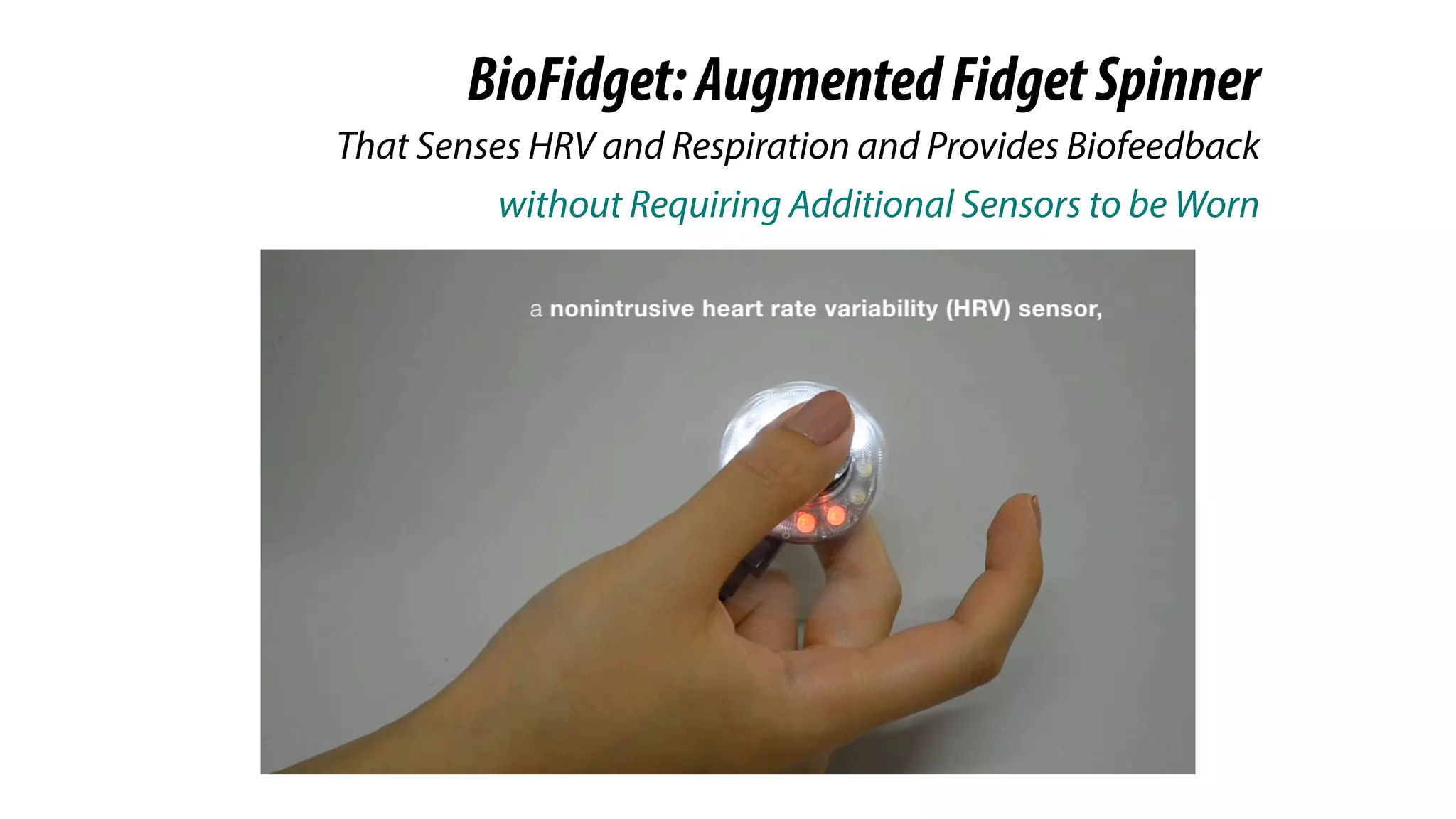
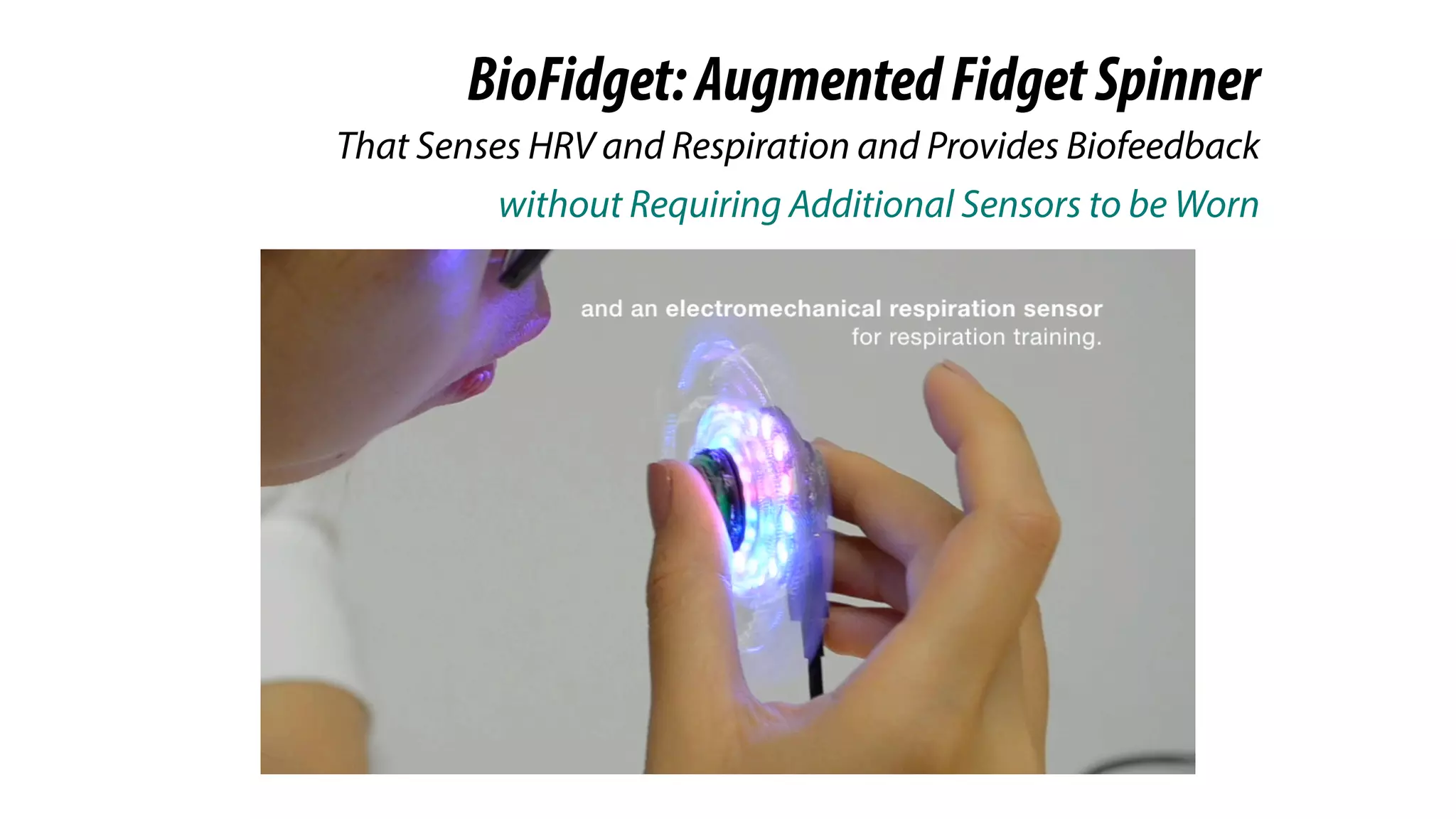
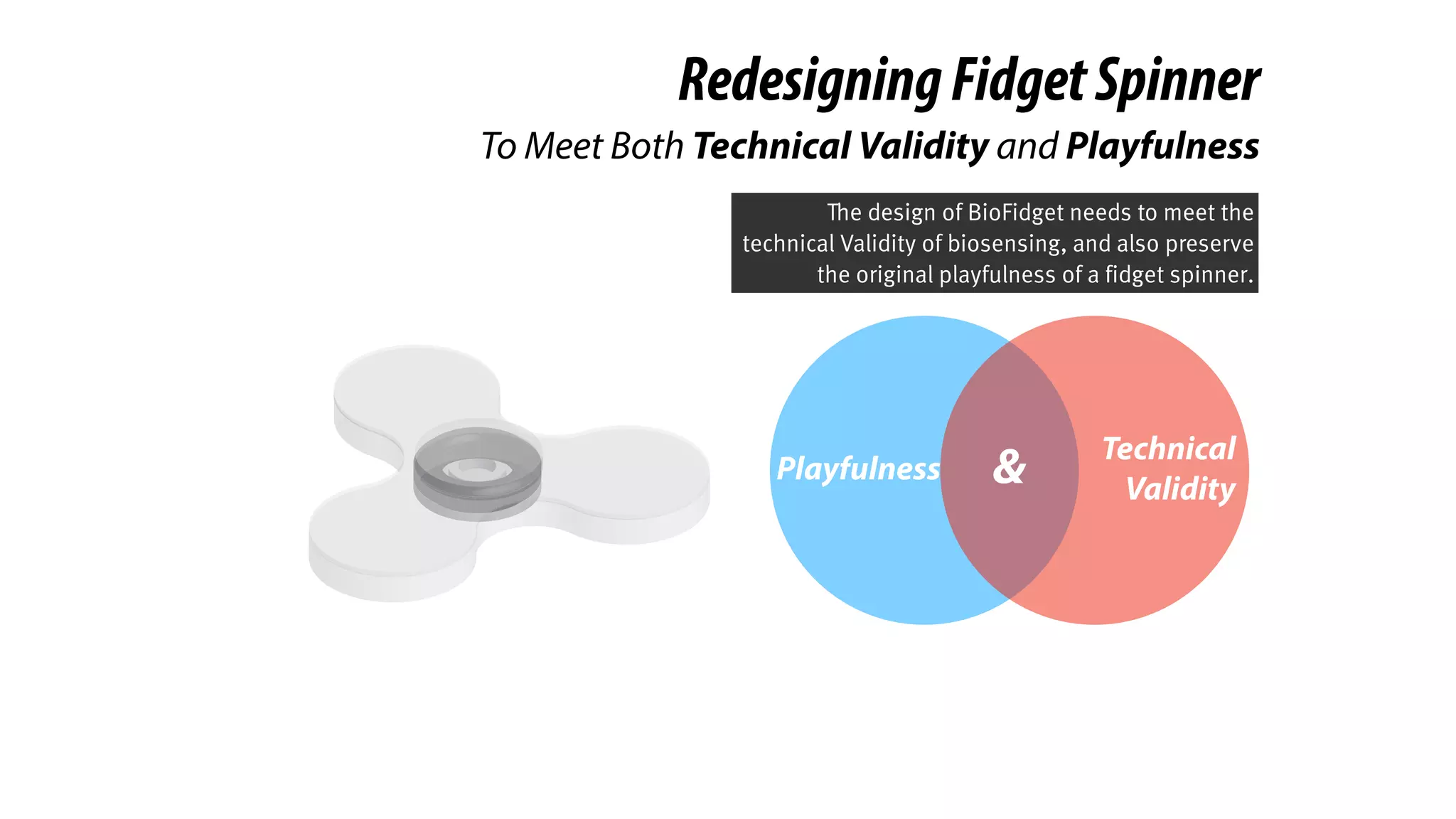
