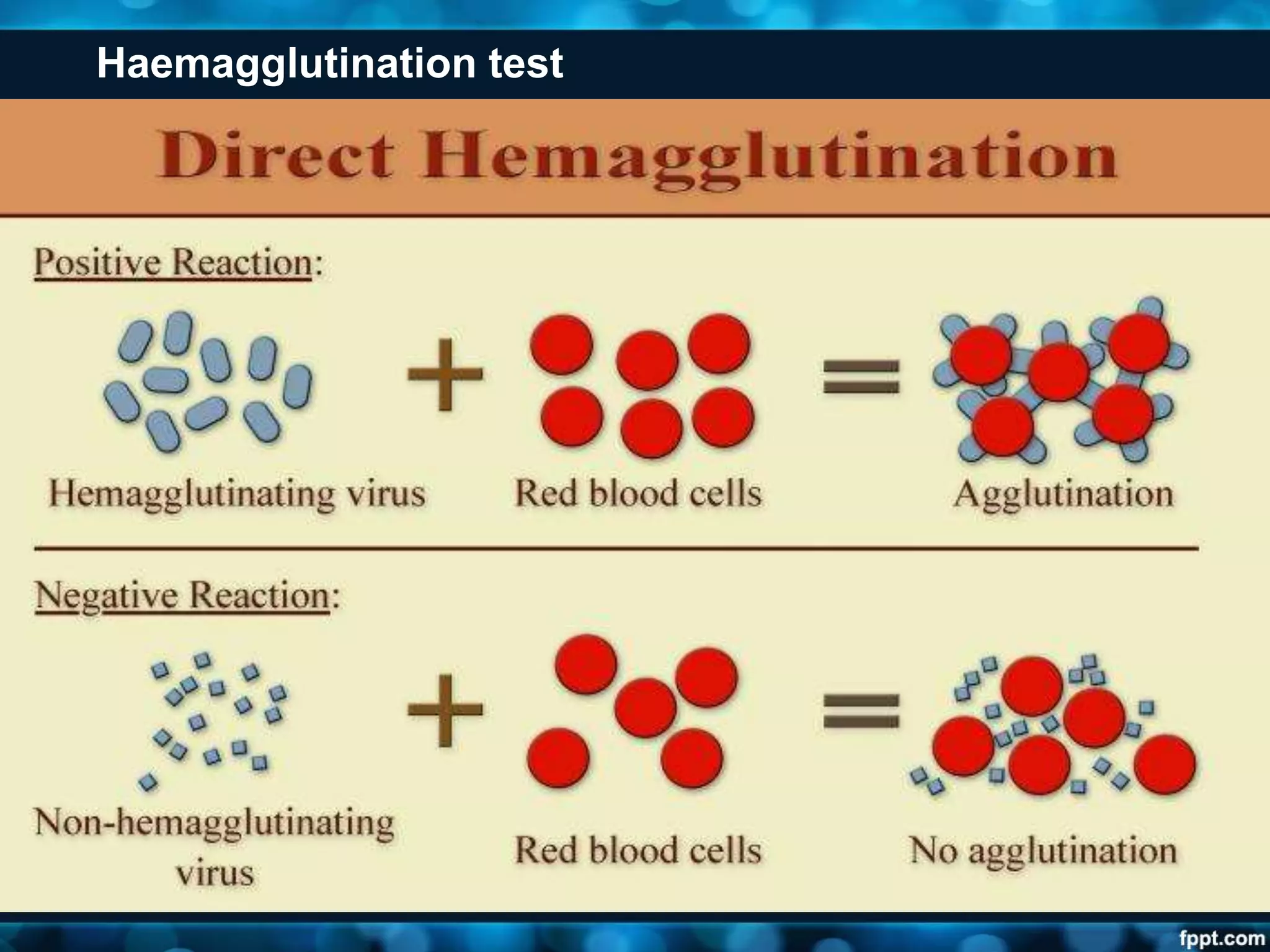
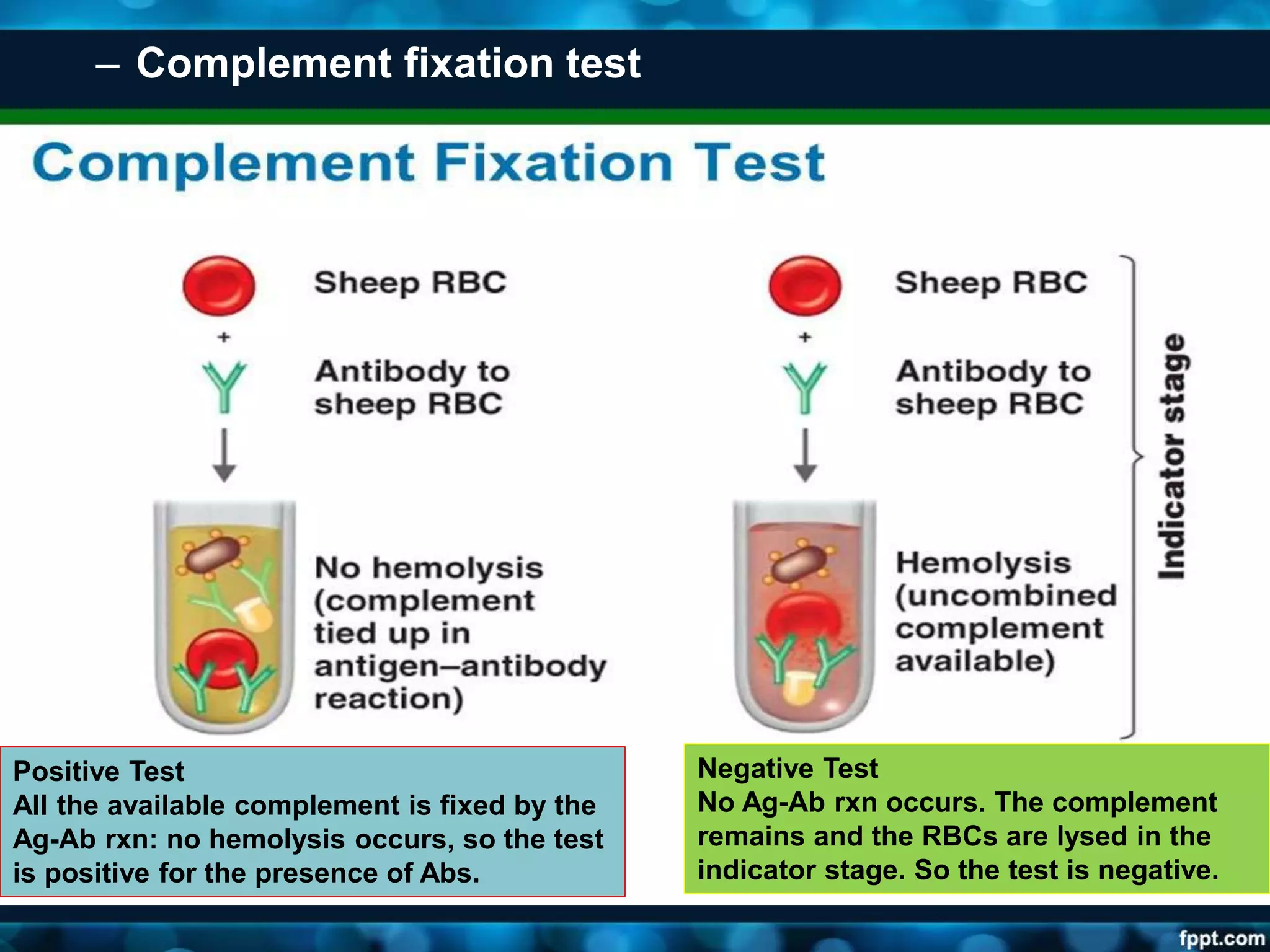
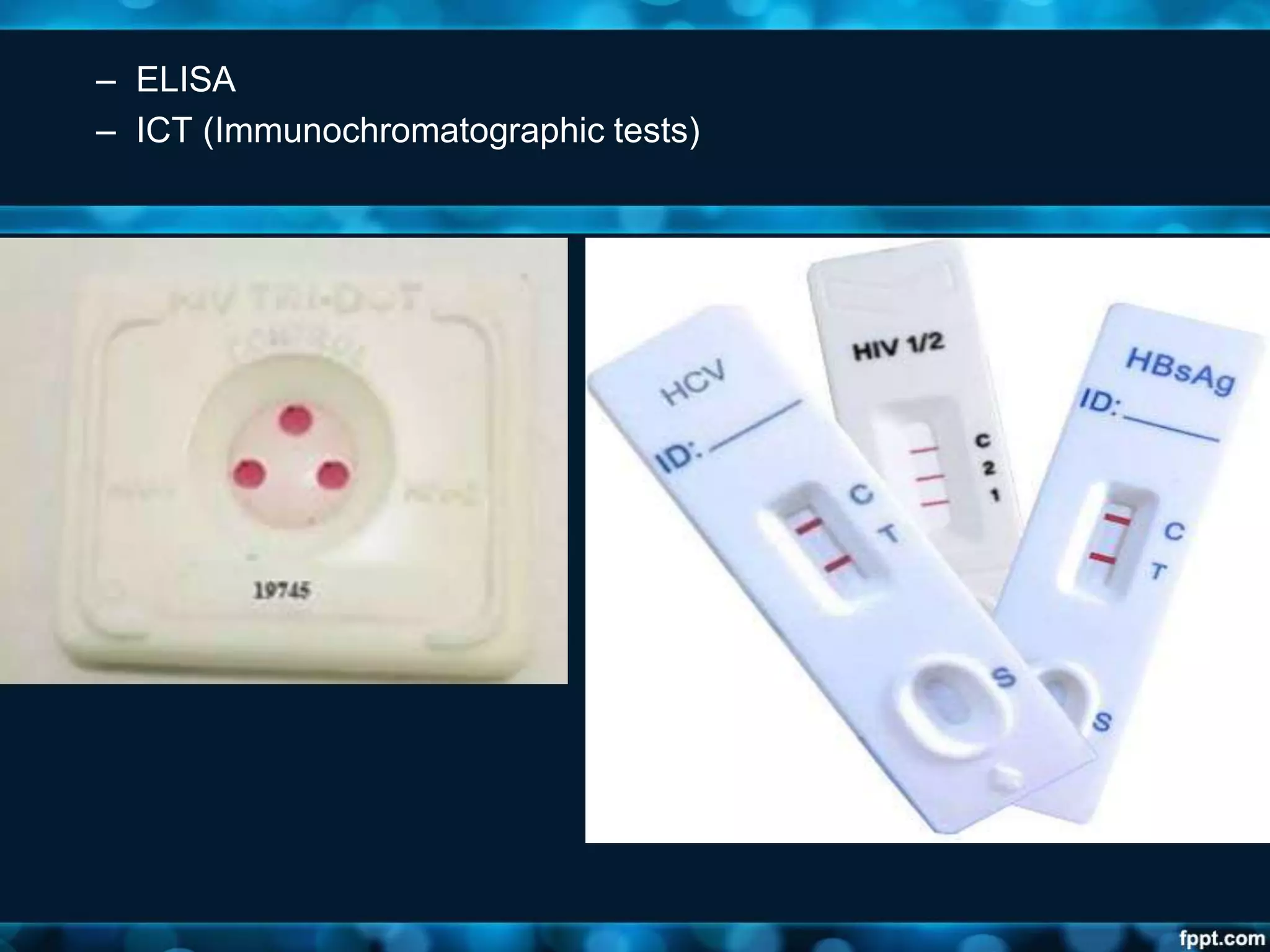
This document discusses viruses, including their