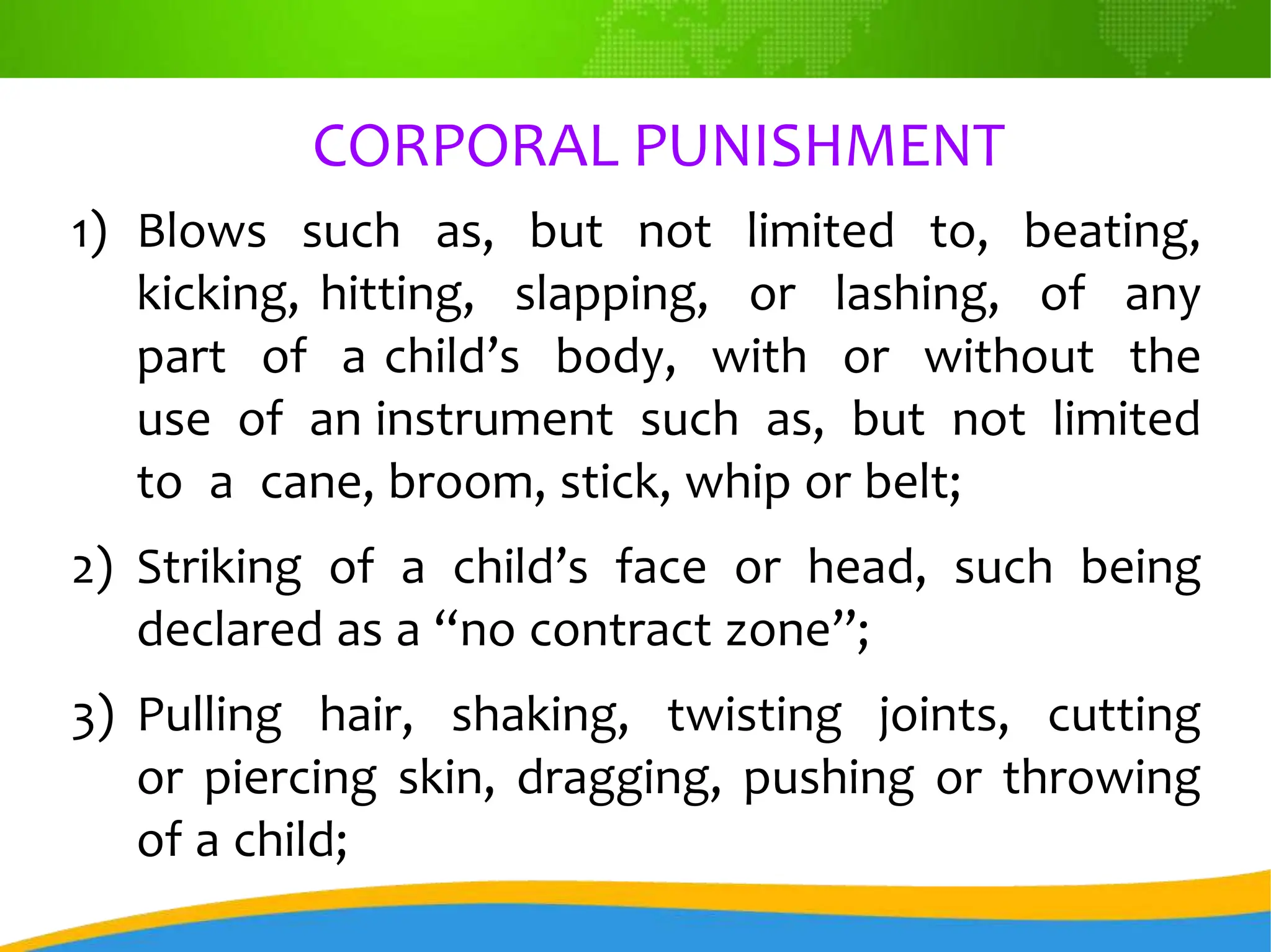
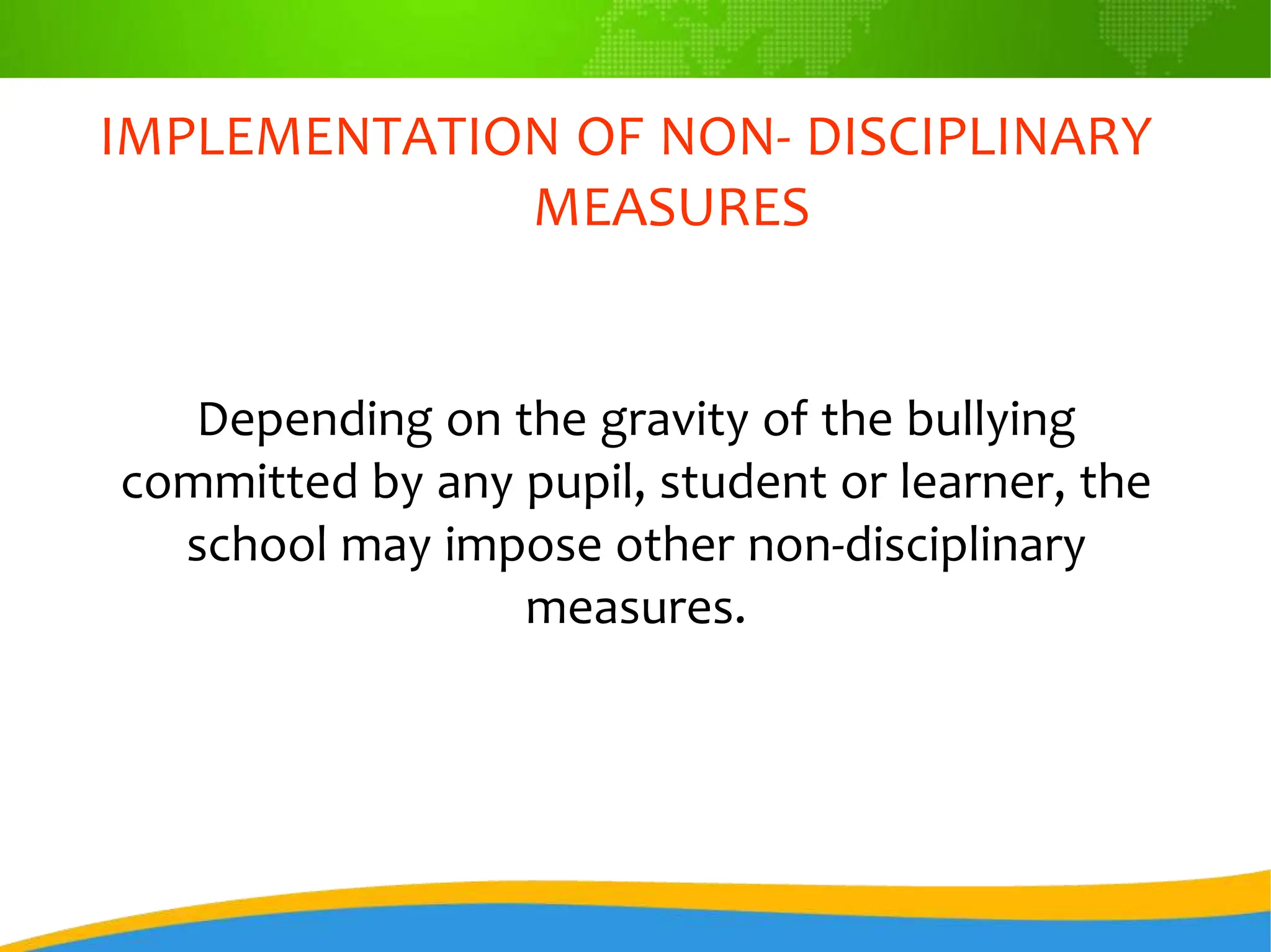
The DEPed Child Protection Policy aims to safeguard children in schools from all forms of violence, abuse, exploitation, and discrimination, promoting a zero-tolerance approach toward such acts. It outlines specific prohibited acts, such as bullying, corporal punishment, and child exploitation, and establishes a framework for schools to implement protective measures and handle incidents effectively. Additionally, the policy emphasizes the responsibilities of school heads, staffs, and children protection committees in ensuring compliance and fostering a safe educational environment.