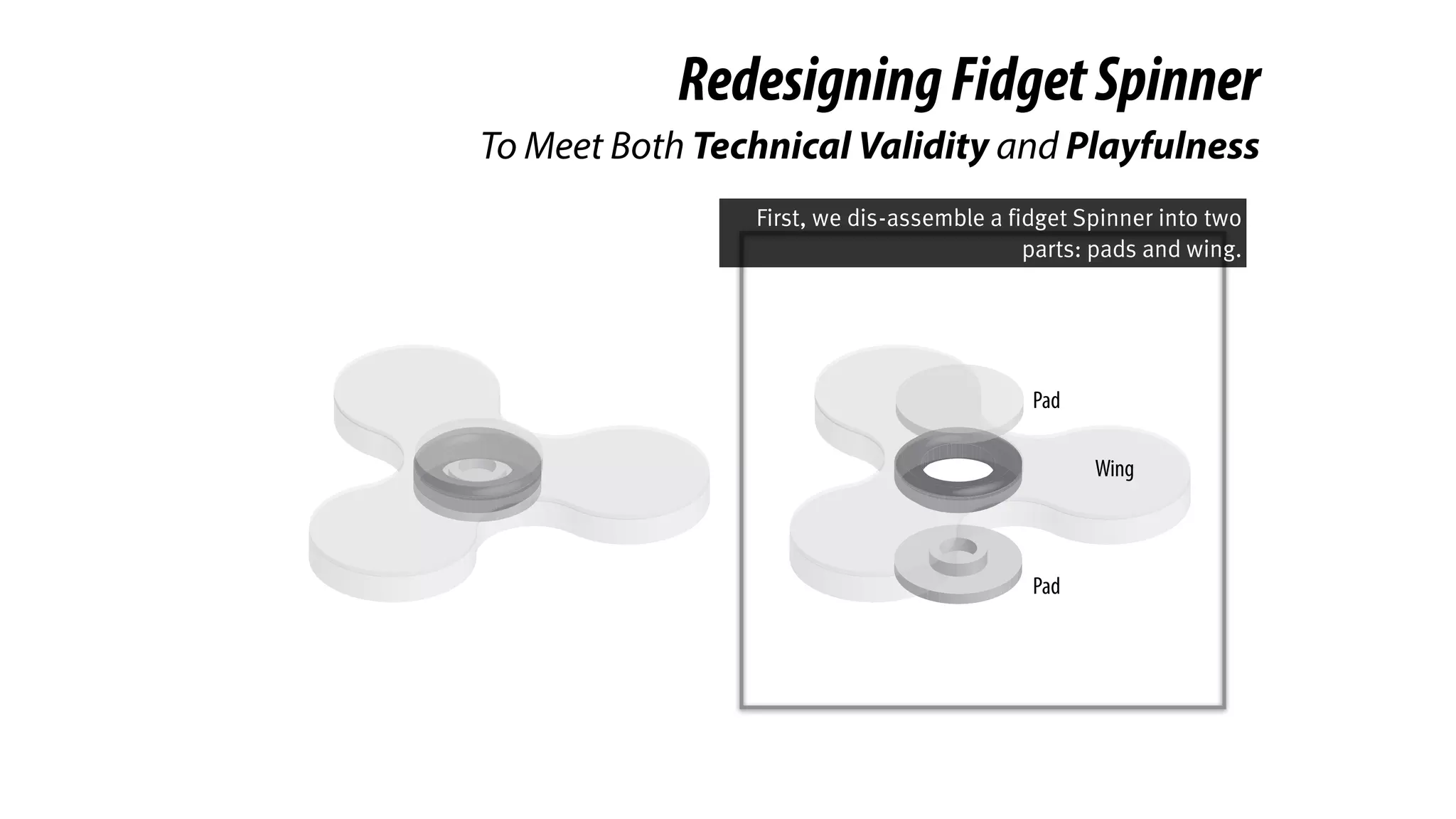
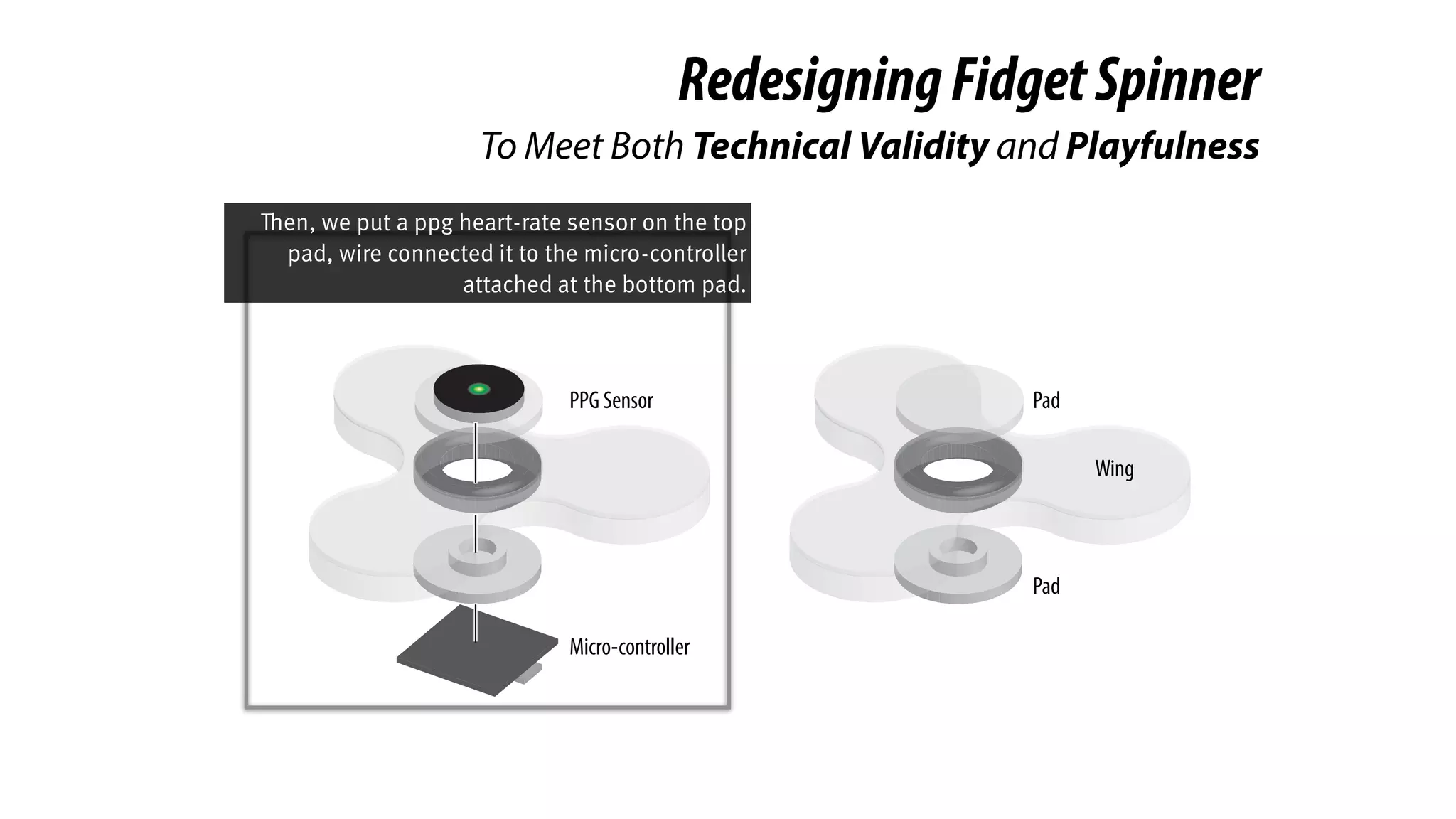
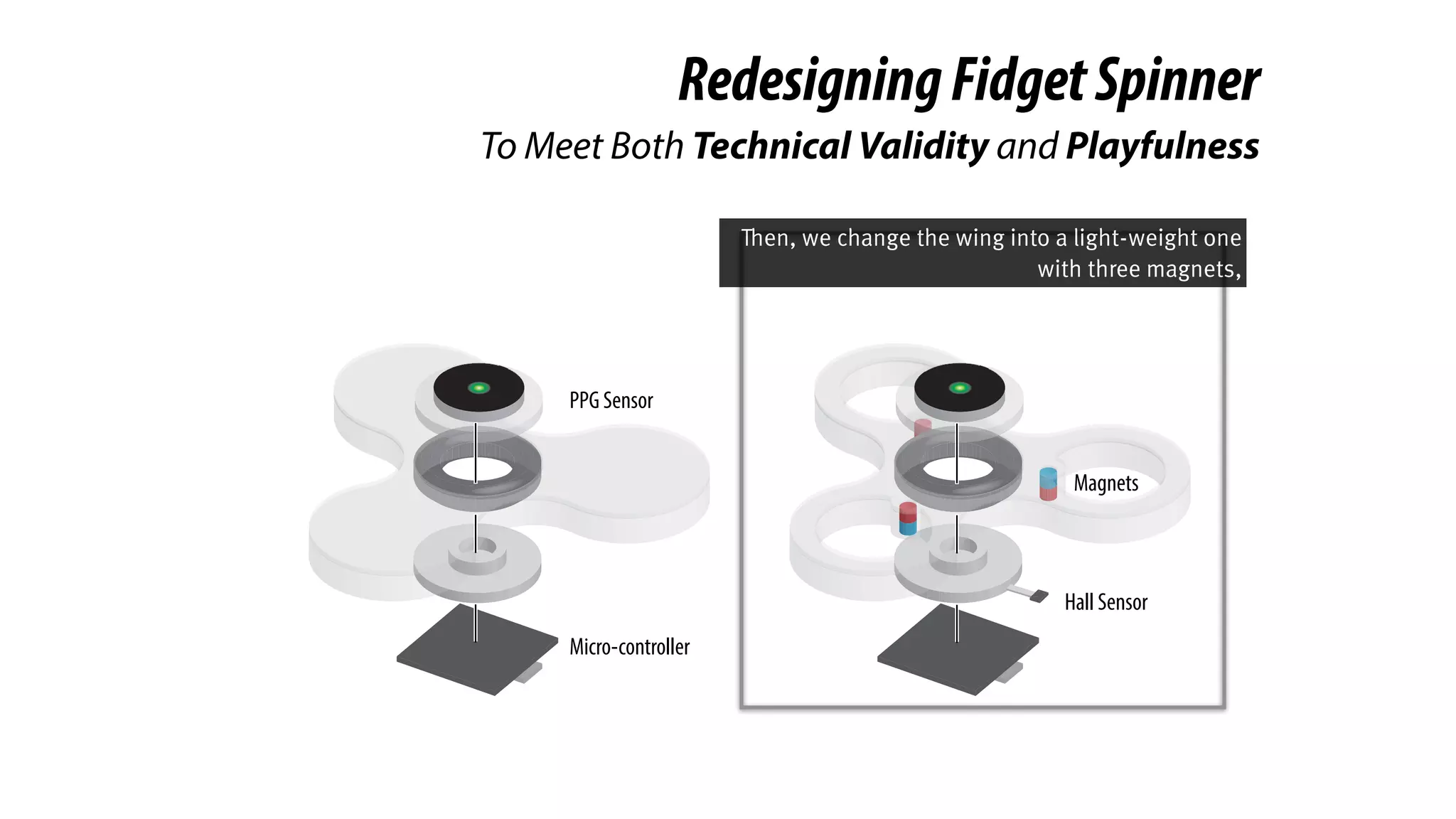
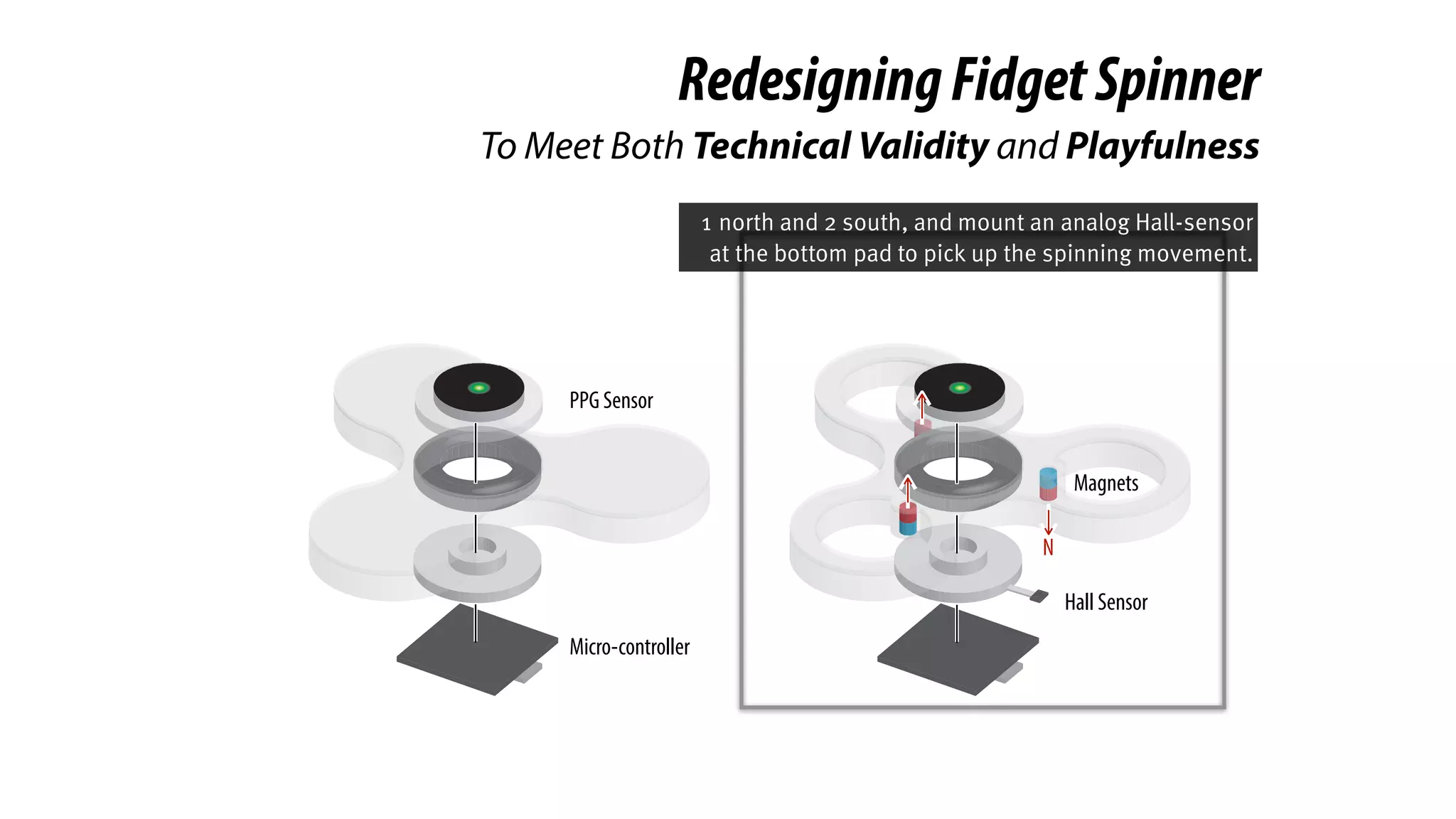