definition, properties, morphology, classification, and methods for detection. Some key points:
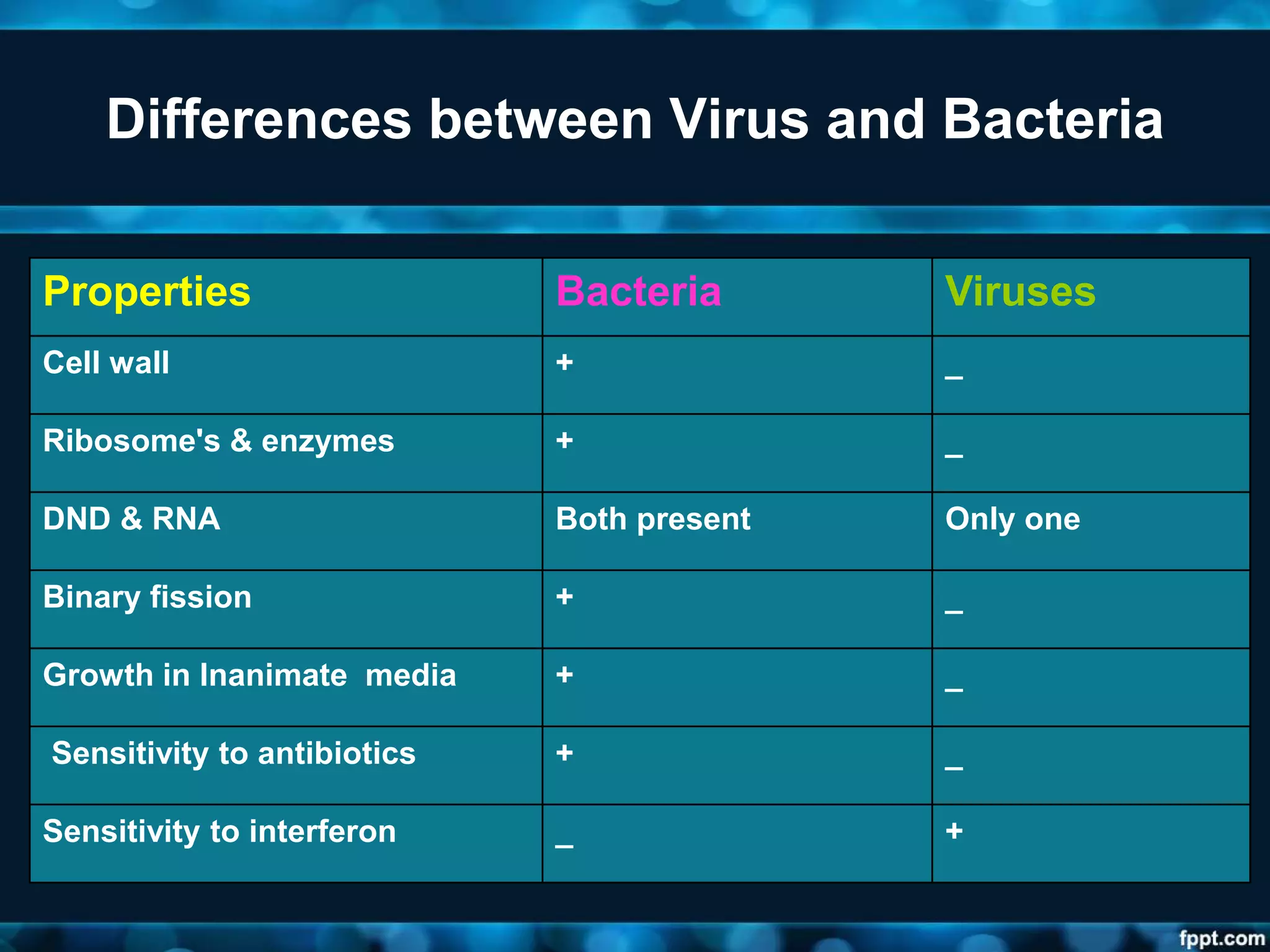
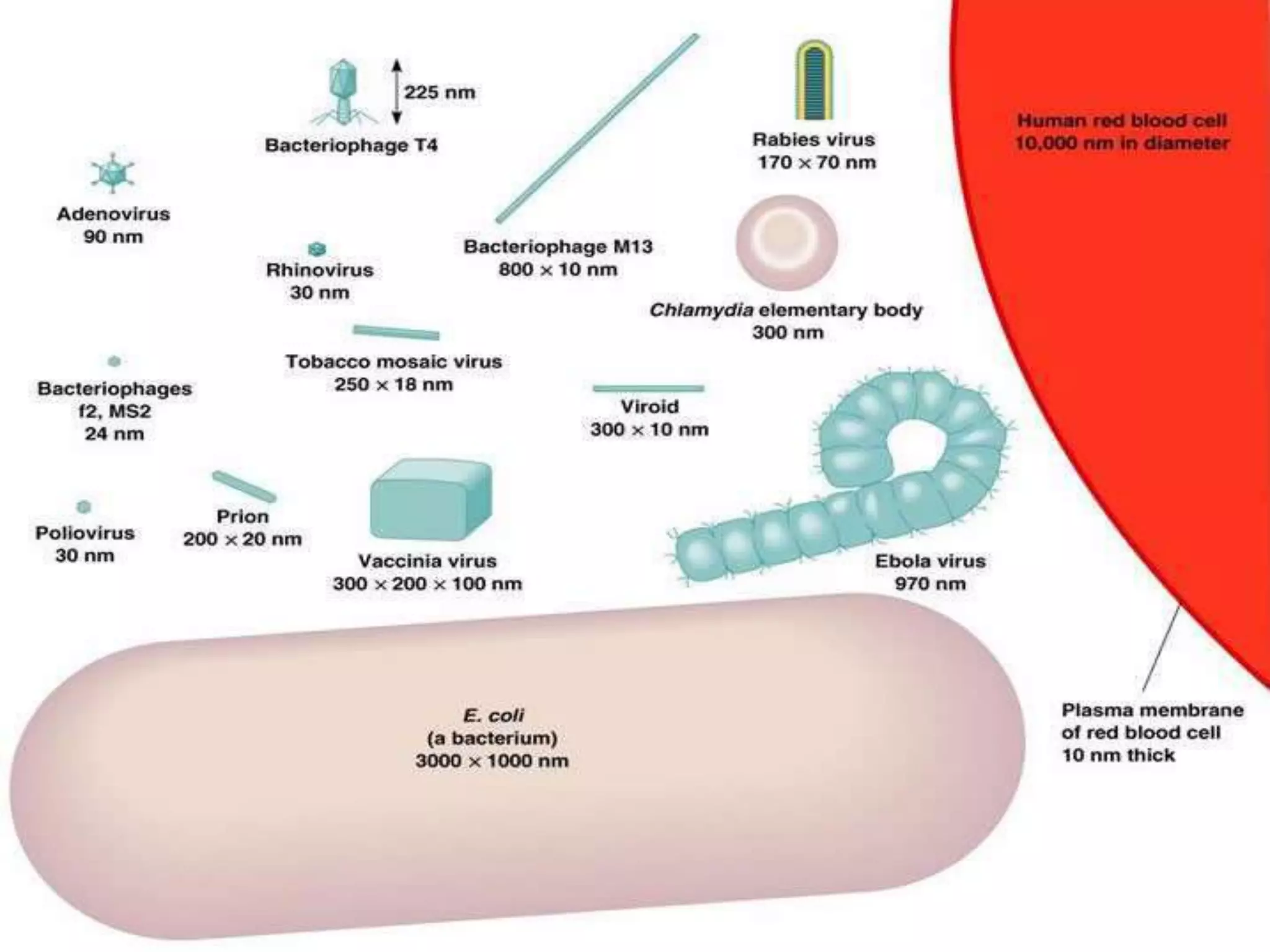
