This document discusses key concepts in corporate strategy including:
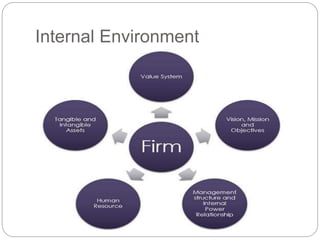
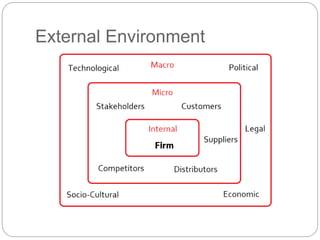
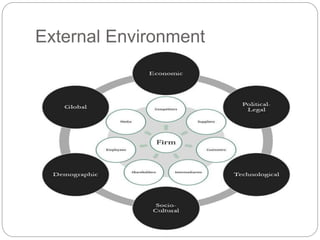
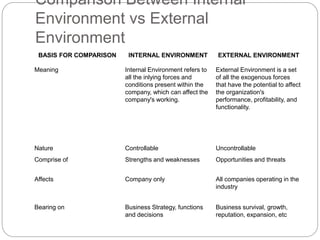
- Definitions of strategy, strategic management, internal environment, external environment, and the differences between them.
- Components of a Strategic Advantage Profile (SAP) and Environmental Threat and Opportunity Profile (ETOP) and how they are used to analyze strengths/weaknesses and opportunities/threats.
- Explanations of SWOC analysis and the conceptual framework for strategic management, outlining the stages of defining vision/mission, strategy formulation through analysis and goal setting, and strategy implementation.