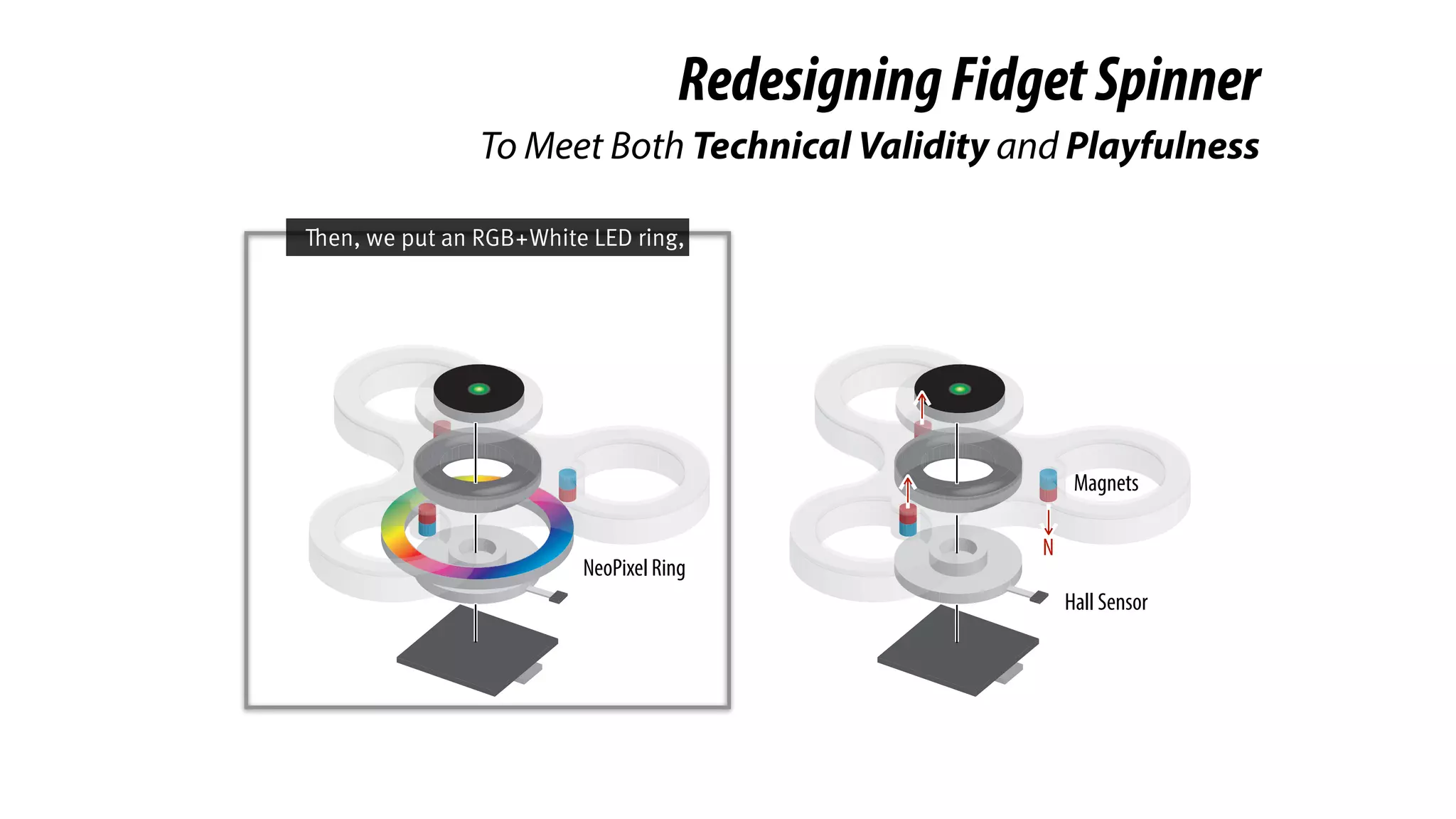
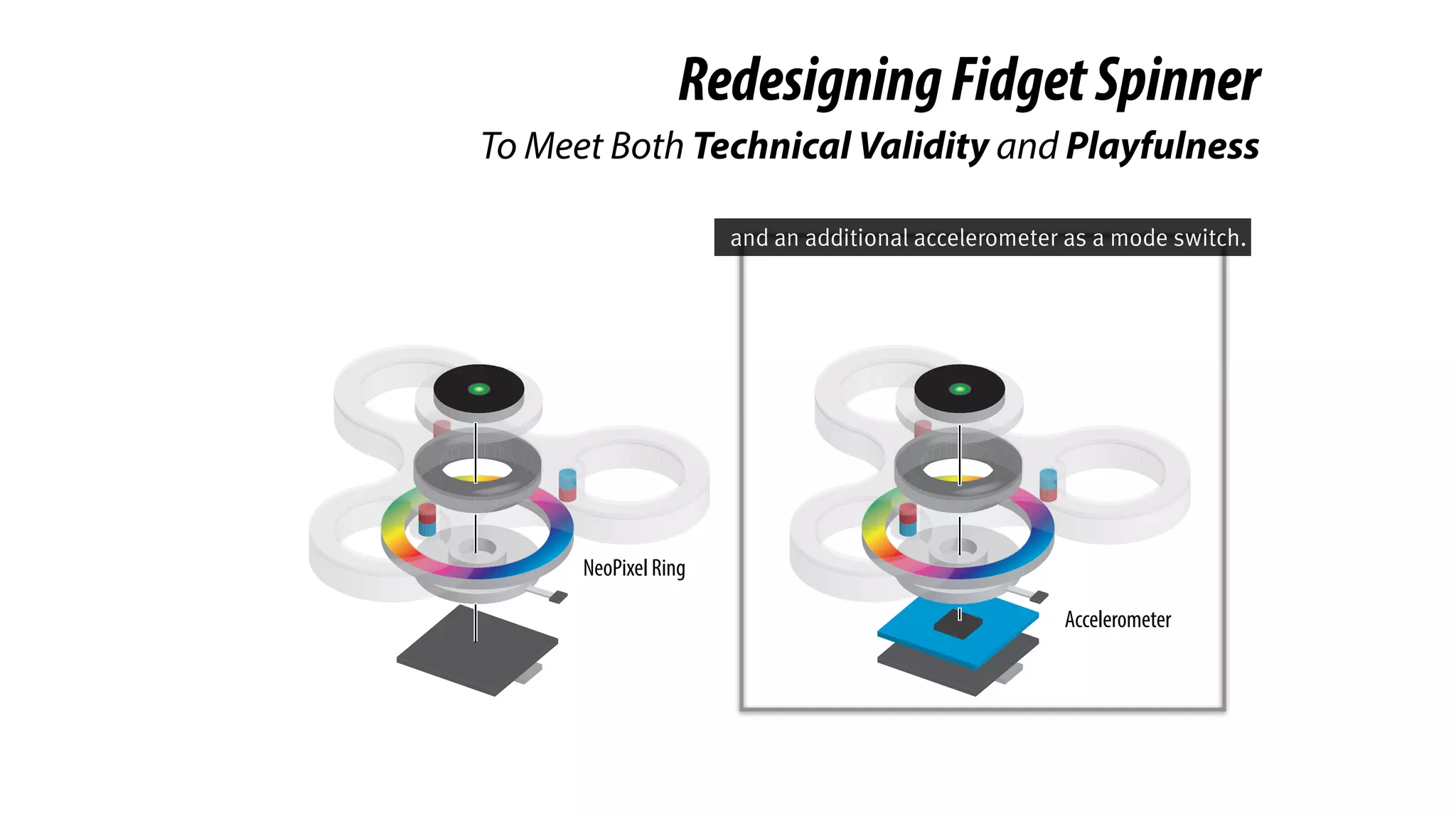
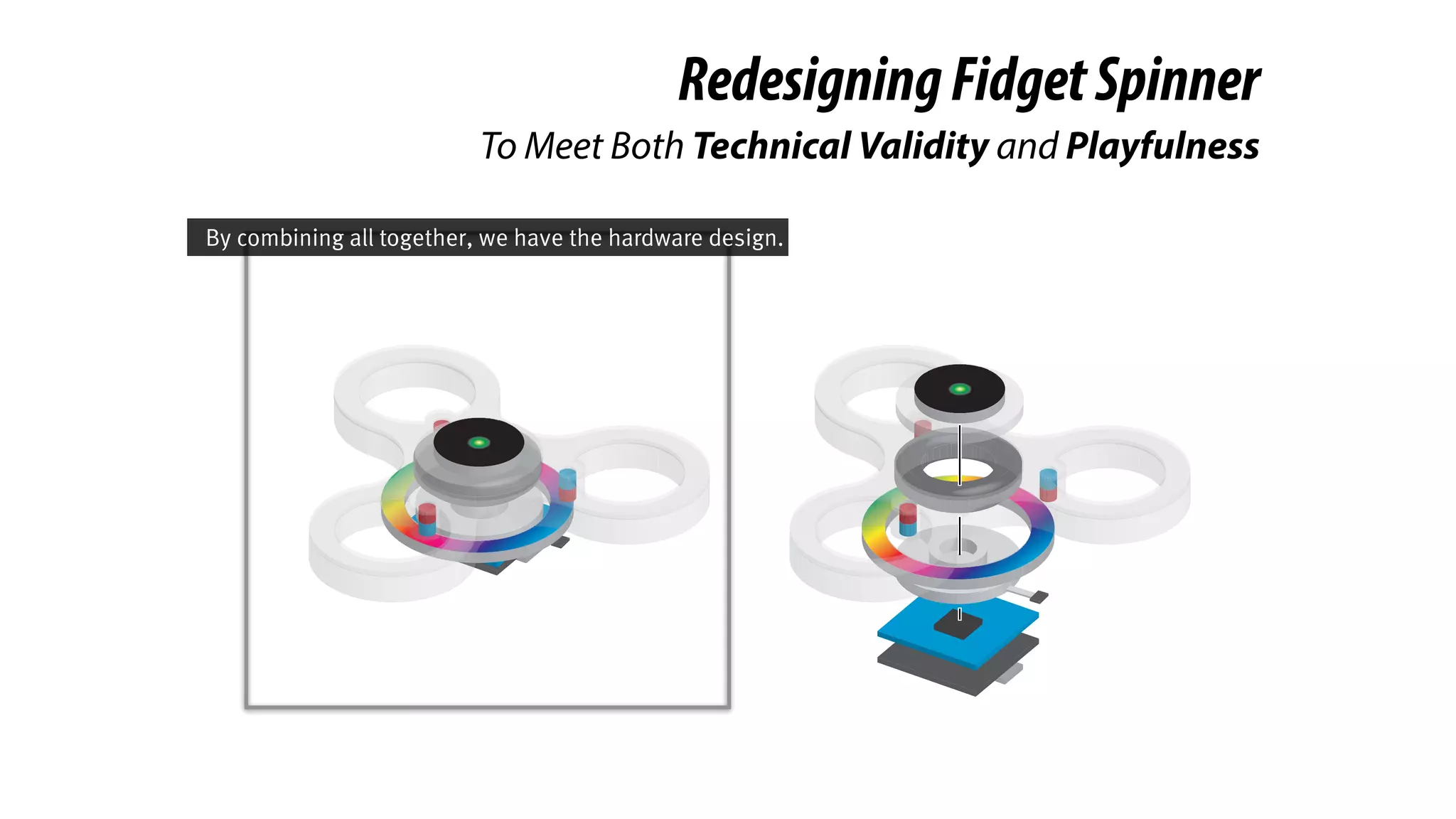