- Viruses are the smallest known infectious agents, containing either DNA or RNA but not both. They lack cellular organization and rely on host cell machinery to replicate.
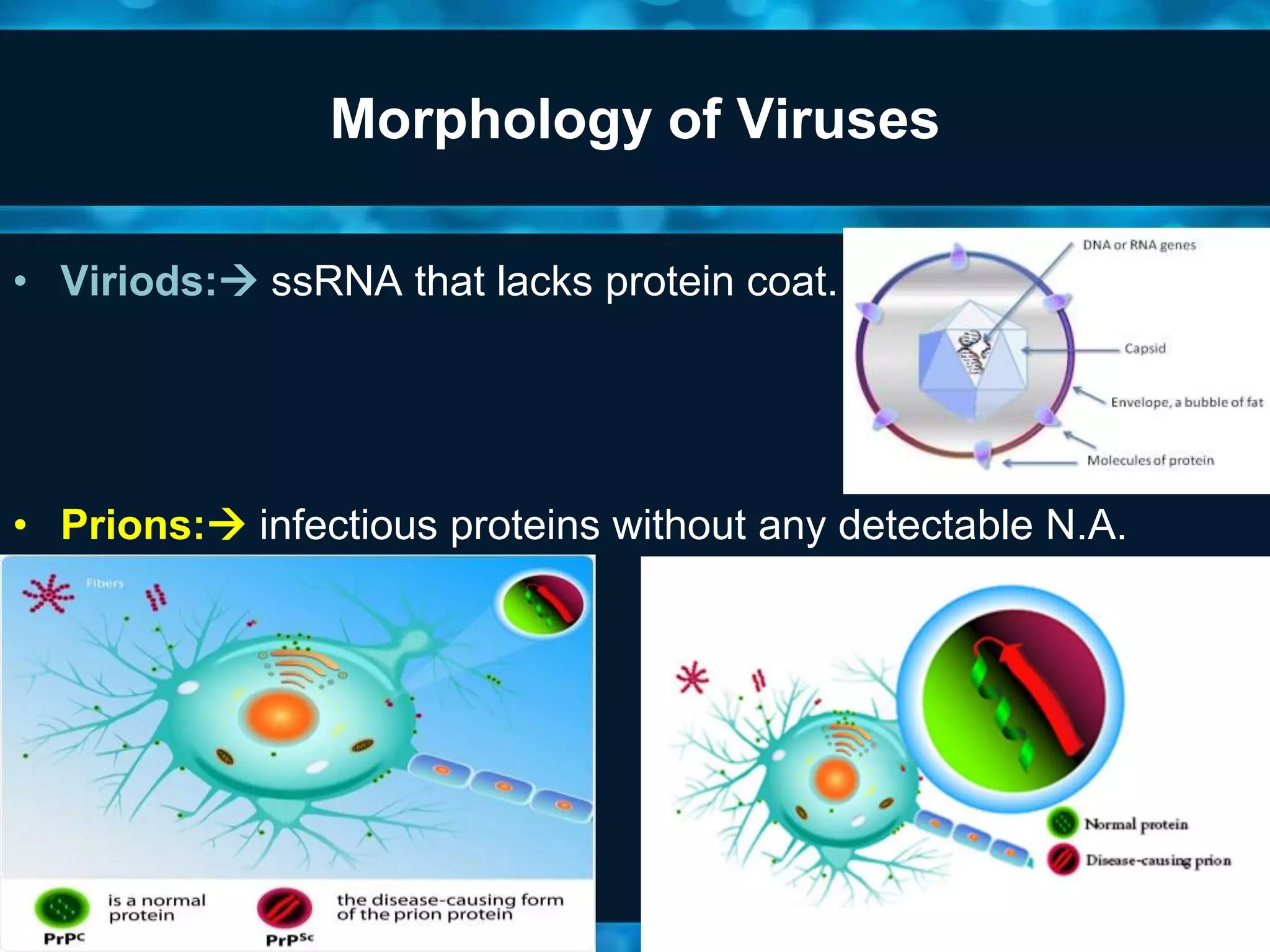
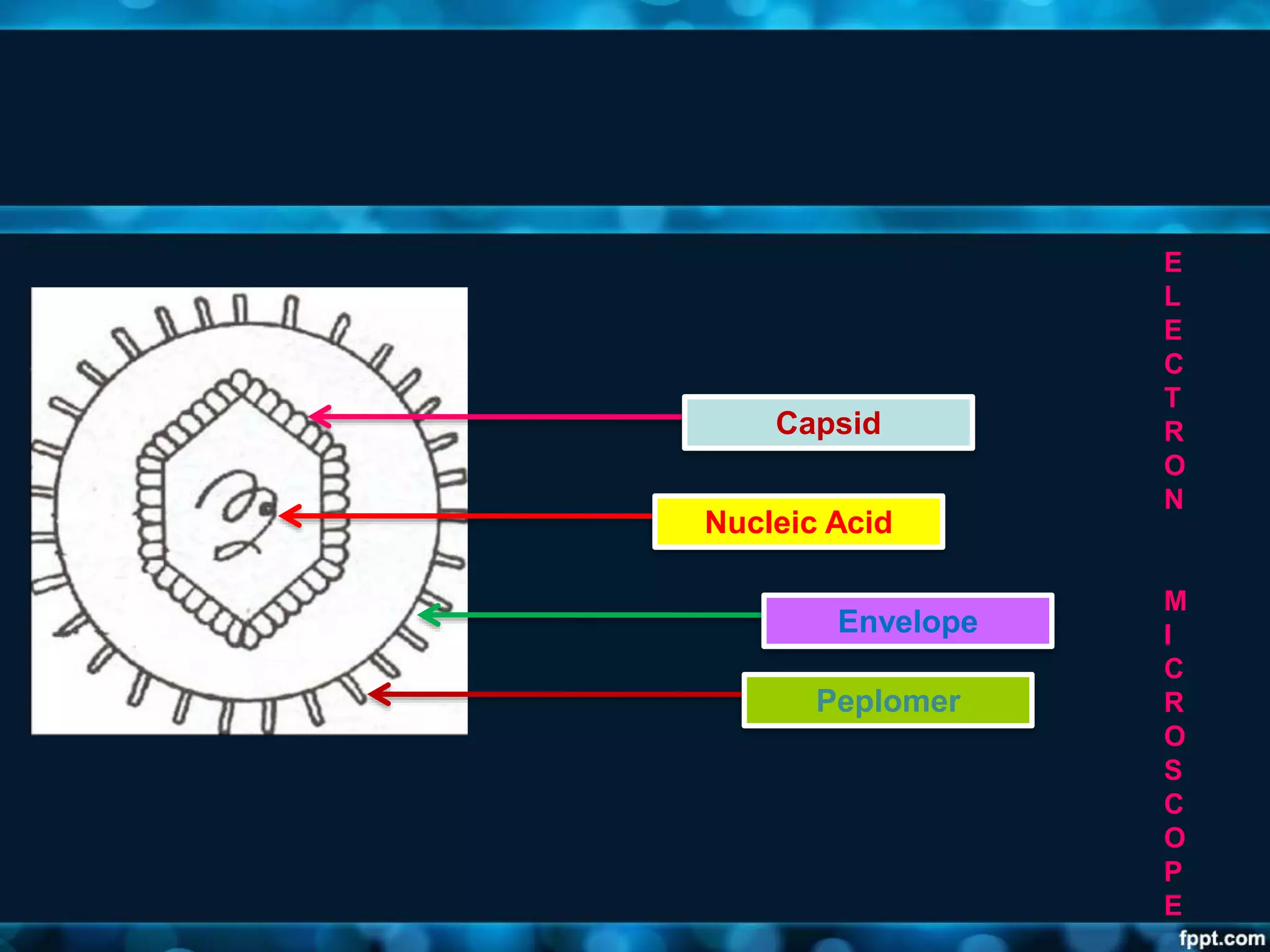
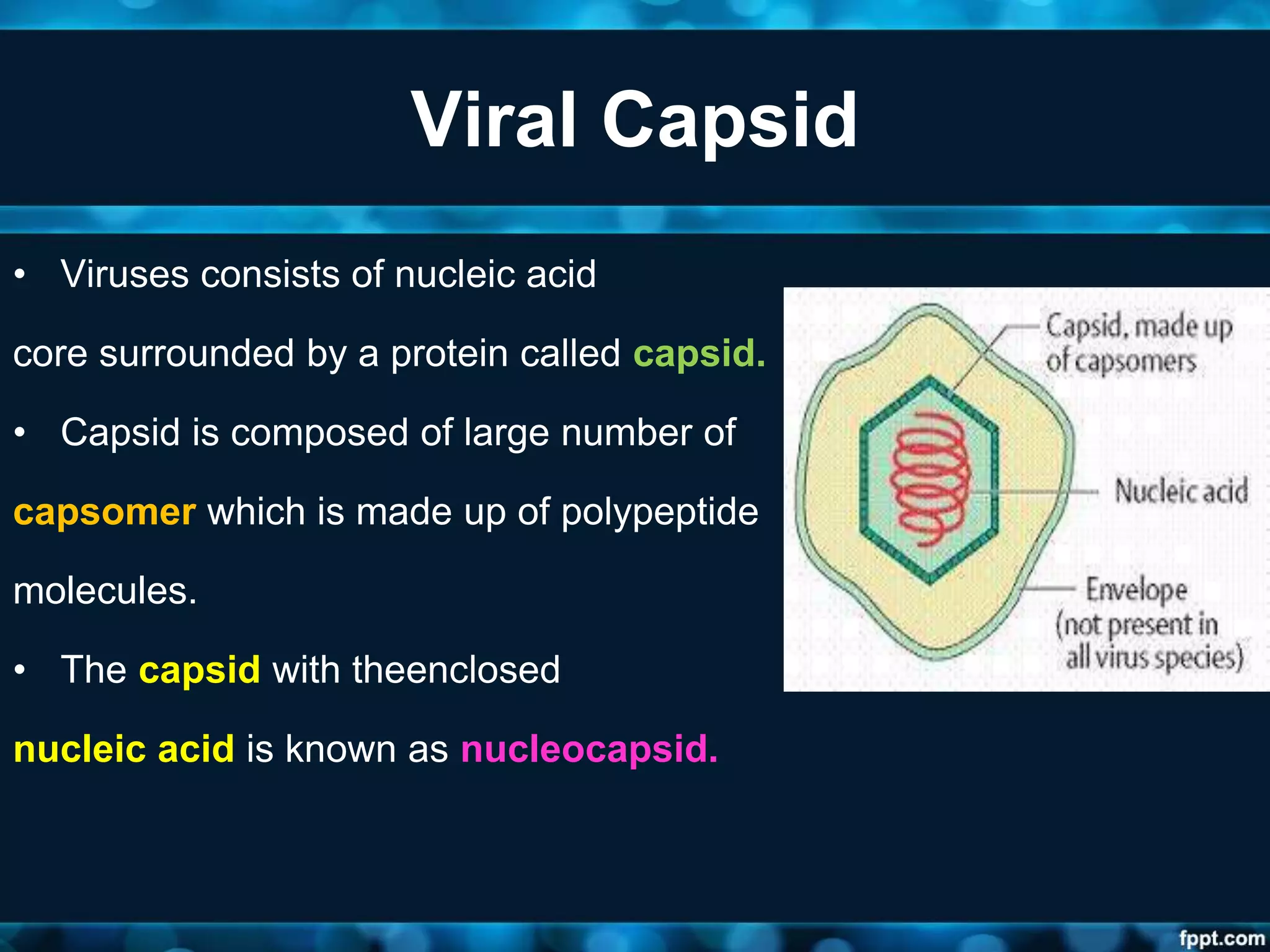
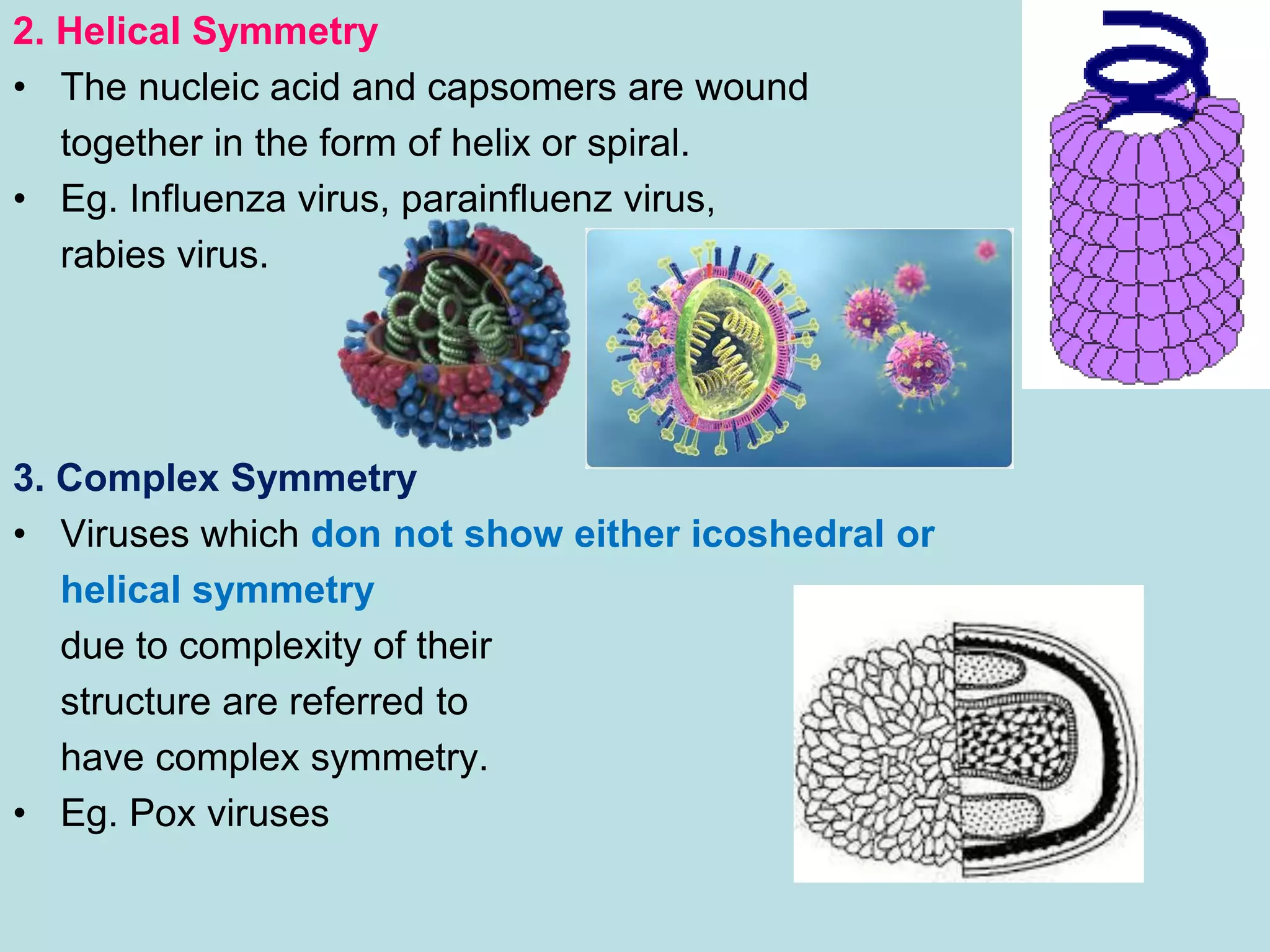
