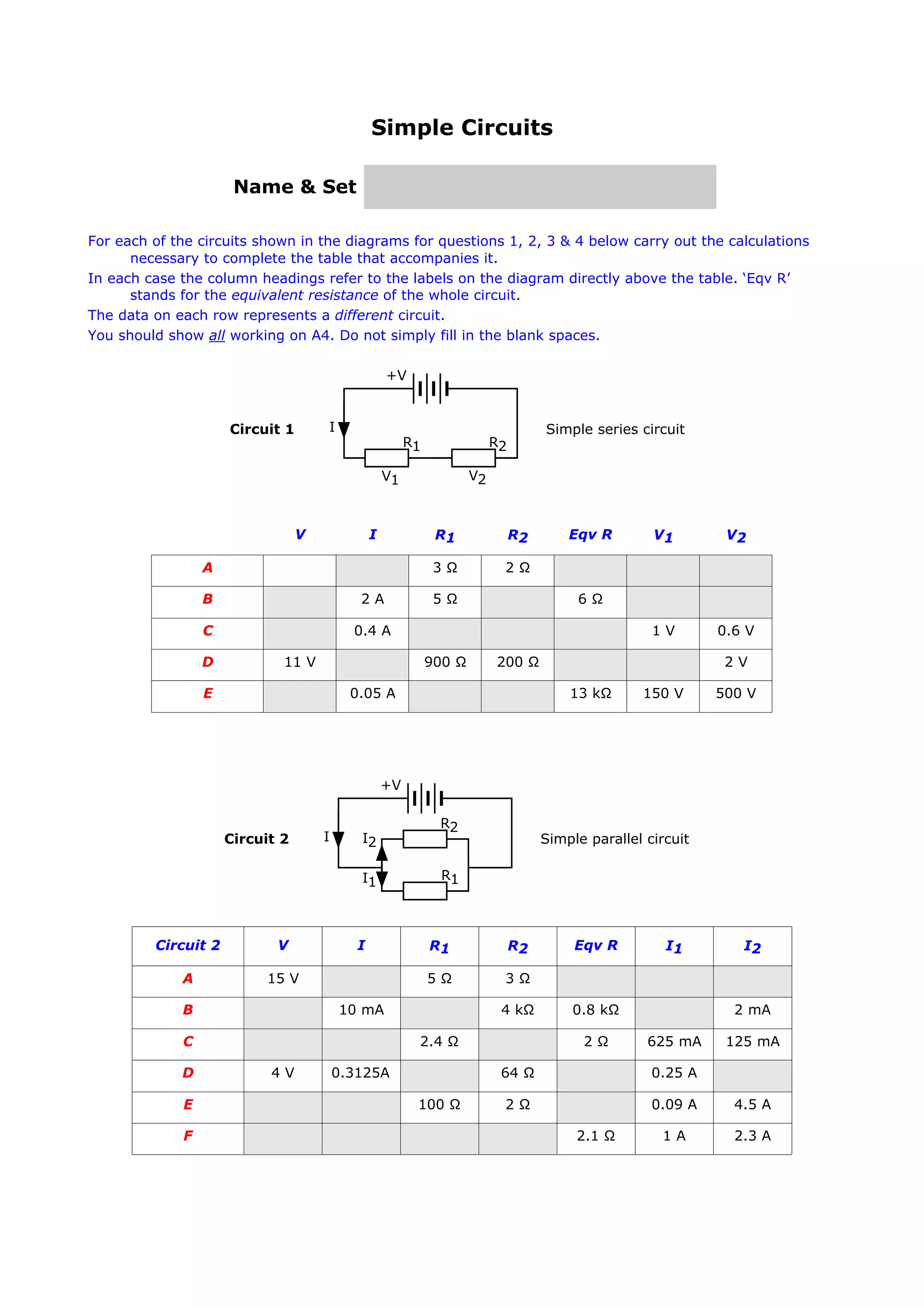
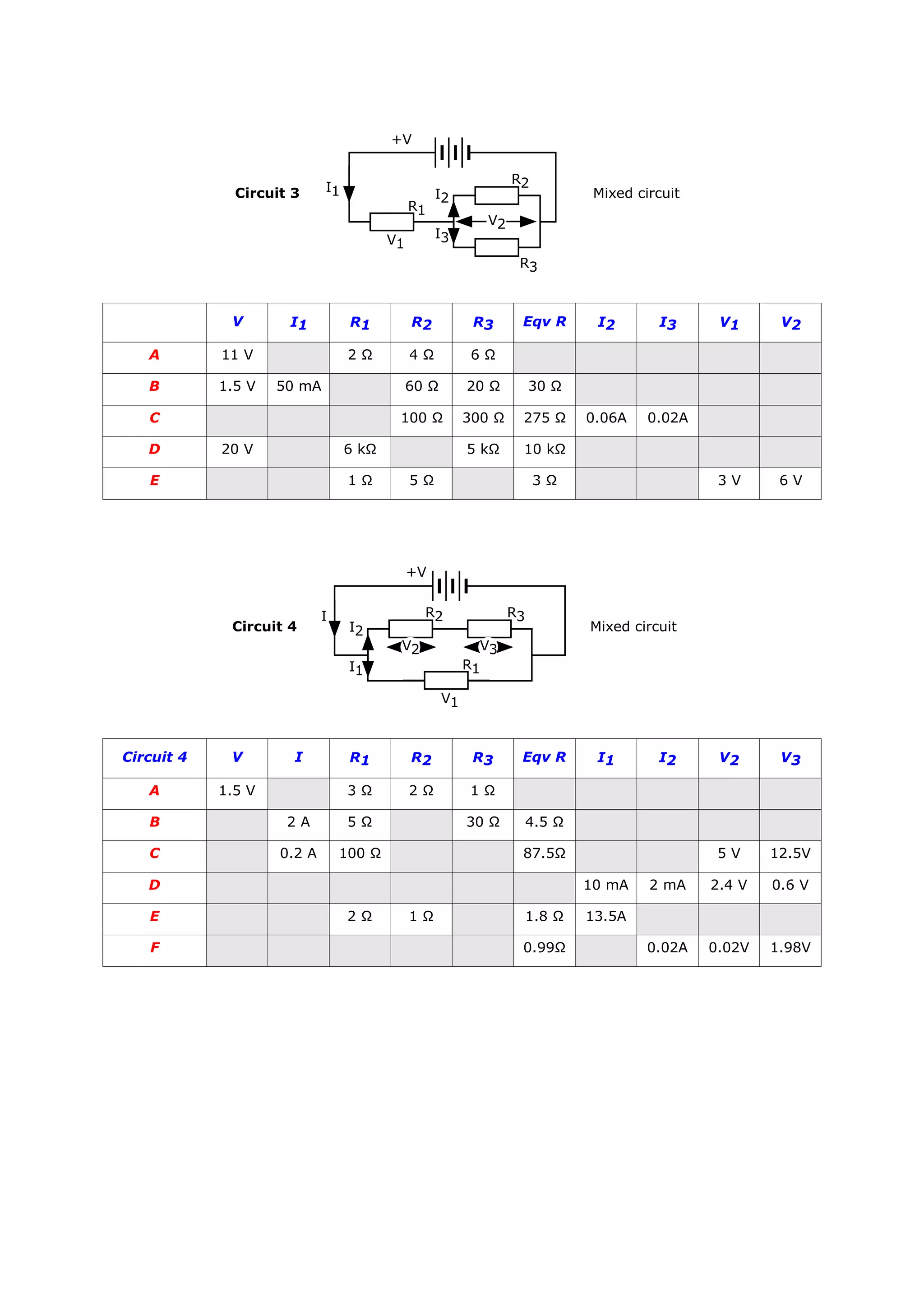
This document provides instructions and diagrams for four simple electric circuits. For each circuit, students are asked to calculate values like equivalent resistance, current, and voltage drops using the component resistances given. They should show their work and fill in a table with the requested values for different scenarios labeled A through F. The circuits include series, parallel and mixed configurations to calculate common circuit parameters.