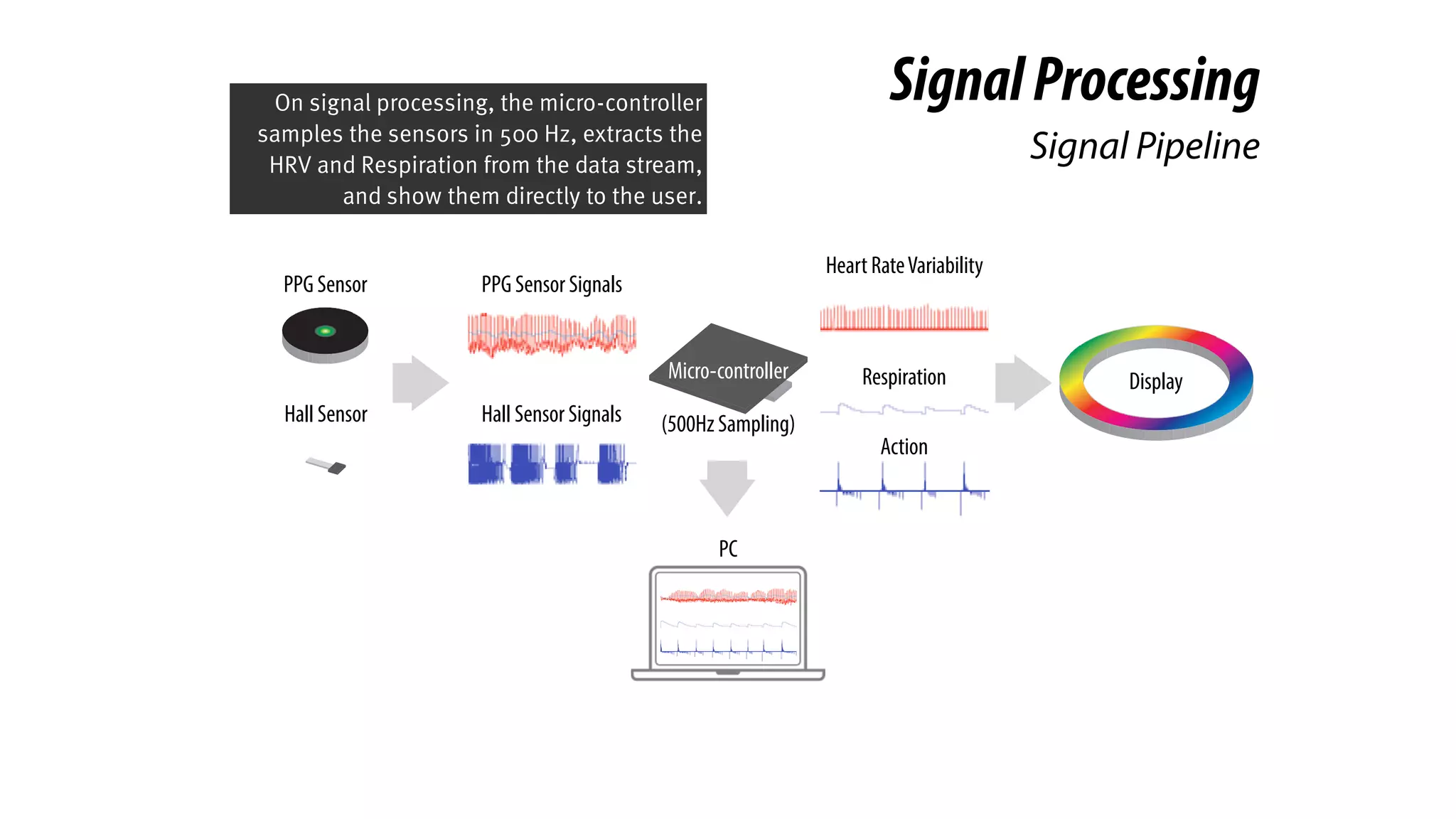
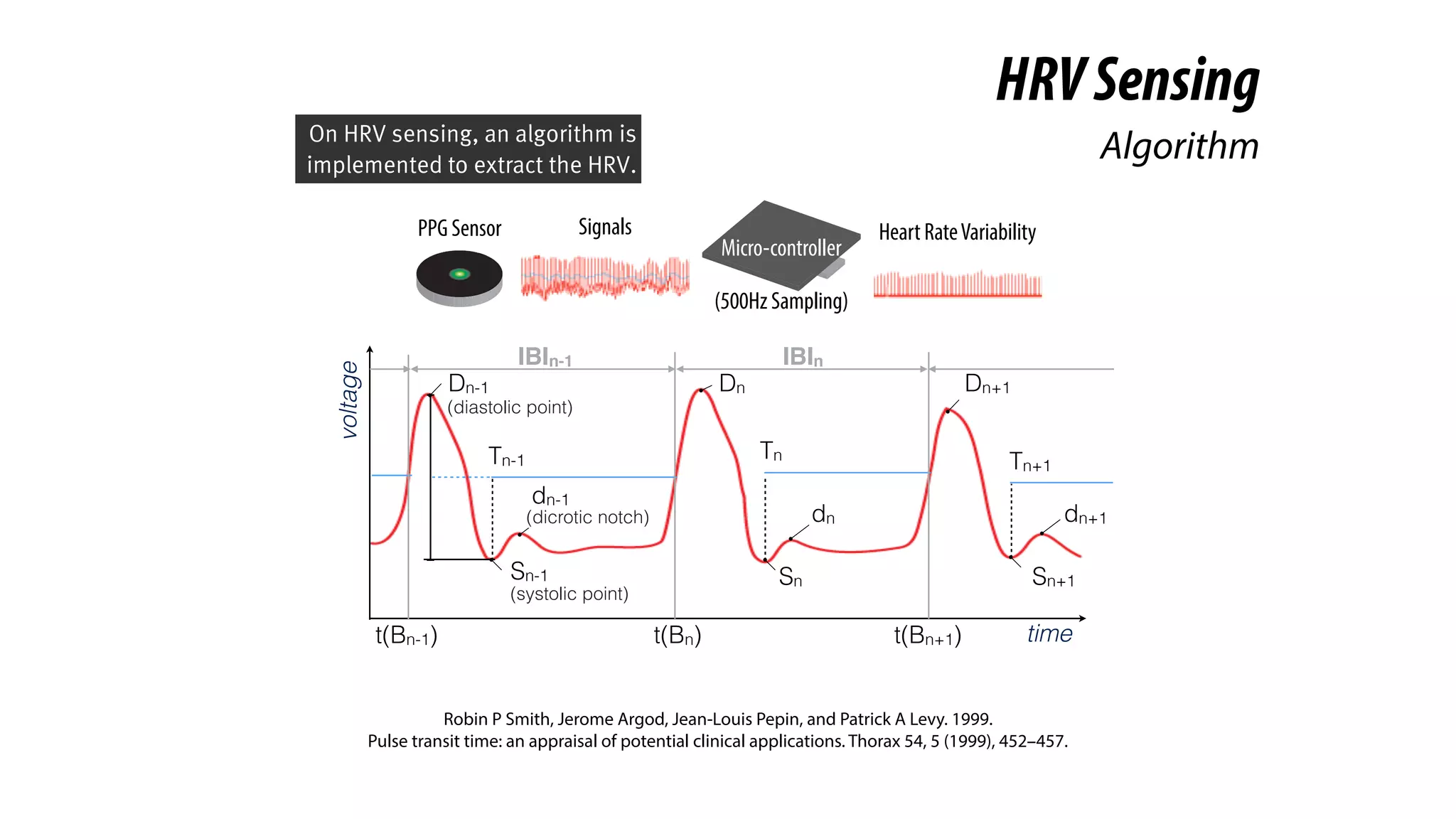
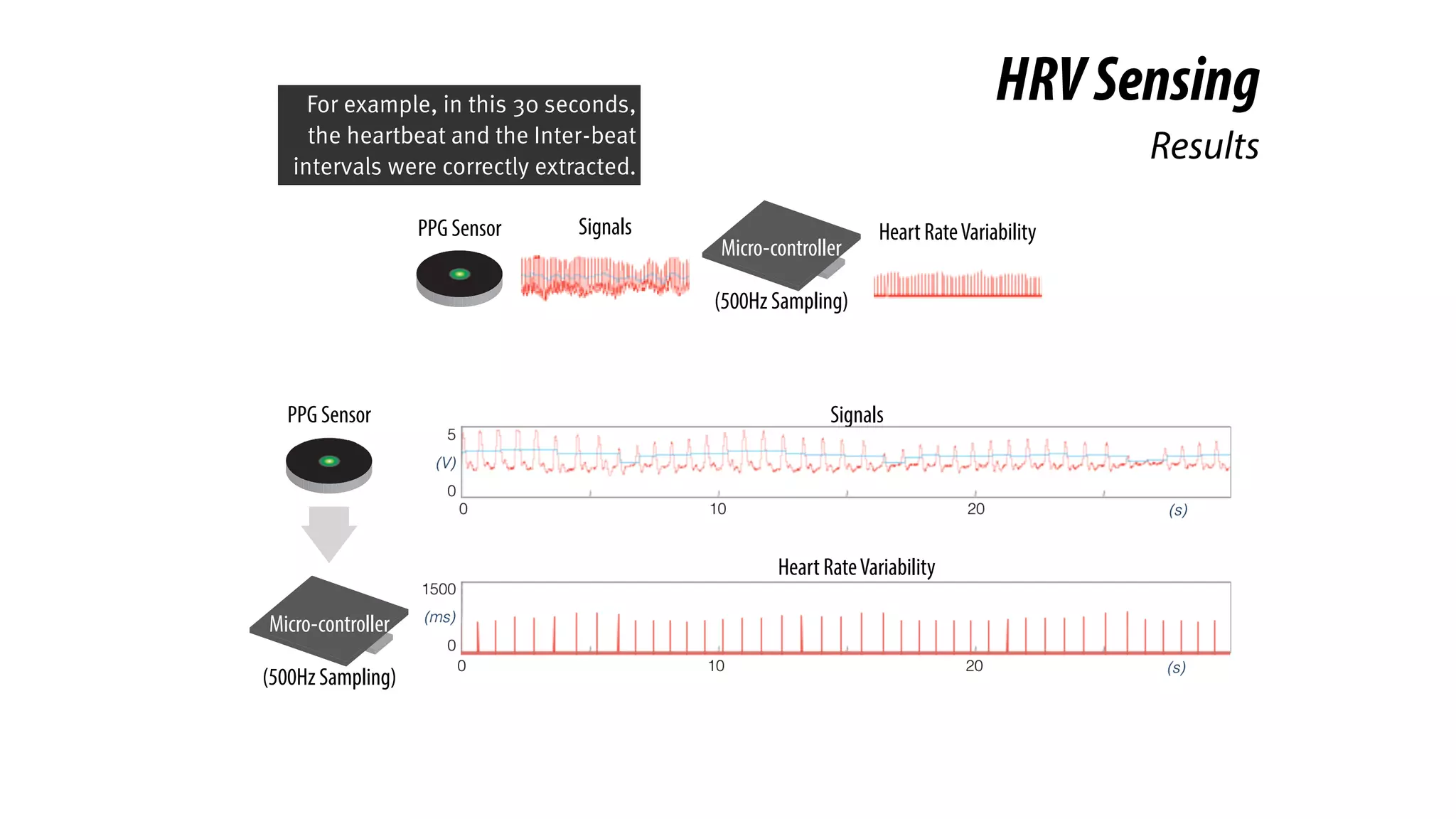
