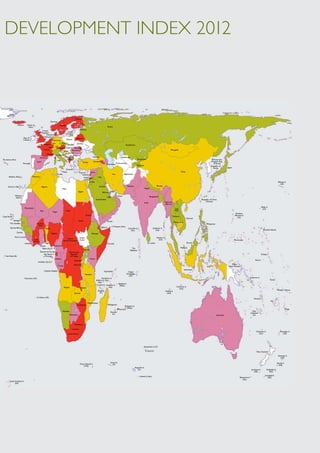
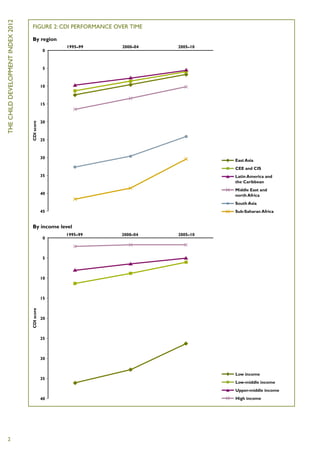
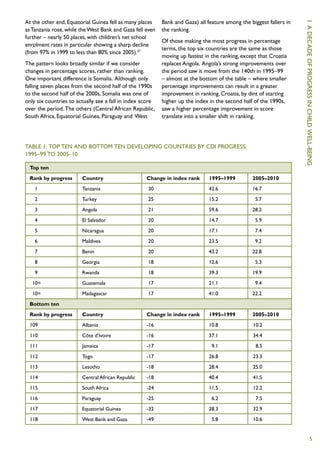
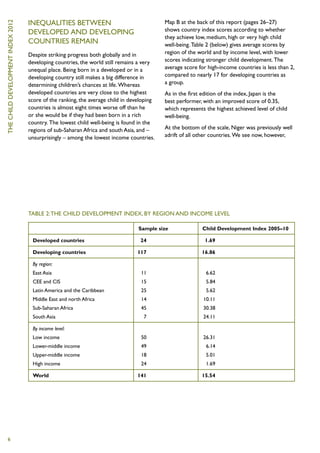
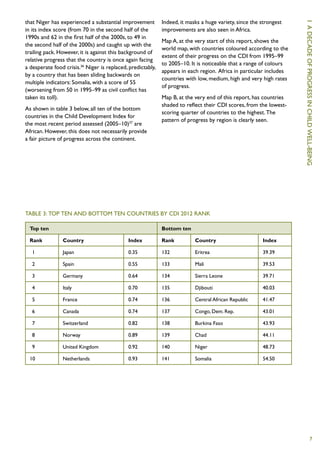
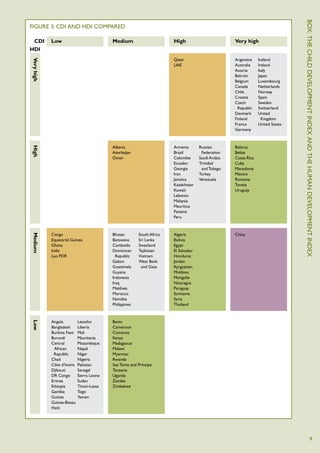
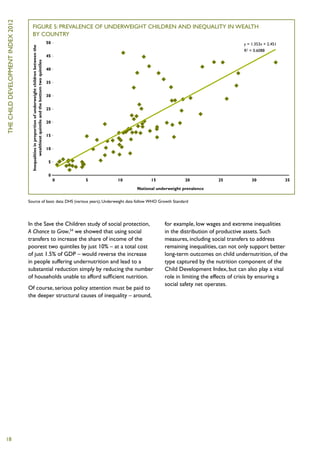
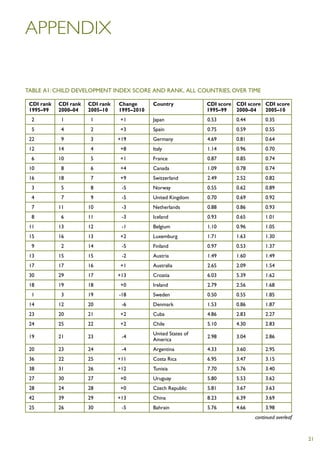
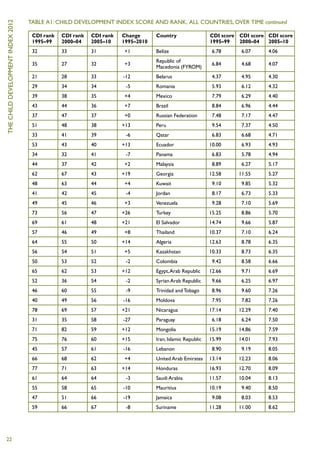
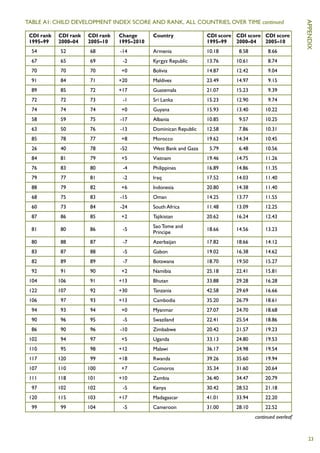
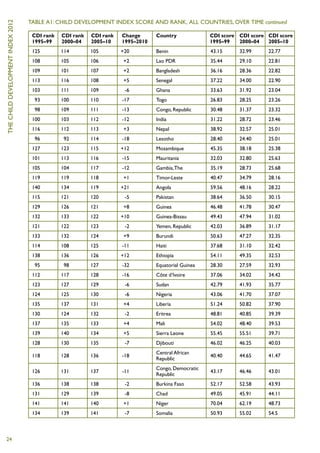
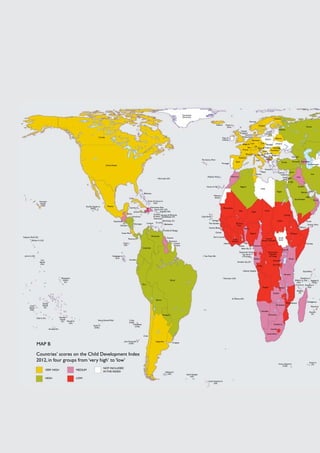