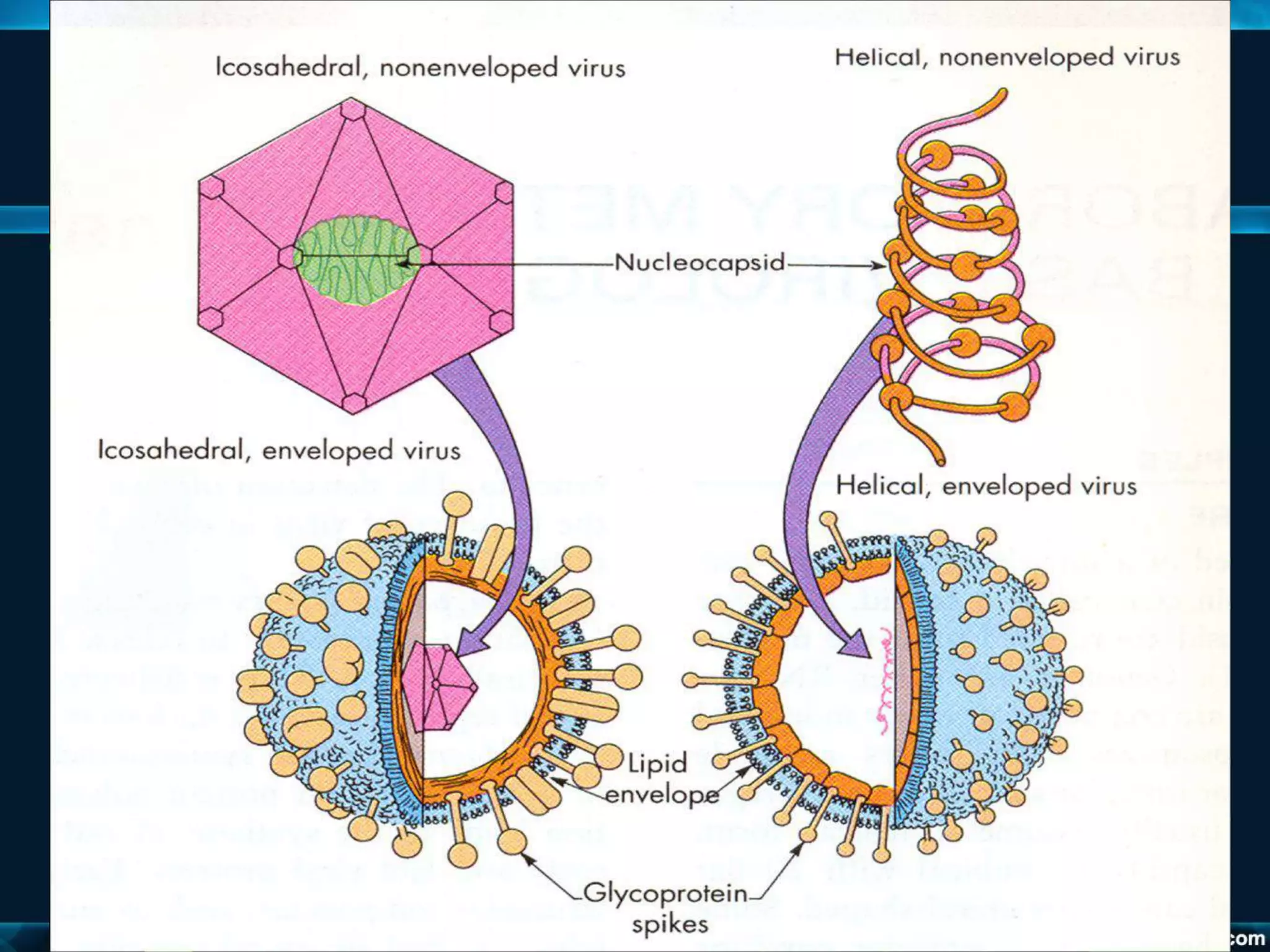
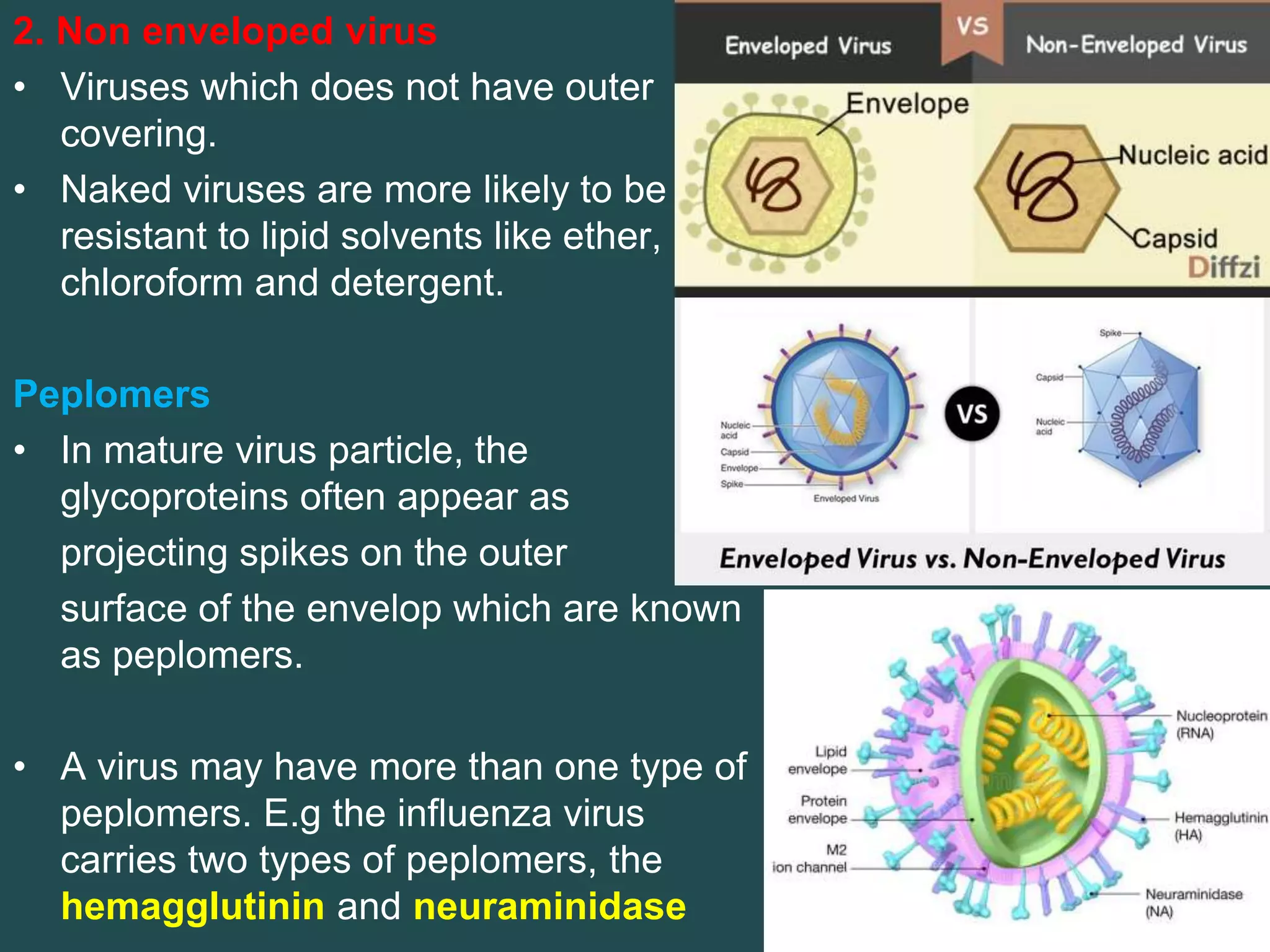
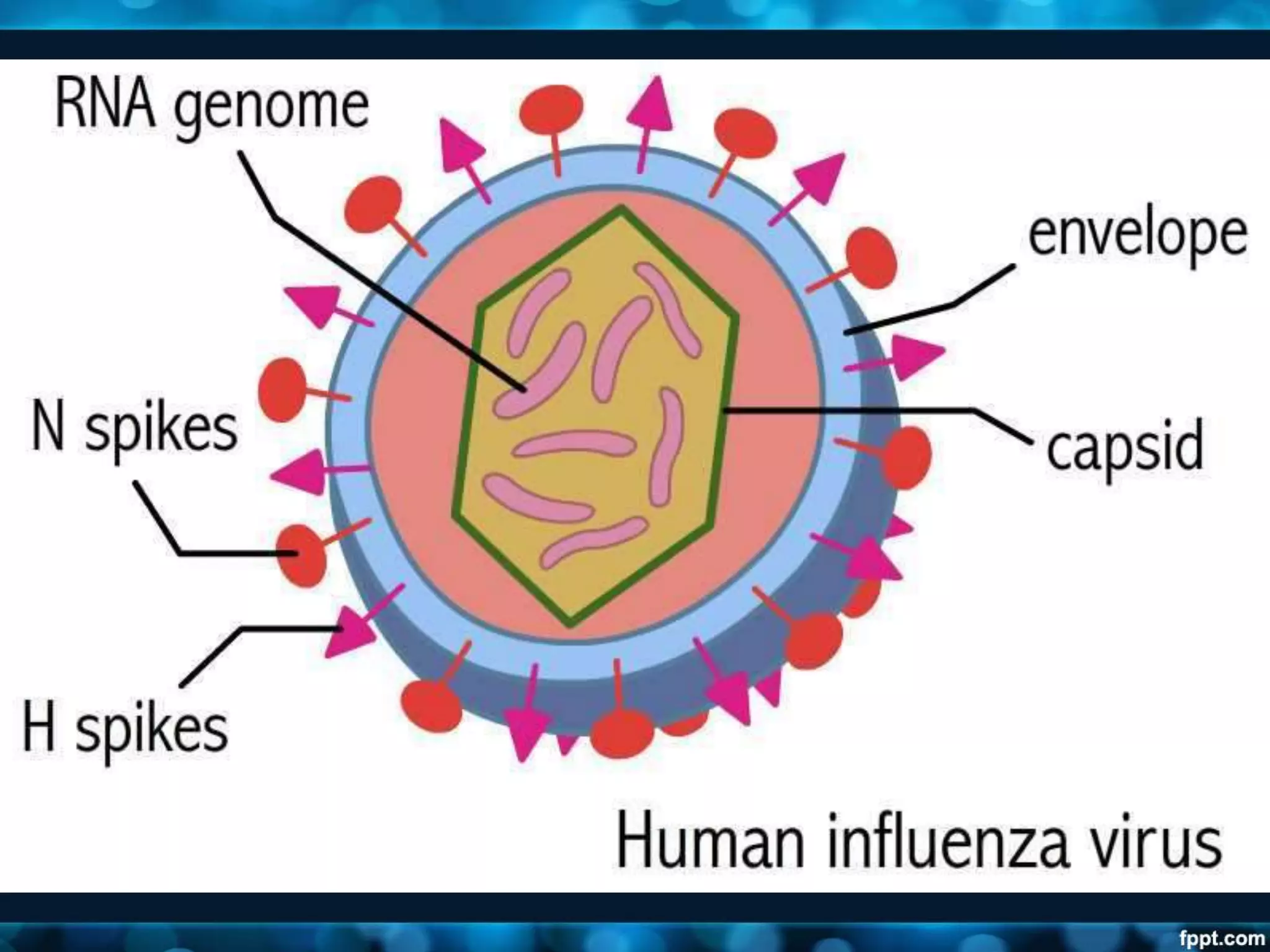
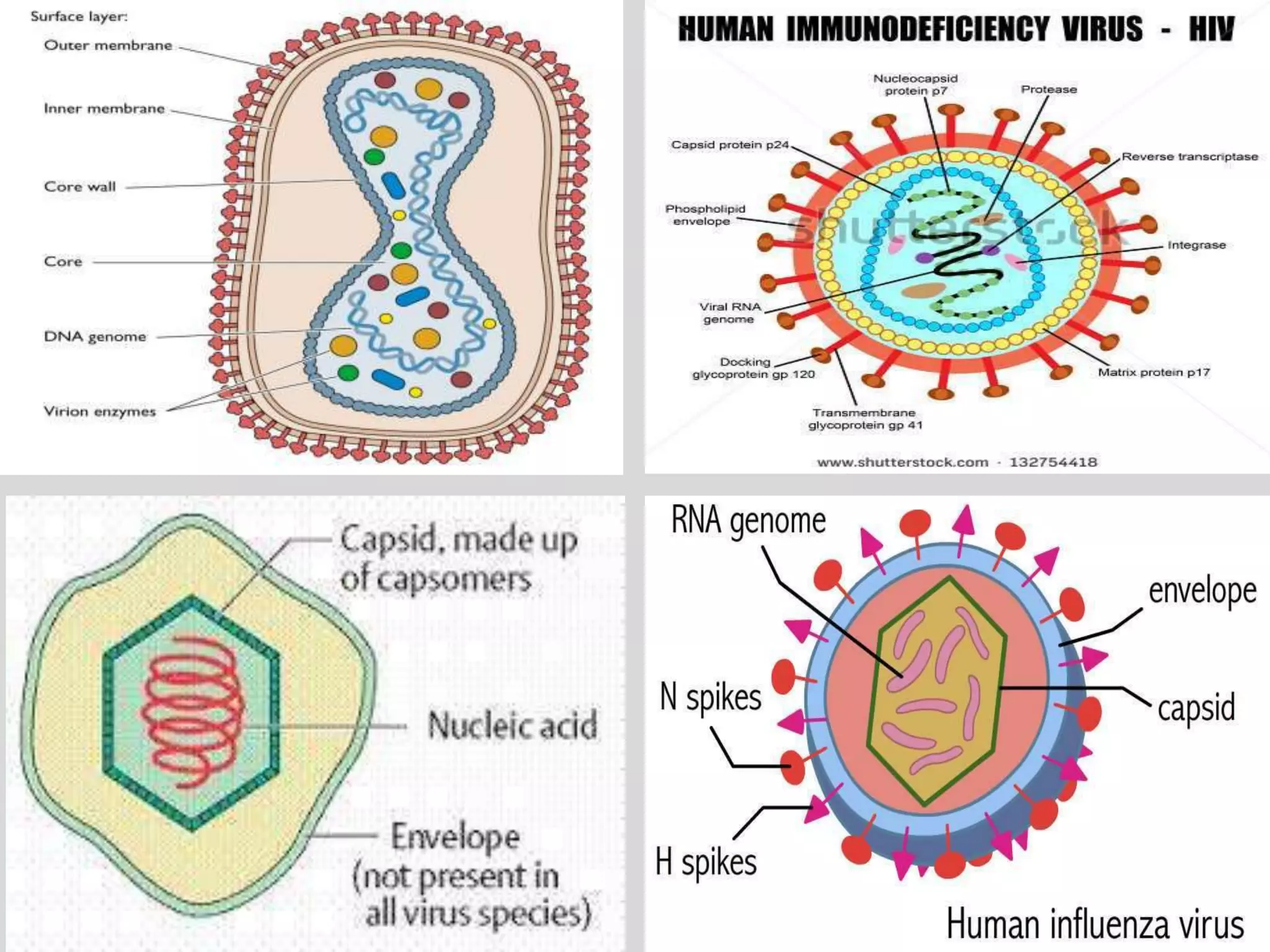
- Viruses have a protein capsid that surrounds and protects their nucleic acid. They can have helical, icosahedral, or complex symmetry. Some are enveloped and others are non-enveloped.