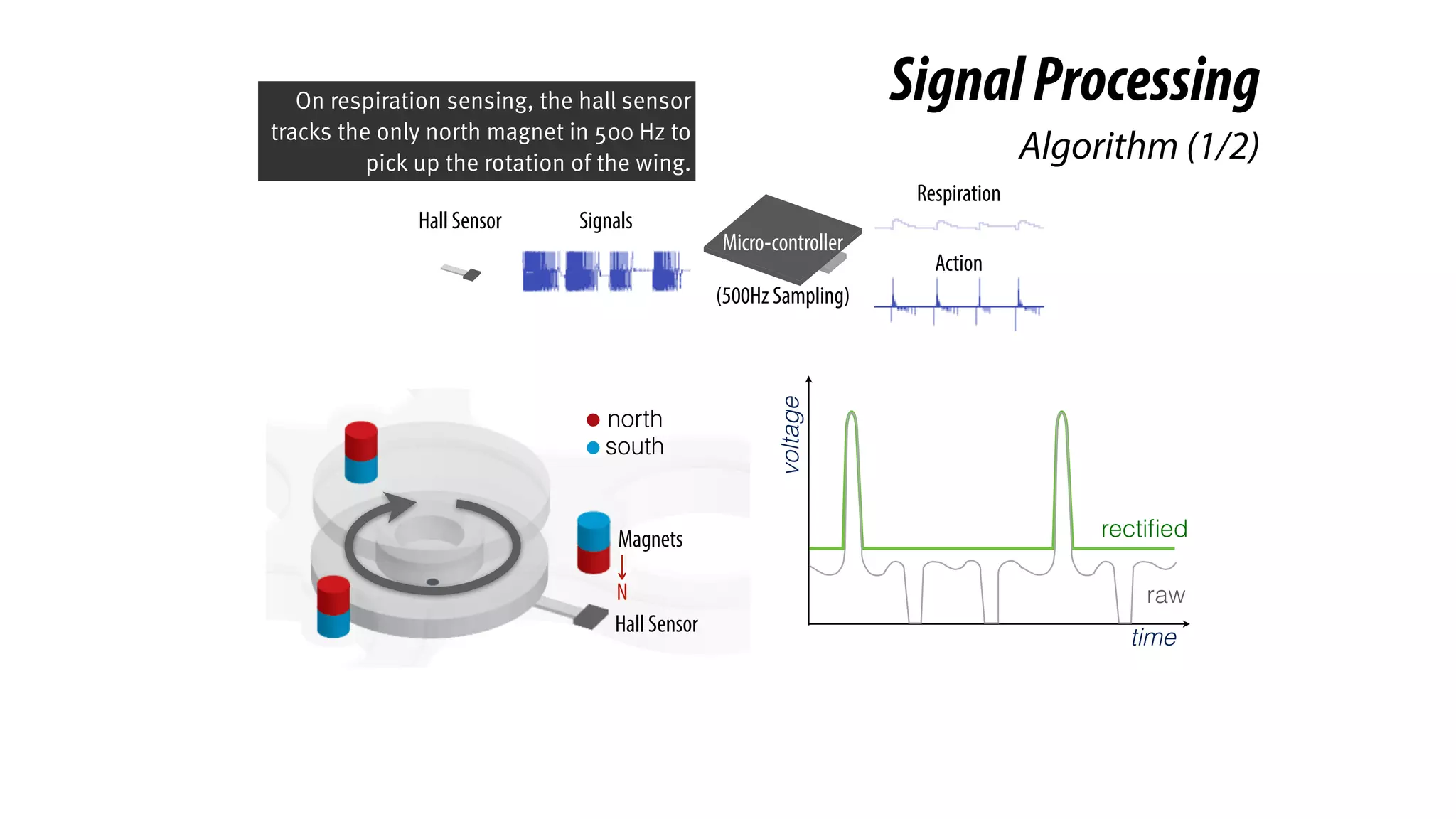
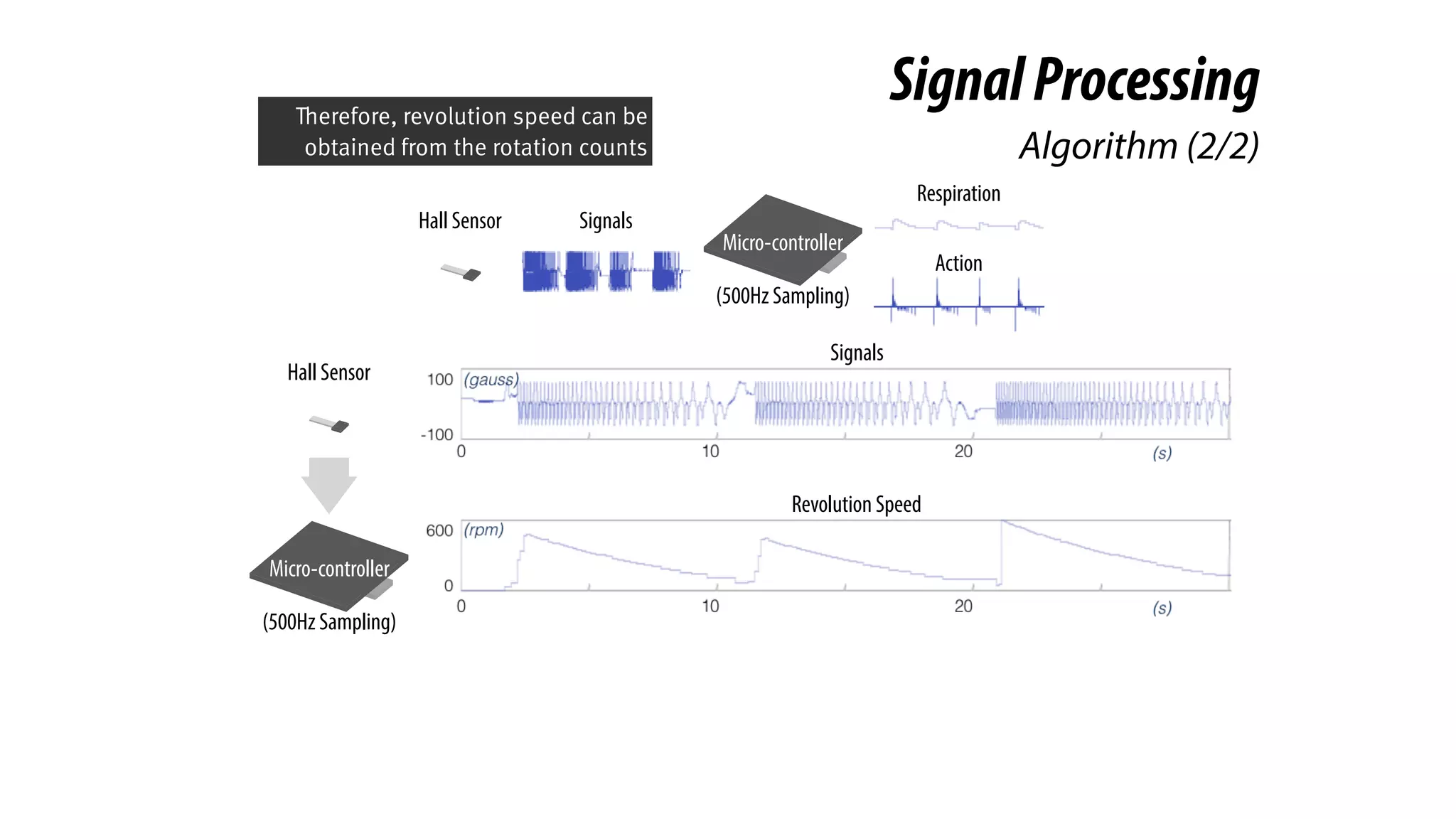
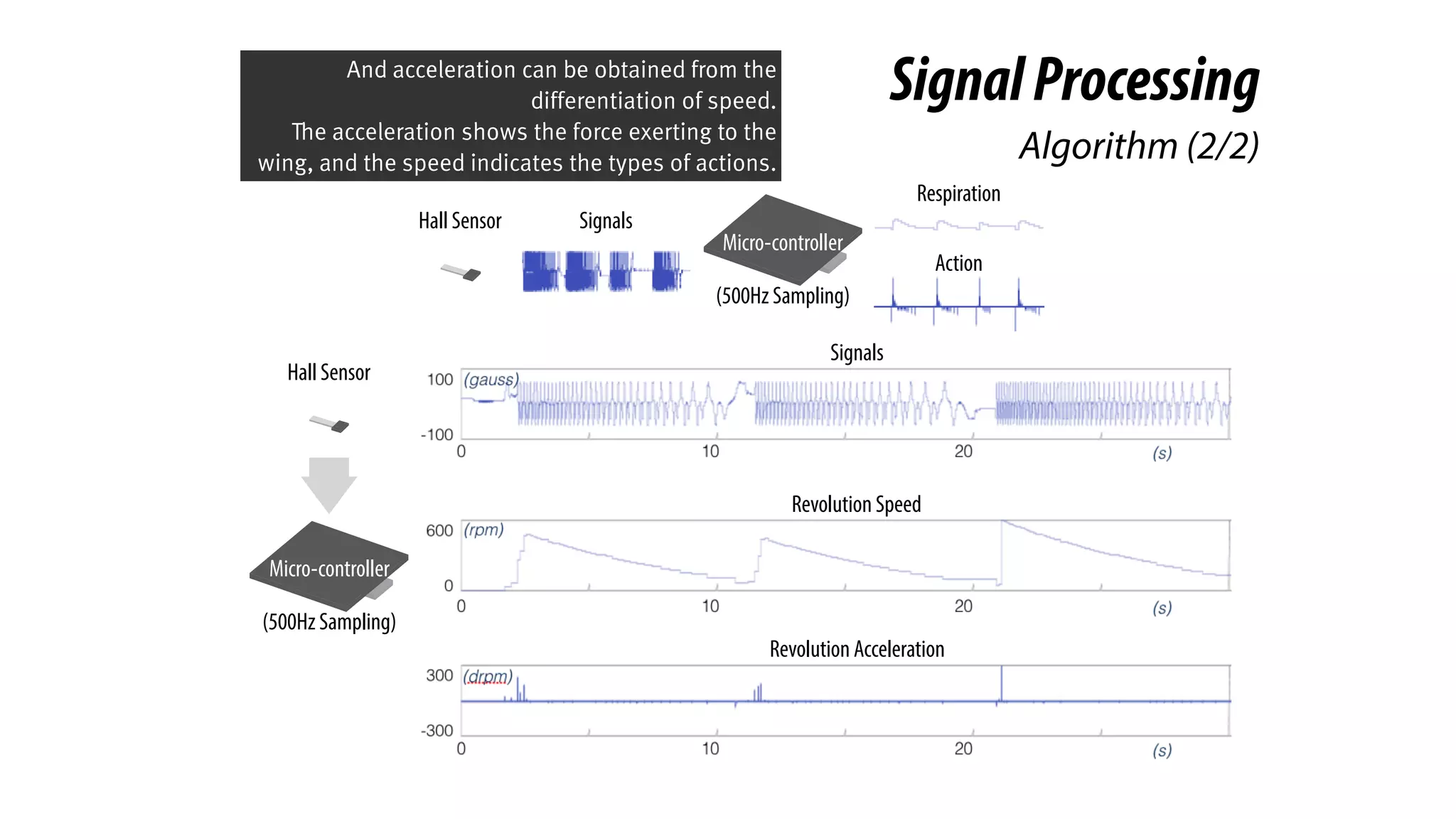
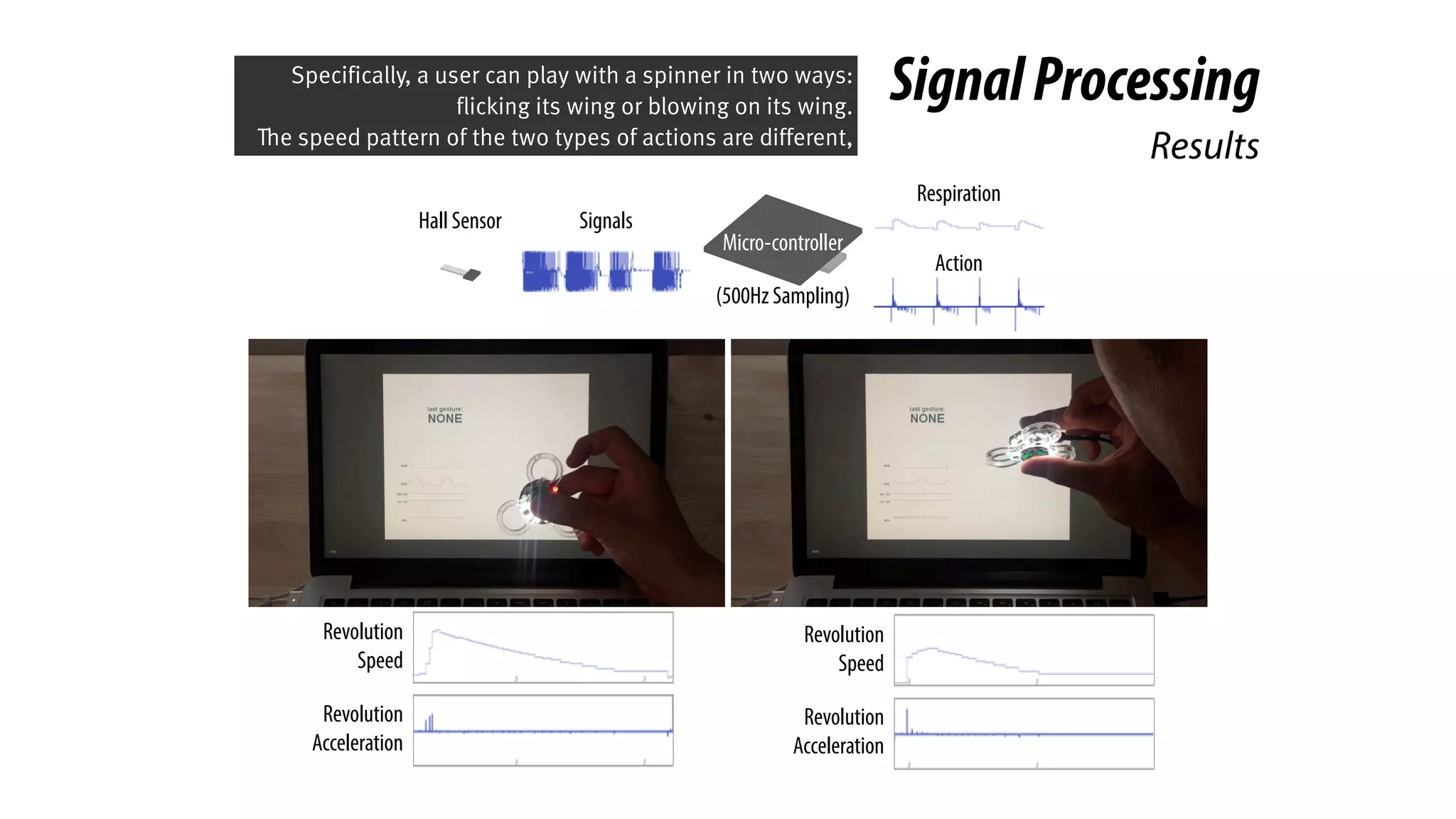
