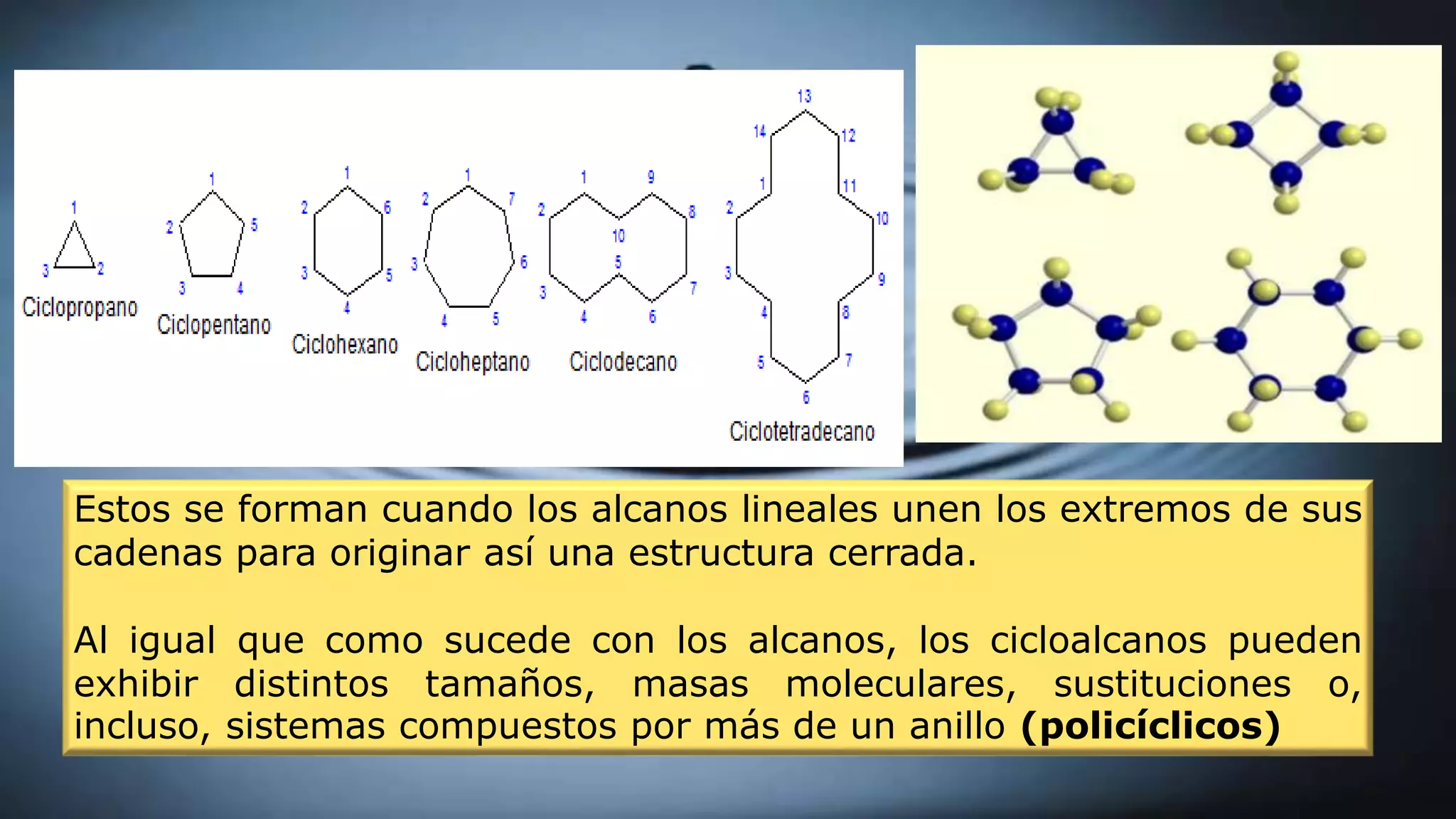
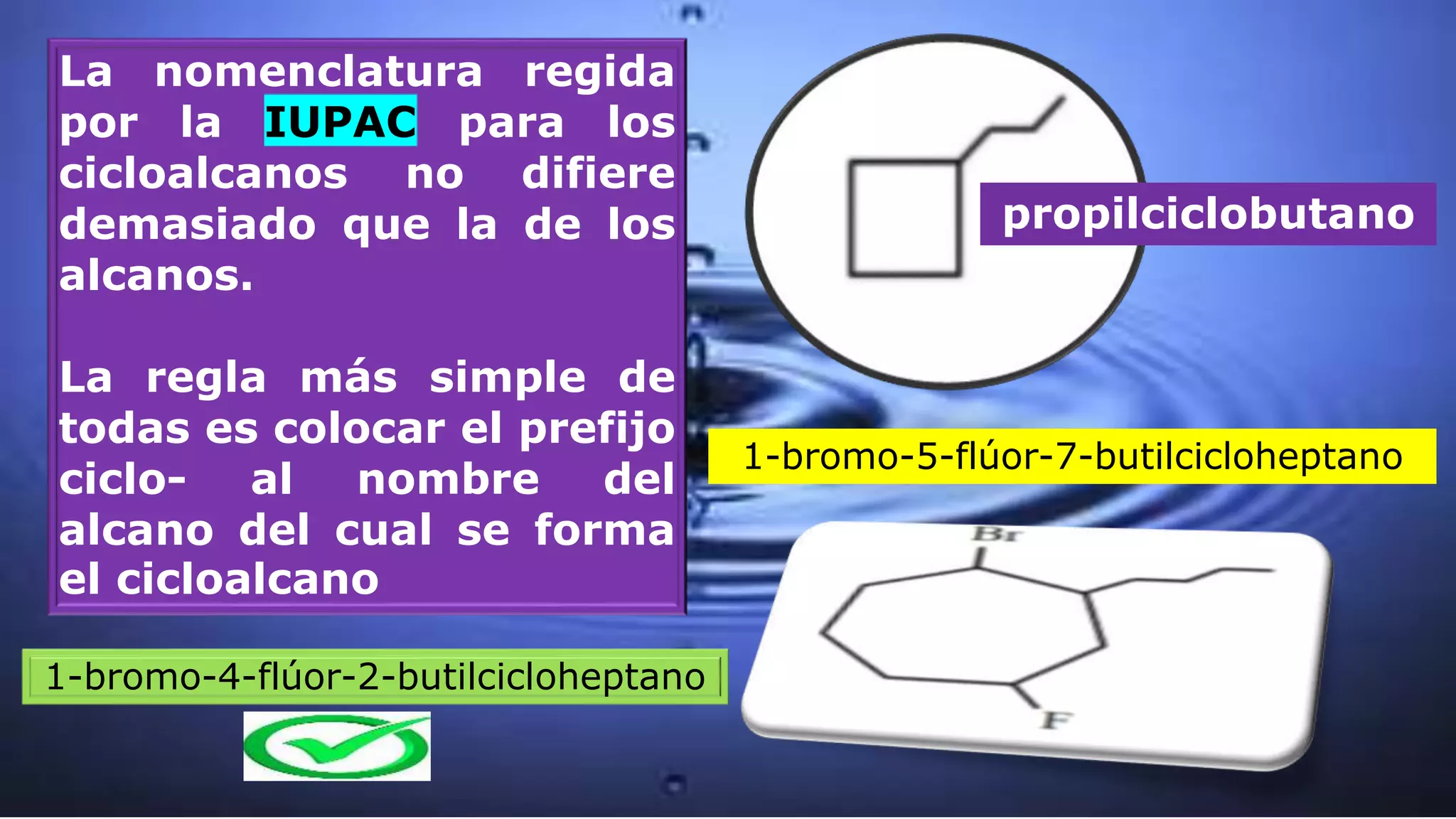
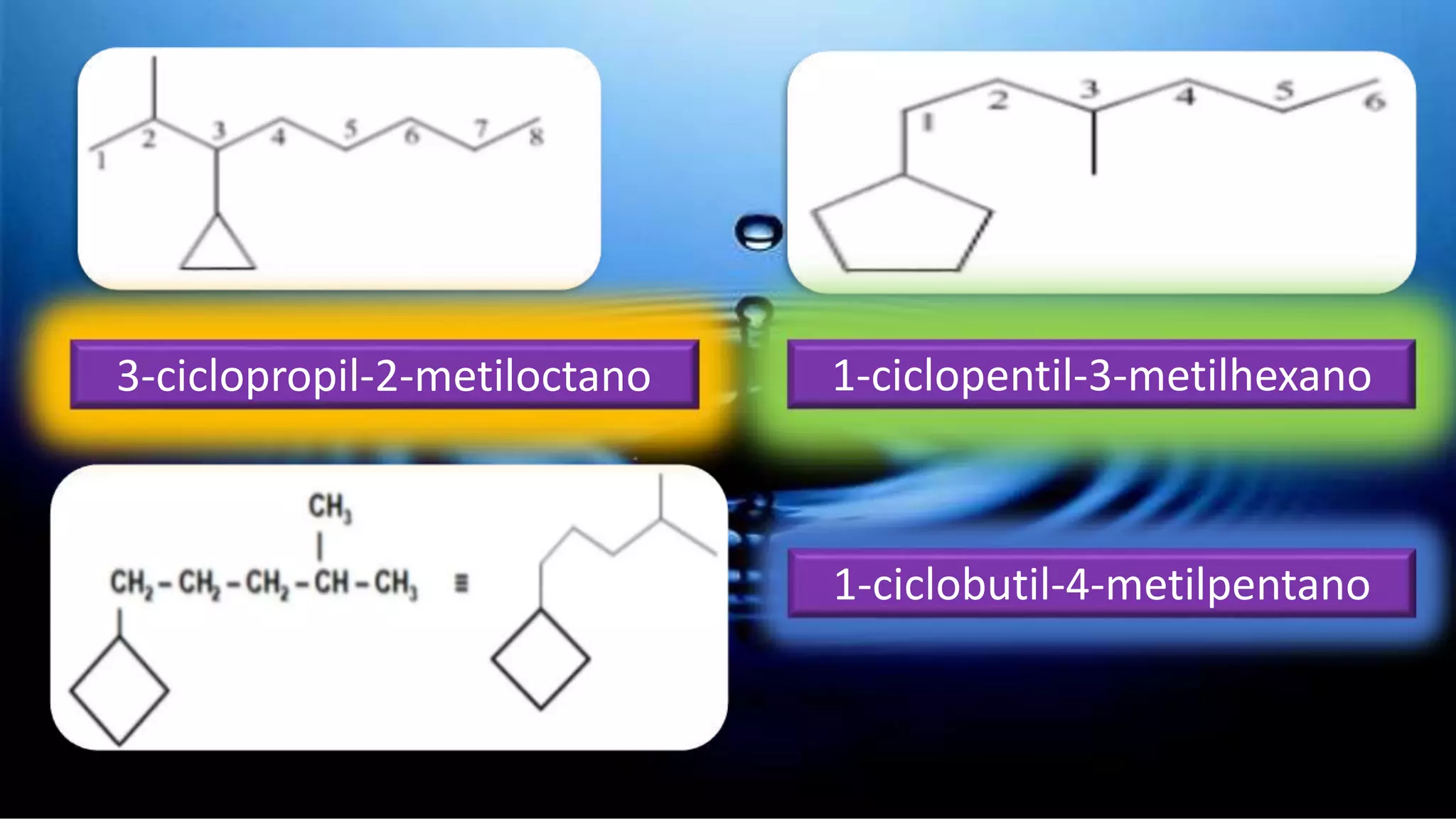
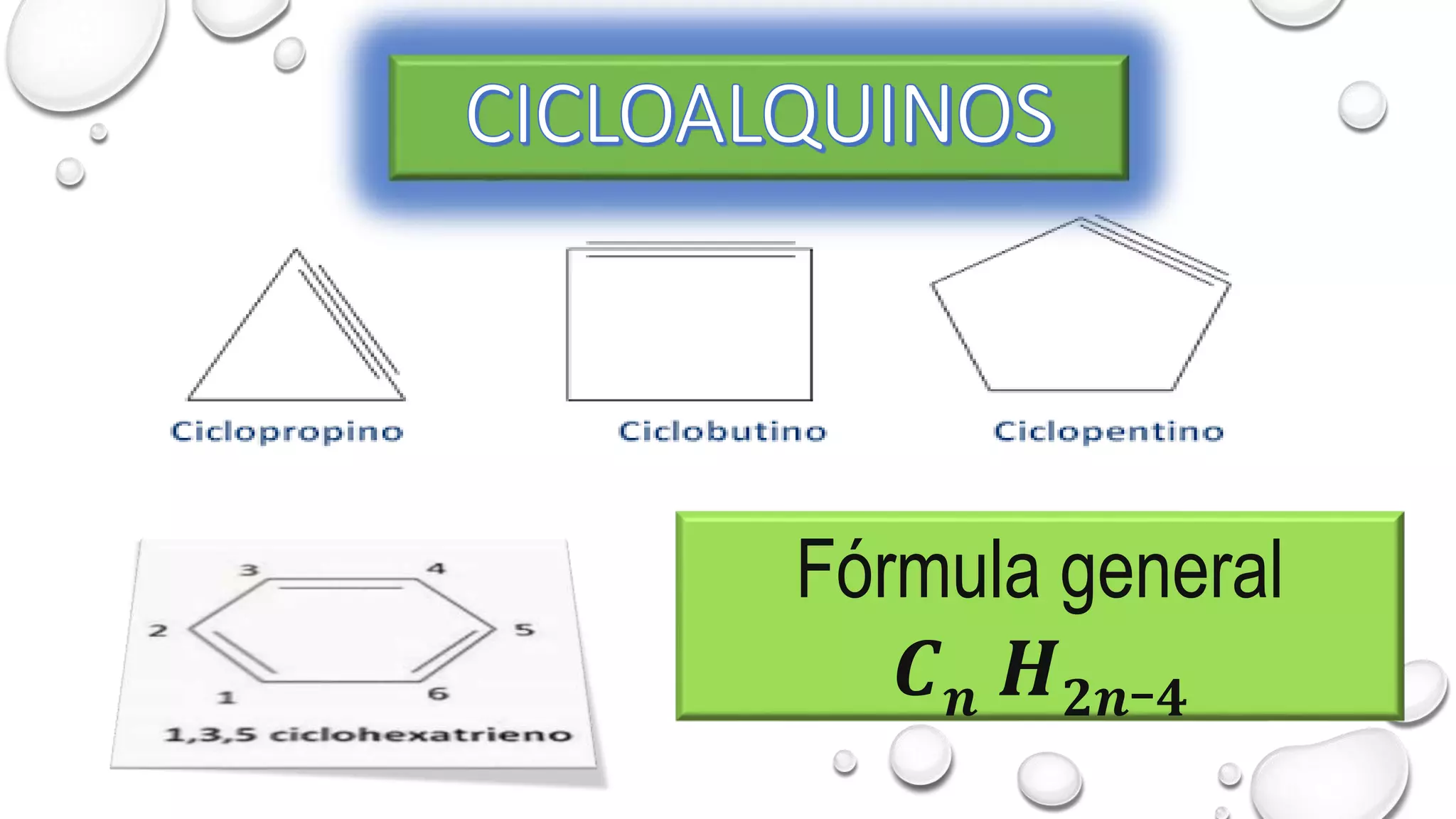