The Child Development Index 2012 report shows that between 2005-2010:
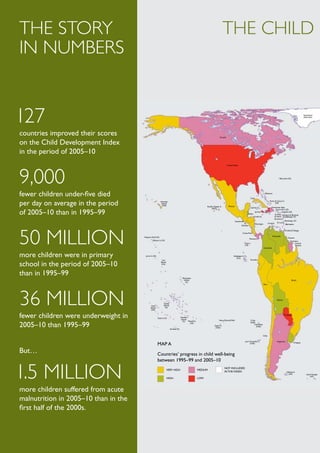
1) 127 countries improved their scores on the Child Development Index.
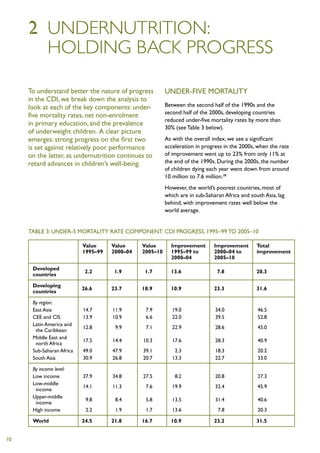
2) An average of 9,000 fewer children under five died per day, compared to 1995-1999.
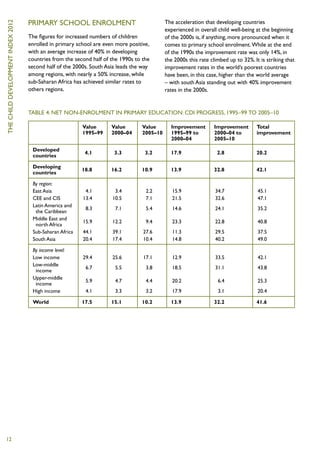
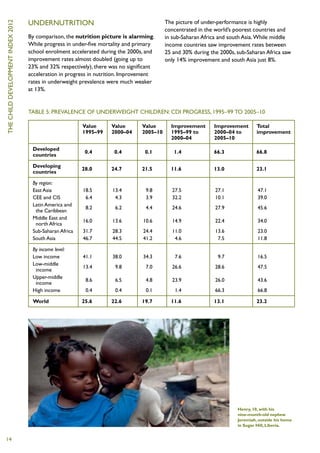
3) 50 million more children were enrolled in primary school, and 36 million fewer children were underweight, compared to 1995-1999.