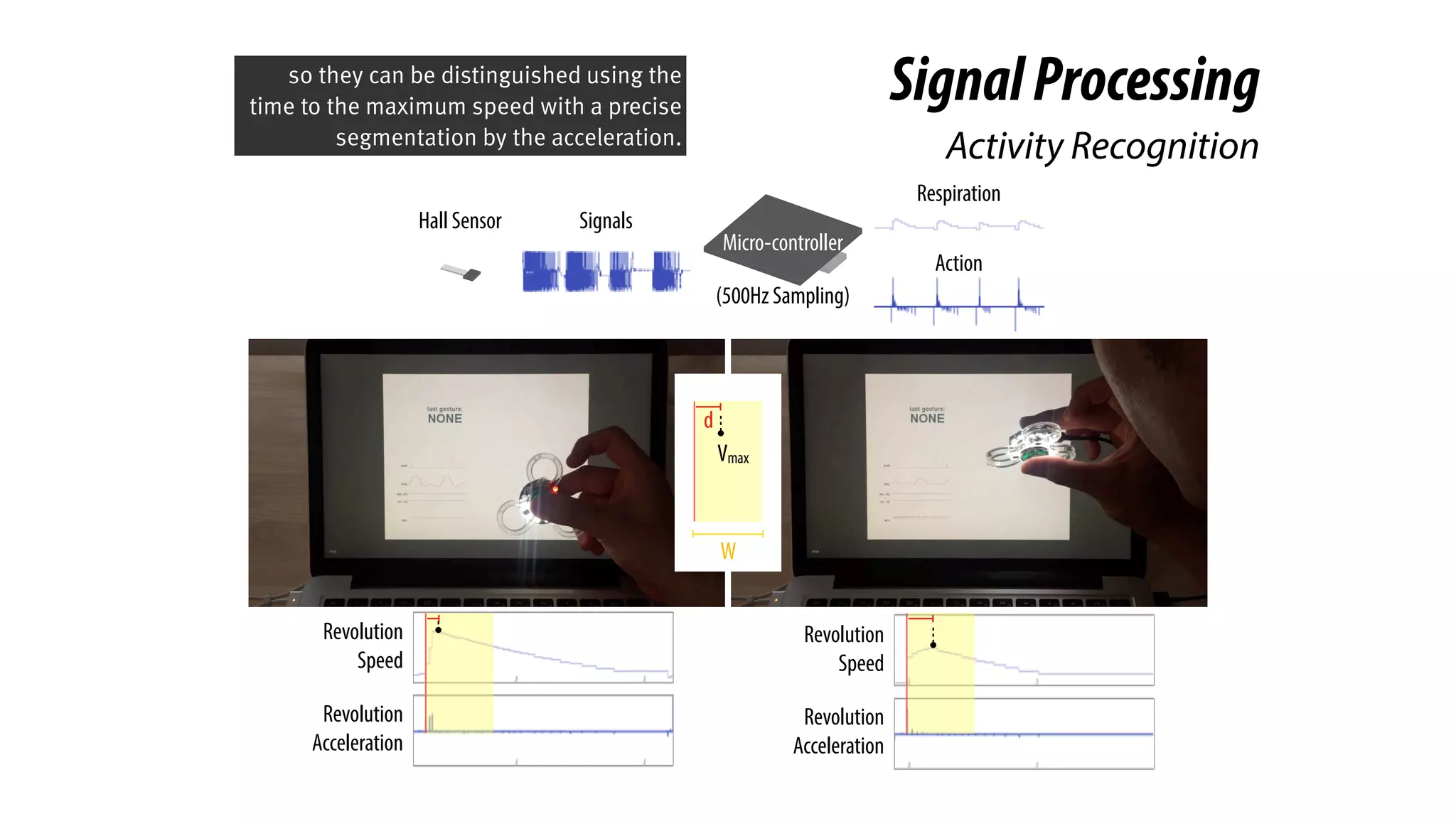
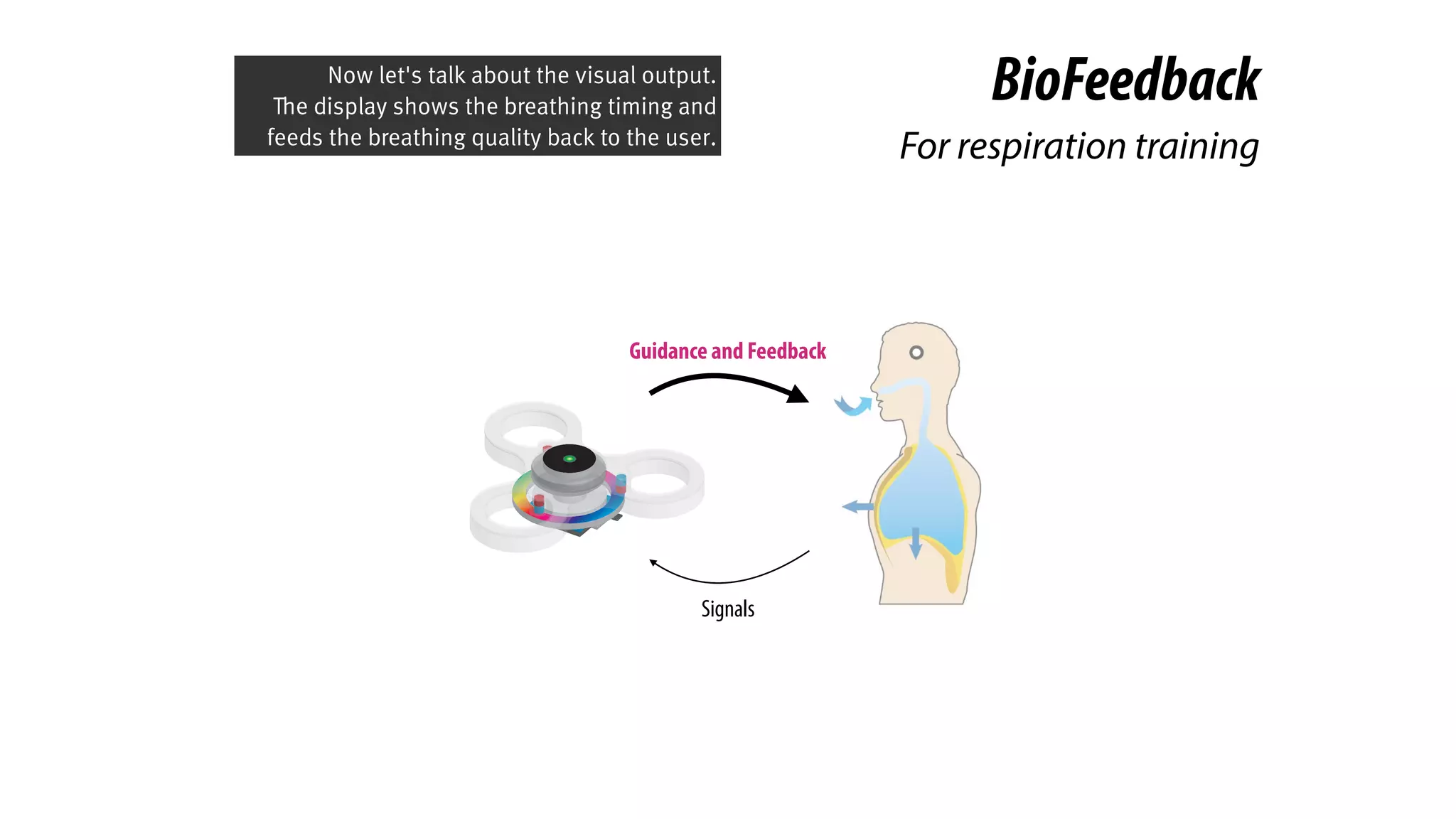
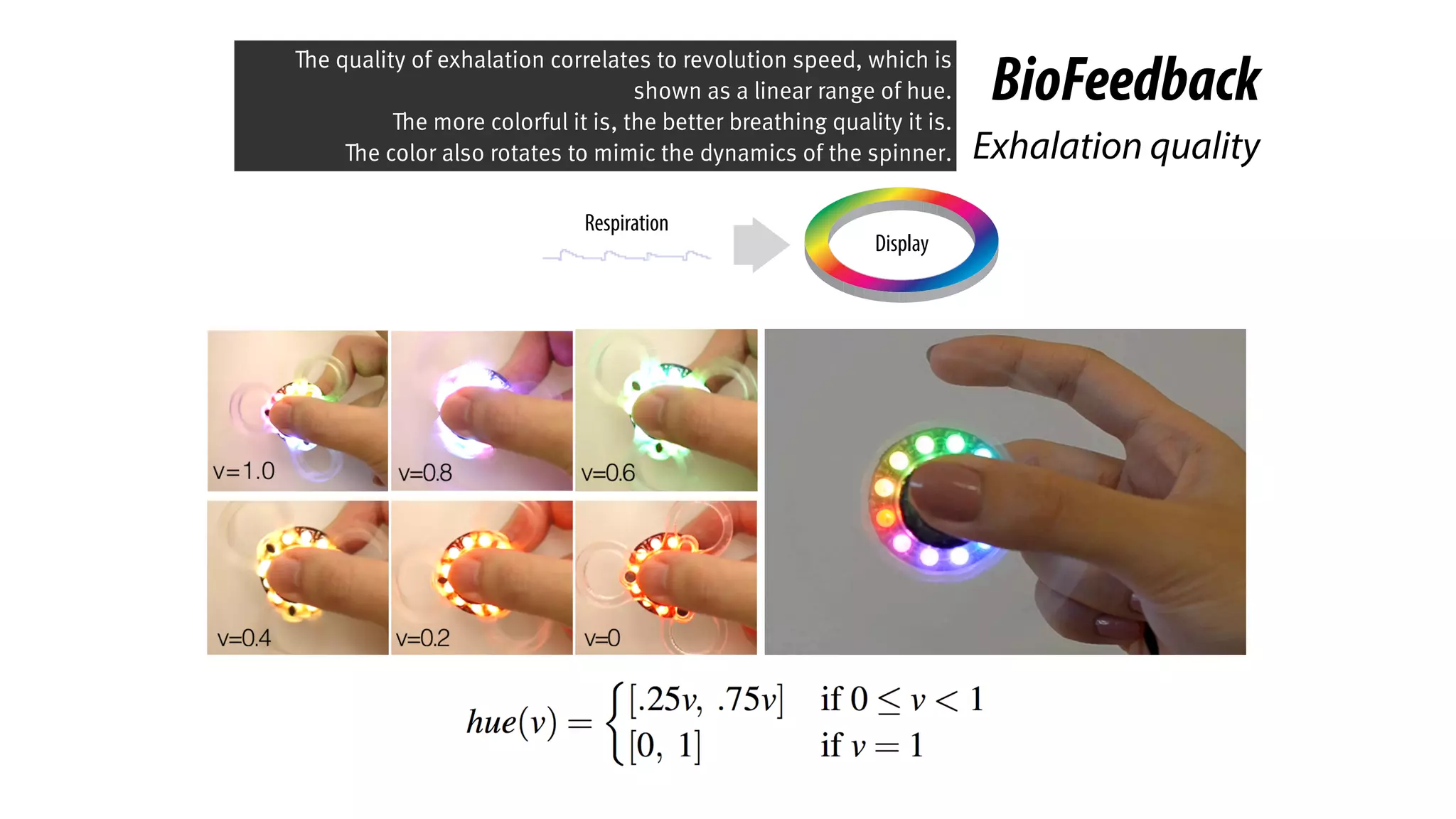