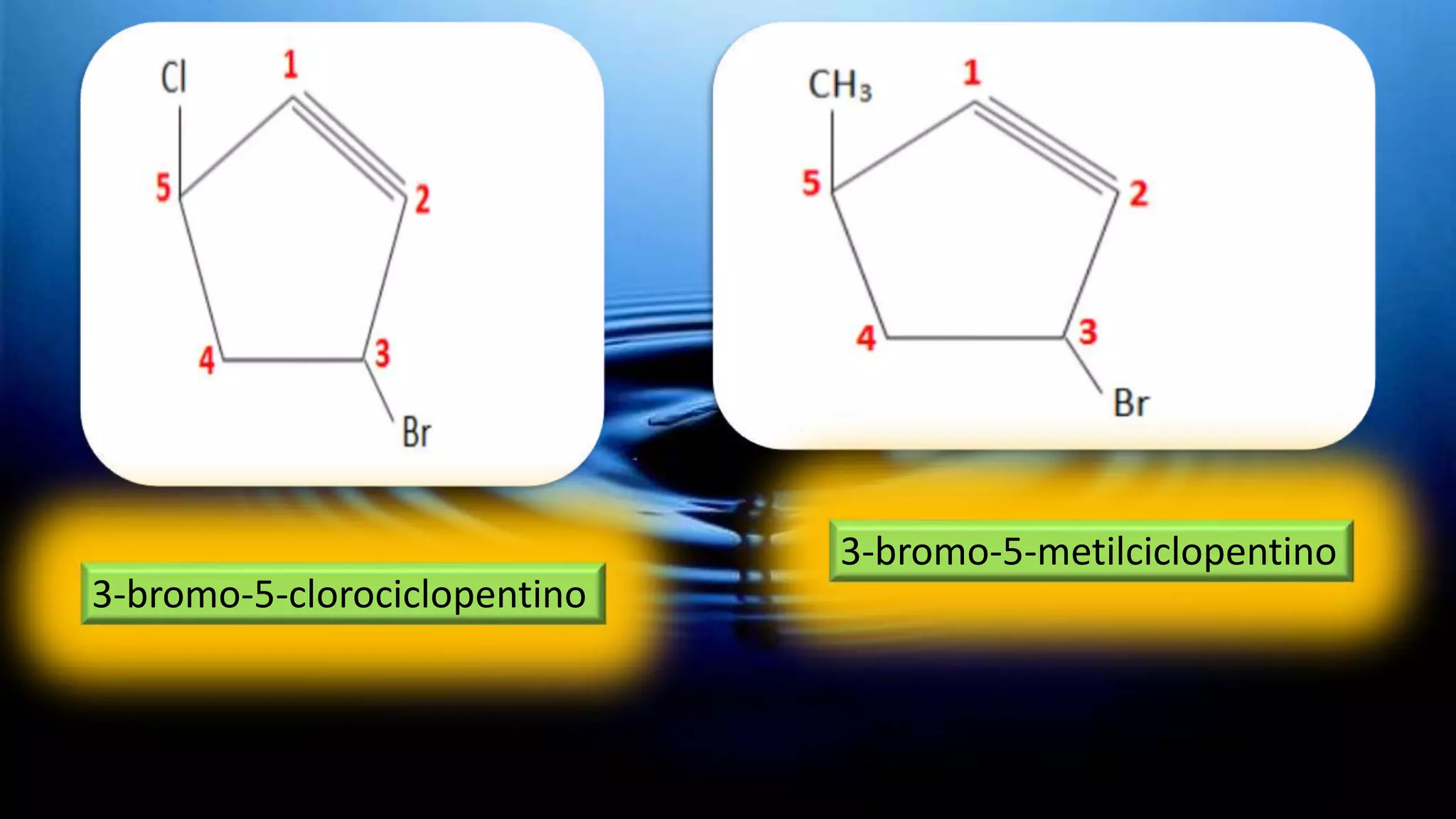
Cycloalkanes are formed when linear alkanes join the ends of their chains to form a closed structure. Like alkanes, cycloalkanes can have different sizes, molecular masses, substitutions, or even multiple ring systems (polycyclic). The IUPAC nomenclature for cycloalkanes is similar to that for alkanes, with the prefix "cyclo-" added to the alkane name to form the cycloalkane. Cycloalkanes are named similarly to alkanes of the same number of carbons, but with the prefix "cyclo-" added. Geometric shapes are used to represent the formula, with each vertex corresponding to -CH2.