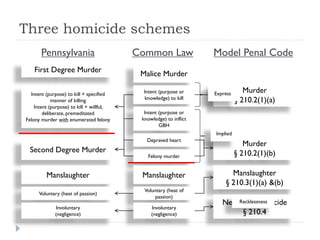
The document discusses three homicide schemes - common law, Pennsylvania, and the Model Penal Code. It provides definitions and examples of first-degree murder, second-degree murder, manslaughter, and related terms. It also summarizes two court cases - State v. Guthrie and the differing definitions of "deliberate and premeditated" from Schrader and Morrin. The last section discusses aggravating and mitigating circumstances in determining sentencing for first-degree murder under Arizona law.

![State v. Guthrie (W. Va. 1995)
“Murder by poison, lying
“[A]ny interval of time in
What verdict?
wait, imprisonment,
between the forming of the
starving, kill and the
intent toor by any willful,
A = First-degree murder
deliberate and
execution of that intent,
B = Second-degree murder
premeditated killing, duration
which is of sufficient or in
C = Manslaughter
the commission of, or
for the accused to be fully
attempt to commit [specific
conscious of what he
felonies] is sufficient the
intended,is murder in to
first degree. All other
support a conviction for first
murder is murder
degree murder” in the
second degree”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class-140226232610-phpapp02/85/Class-17-posted-3-320.jpg)
![Discussion
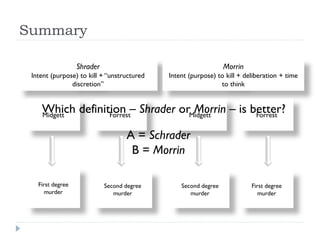
Schrader definition of “deliberate and premeditated”
Deliberate and premeditated = “[W]hat is really
meant by the language ‘willful, deliberate and
premeditated’… is that the killing be intentional
[purposeful]”
Morrin definition of “deliberate and premeditated”
Second degree murder = purpose or knowledge
Deliberate = “[T]o deliberate is to measure and
“Unstructured discretion”
Firstevaluate murder = willful, deliberate and problem”
degree the major facets of a choice or premeditated
Premeditated = “[T]o premeditate is to think about
beforehand”
purpose
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class-140226232610-phpapp02/85/Class-17-posted-4-320.jpg)



![Discussion – Ariz. Rev. Stat. Ann. § 13-751
of [i]ntending or of
The trier of fact shall impose a sentence Mitigating circumstances fact finds one
Aggravating circumstances
A person commits first degree murder if:death if the trierknowing that
or more aggravating circumstances andThe defendant’s capacity there are no
the person’s has been or cause death,thenperson causes the death of
the determines that to appreciate
The defendant conduct willwas
the wrongfulness
mitigating circumstances sufficiently premeditationcallhis conduct or to
another person, with substantial to of for leniency
previously convicted of a serious
conform his conduct to the
requirements of law was significantly
impaired, but not so impaired as to
constitute a defense;
offense;
The defendant knowingly created a
grave risk of death to another
person in addition to the person
murdered;
The defendant committed the
offense in an especially heinous,
cruel or depraved manner;
The offense was committed in a
cold, calculated manner without
pretense of moral or legal
justification
The defendant was under unusual and
substantial duress, although not such as
to constitute a defense;
Any factors proffered by the defendant
that are relevant to determining whether
to impose a sentence less than death,
including any aspect of the defendant’s
character, propensities or record and any
of the circumstances of the offense](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class-140226232610-phpapp02/85/Class-17-posted-9-320.jpg)