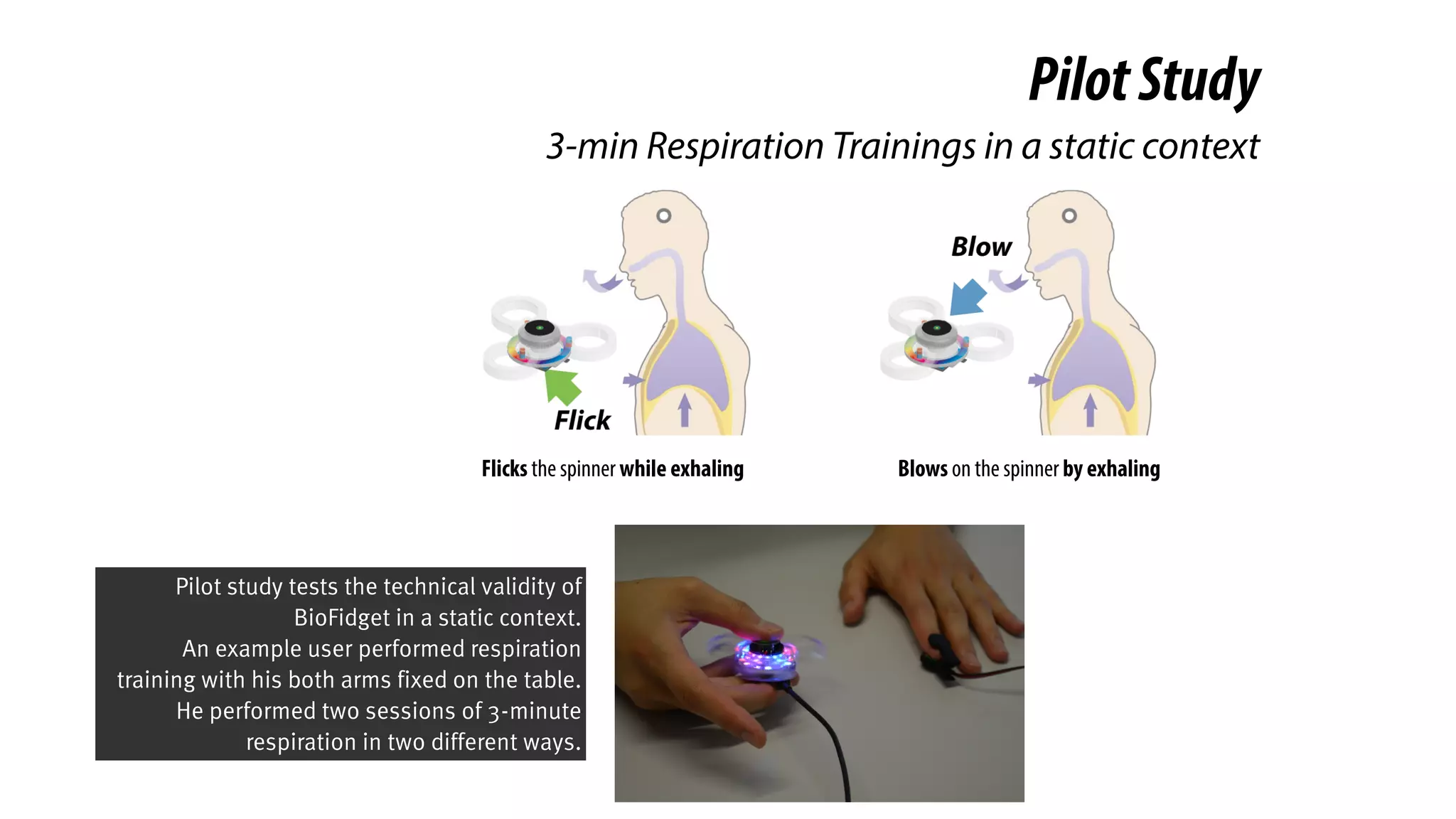
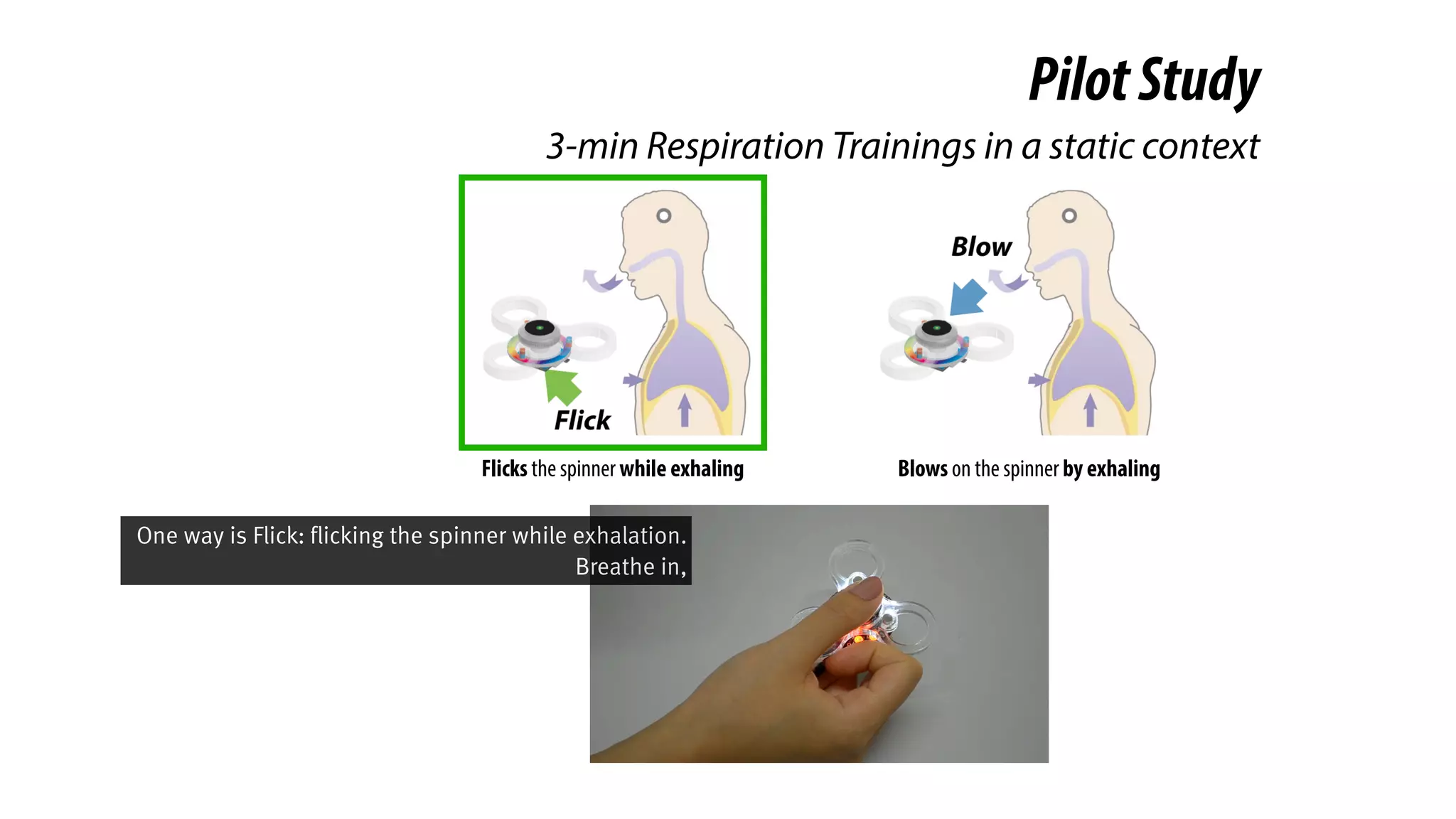
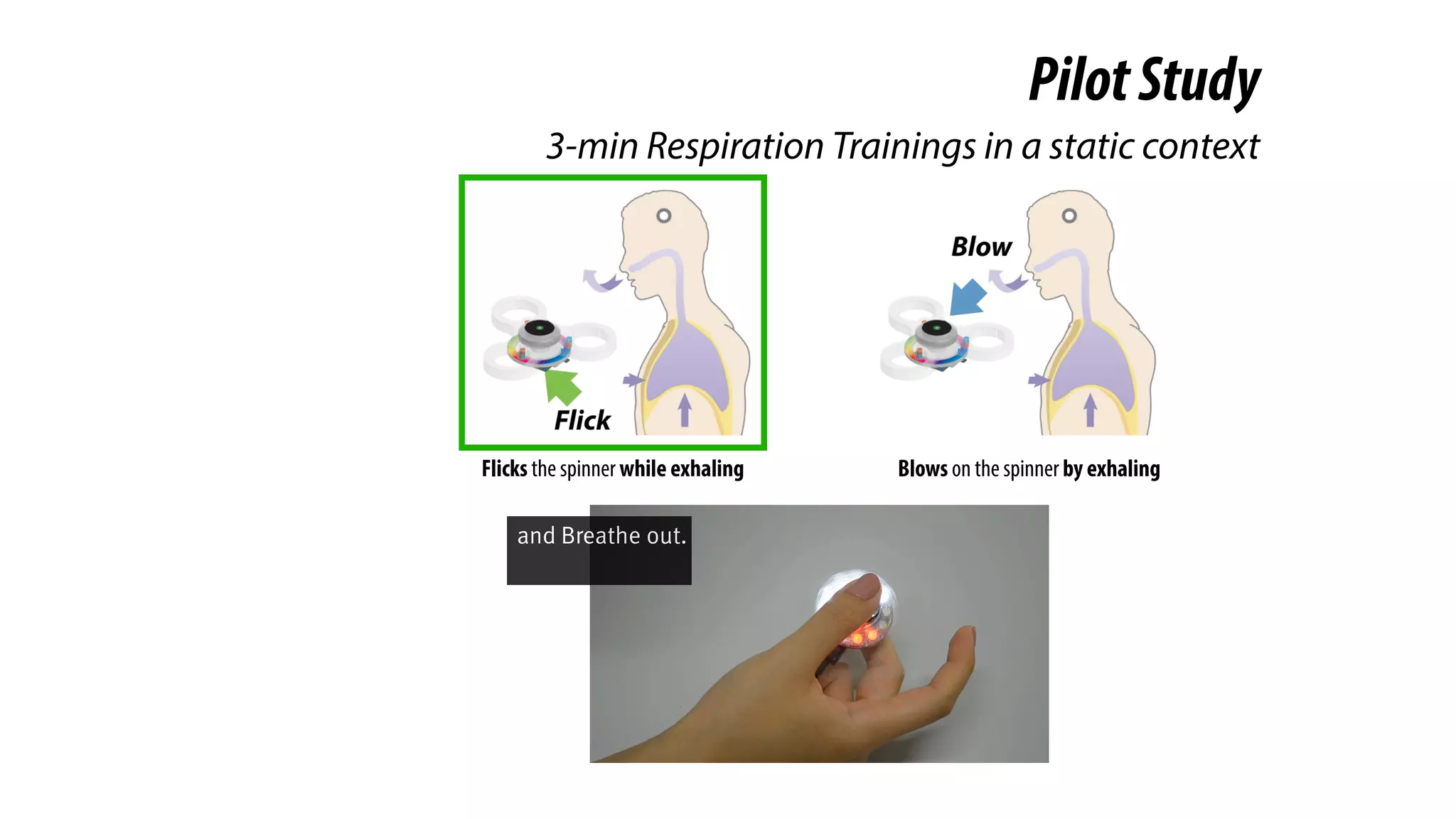
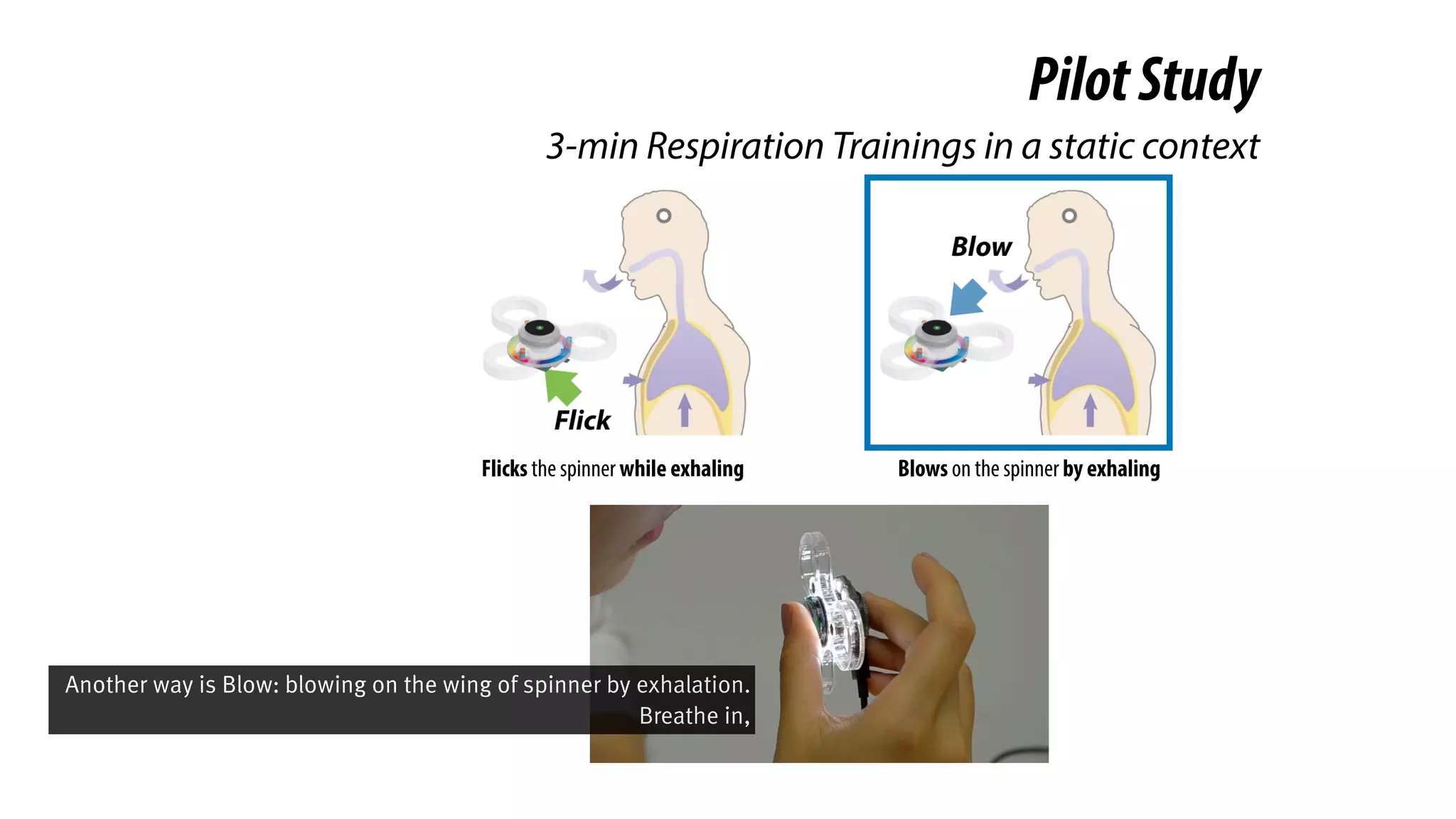