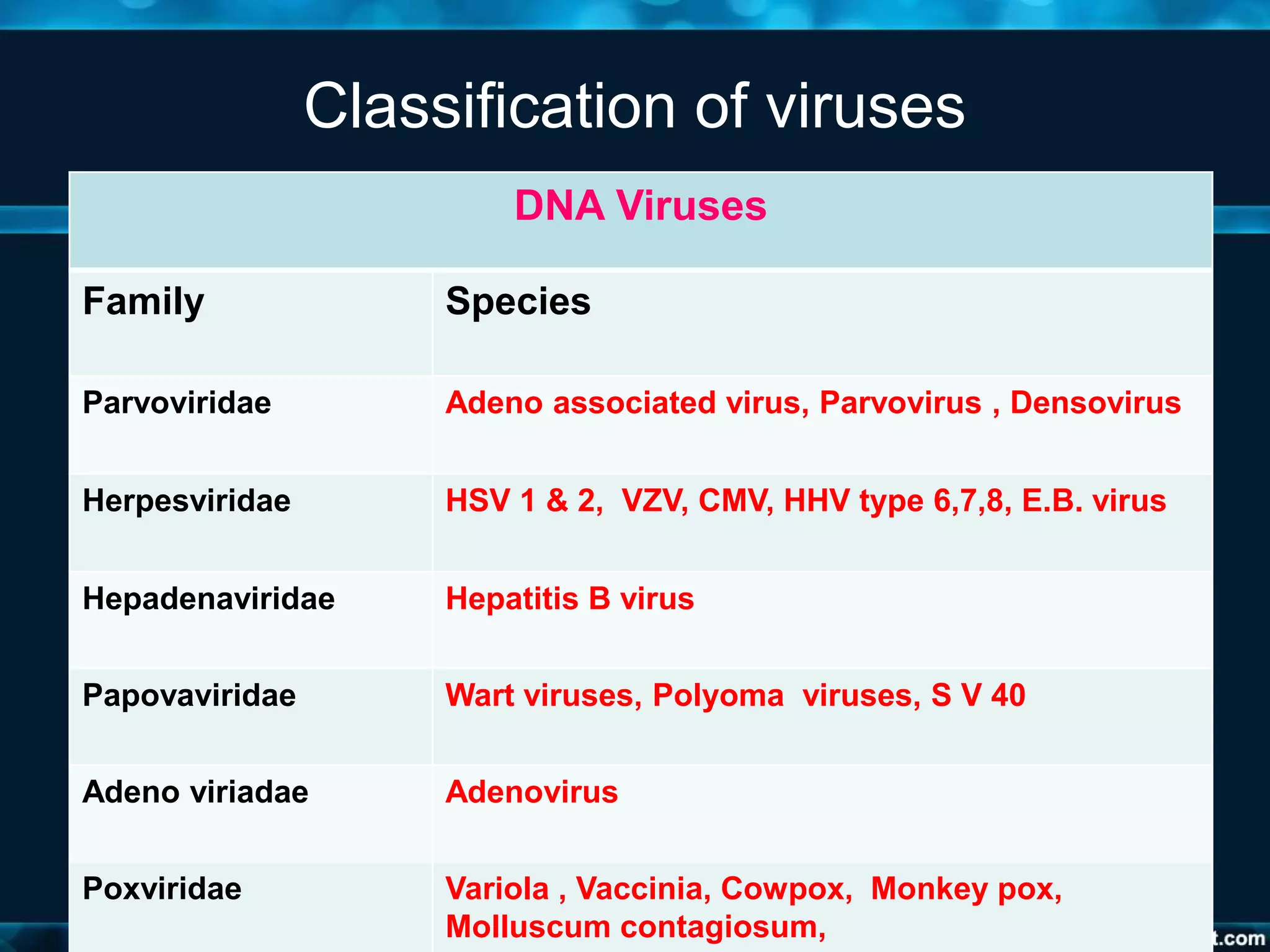
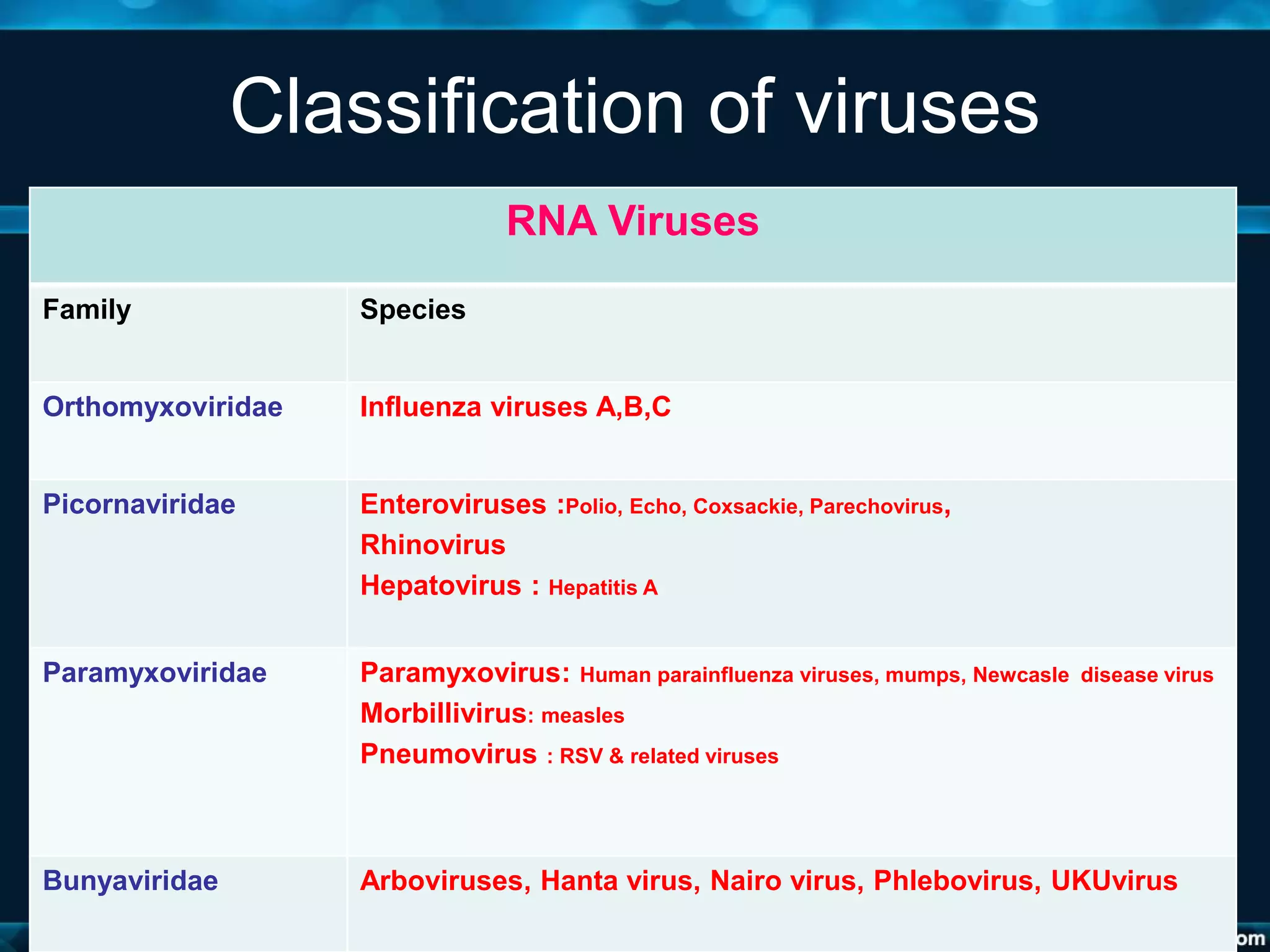
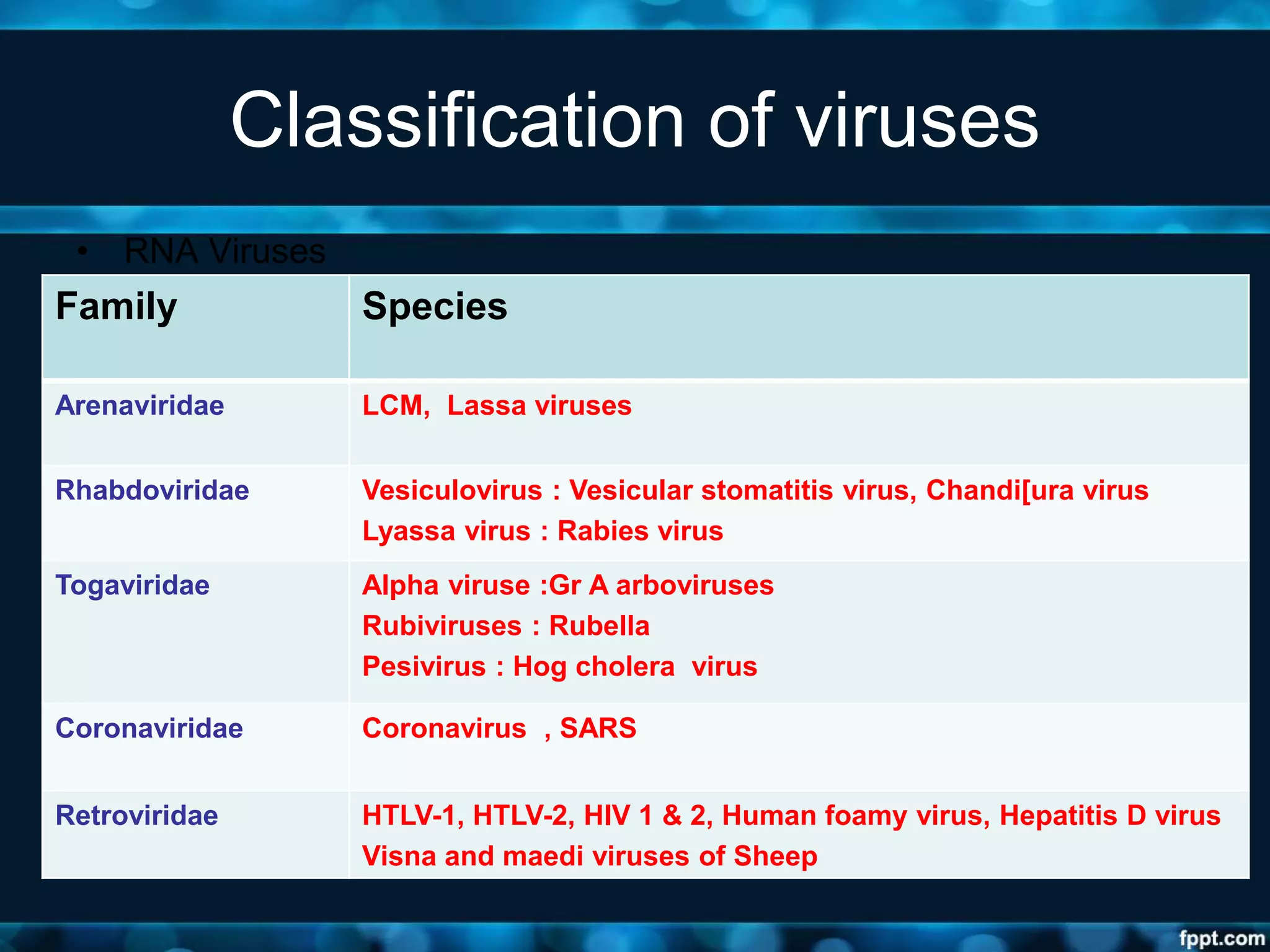
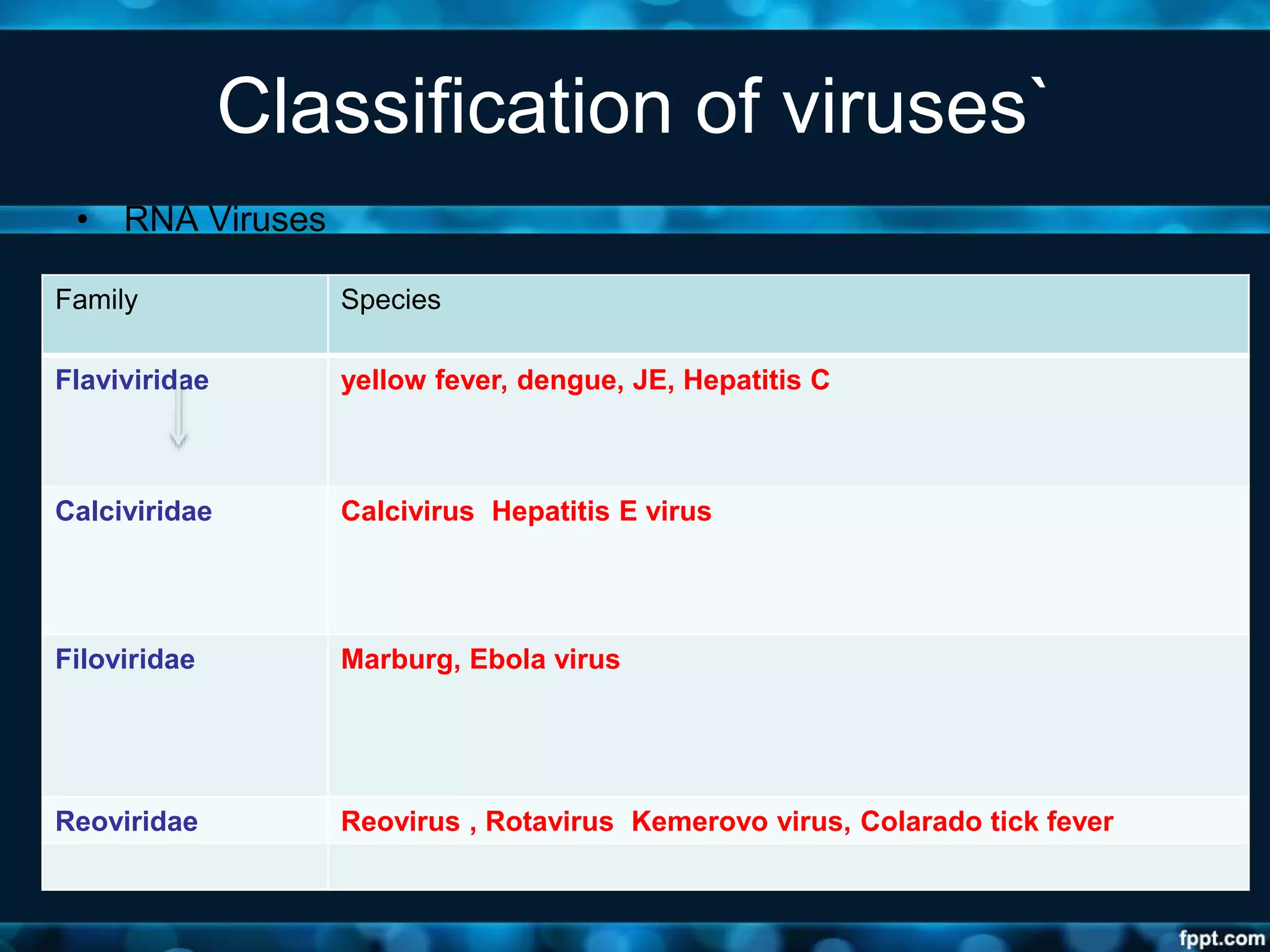
- Viruses are classified based on their nucleic acid type, number of strands, genome structure, and other properties. This includes DNA and RNA virus families such as Adenoviridae, Herpes