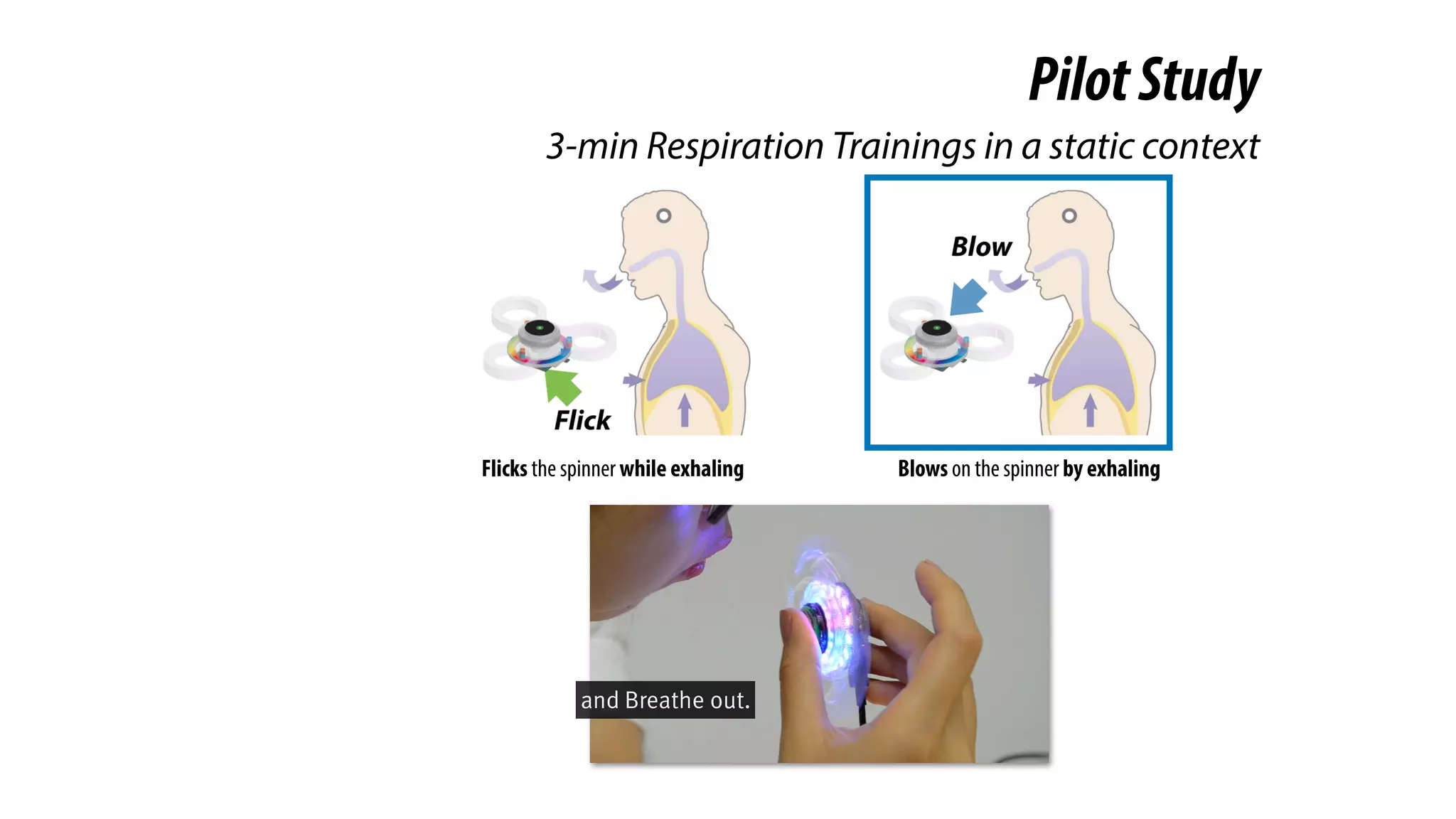
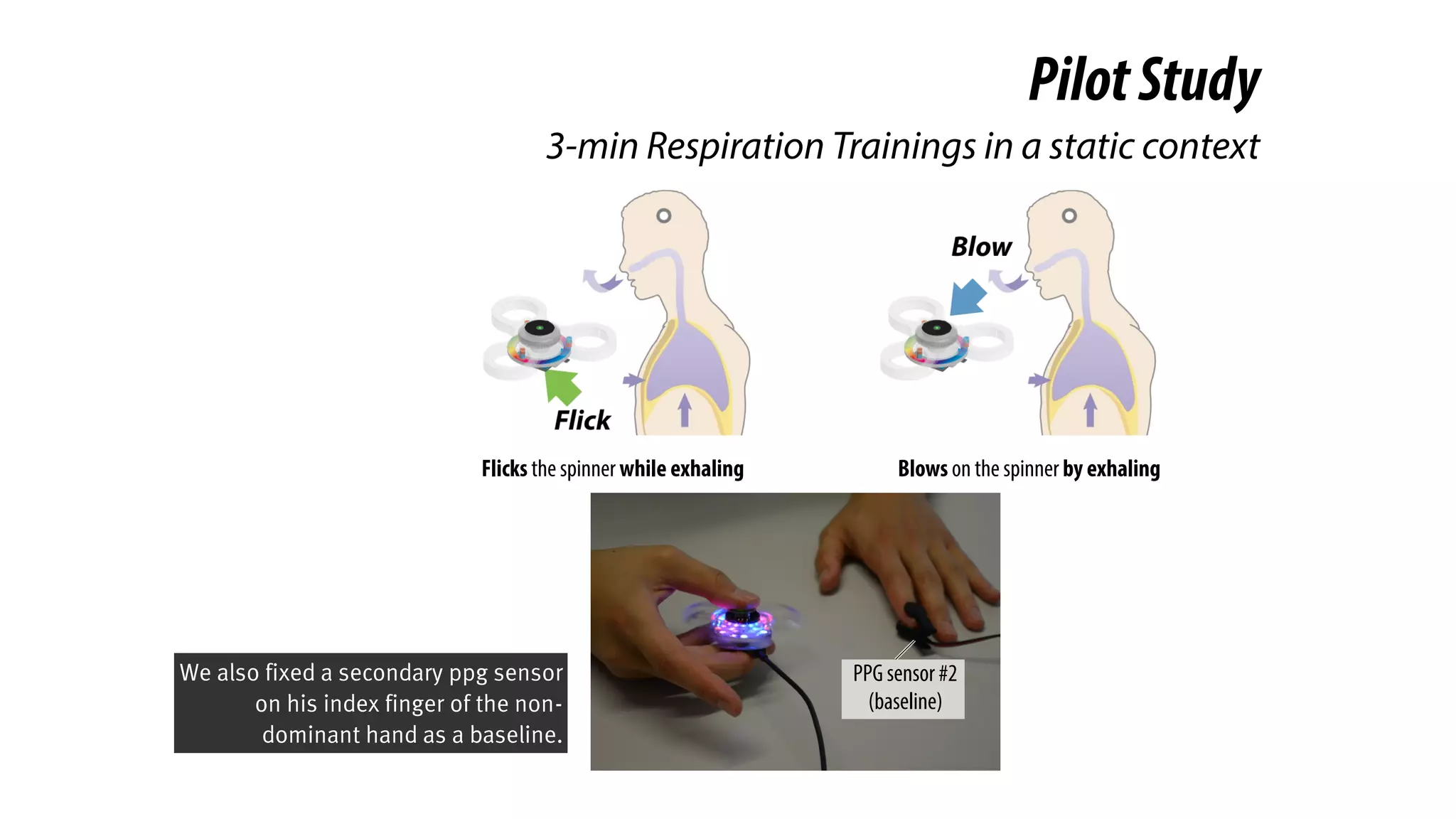
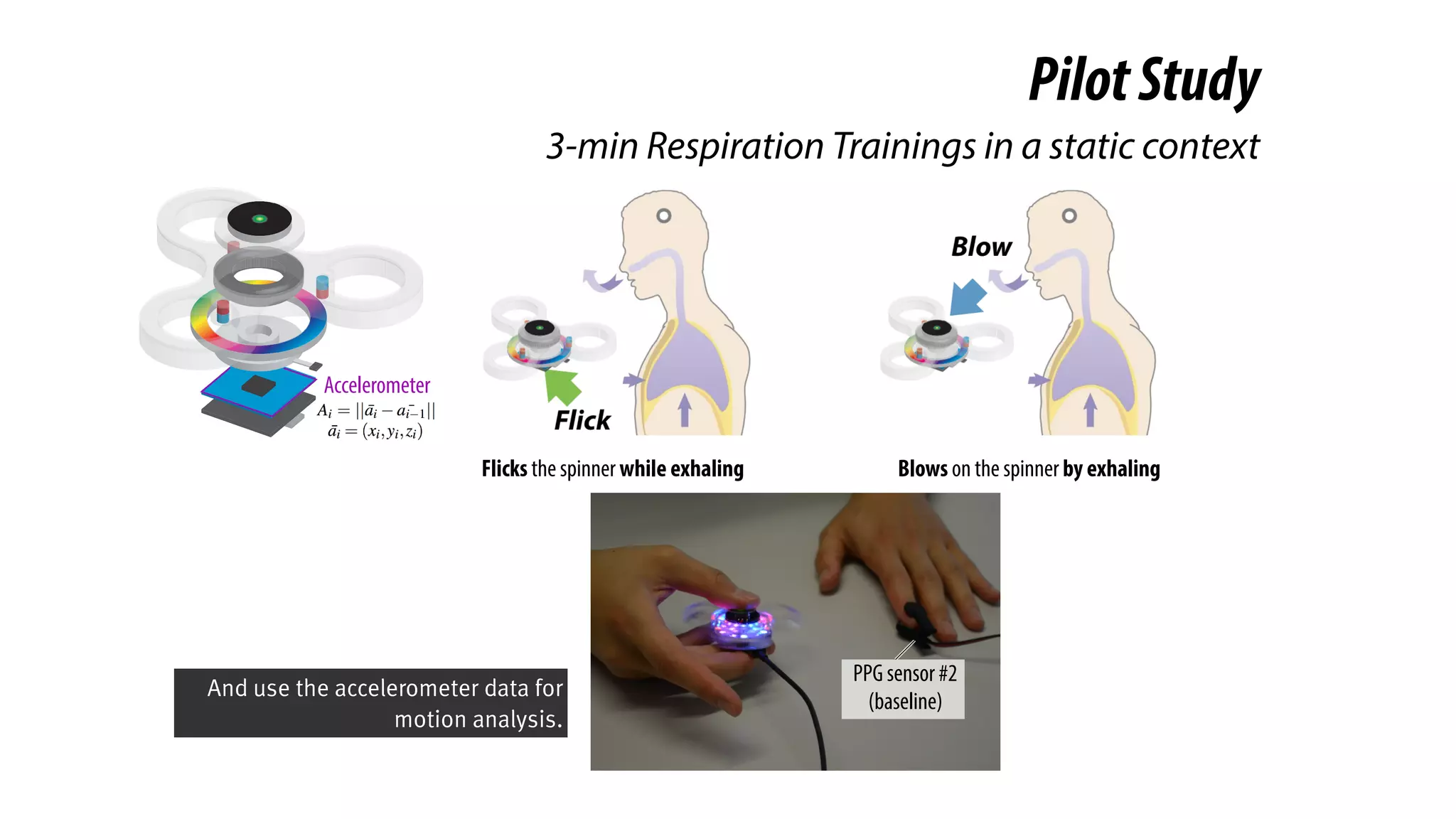
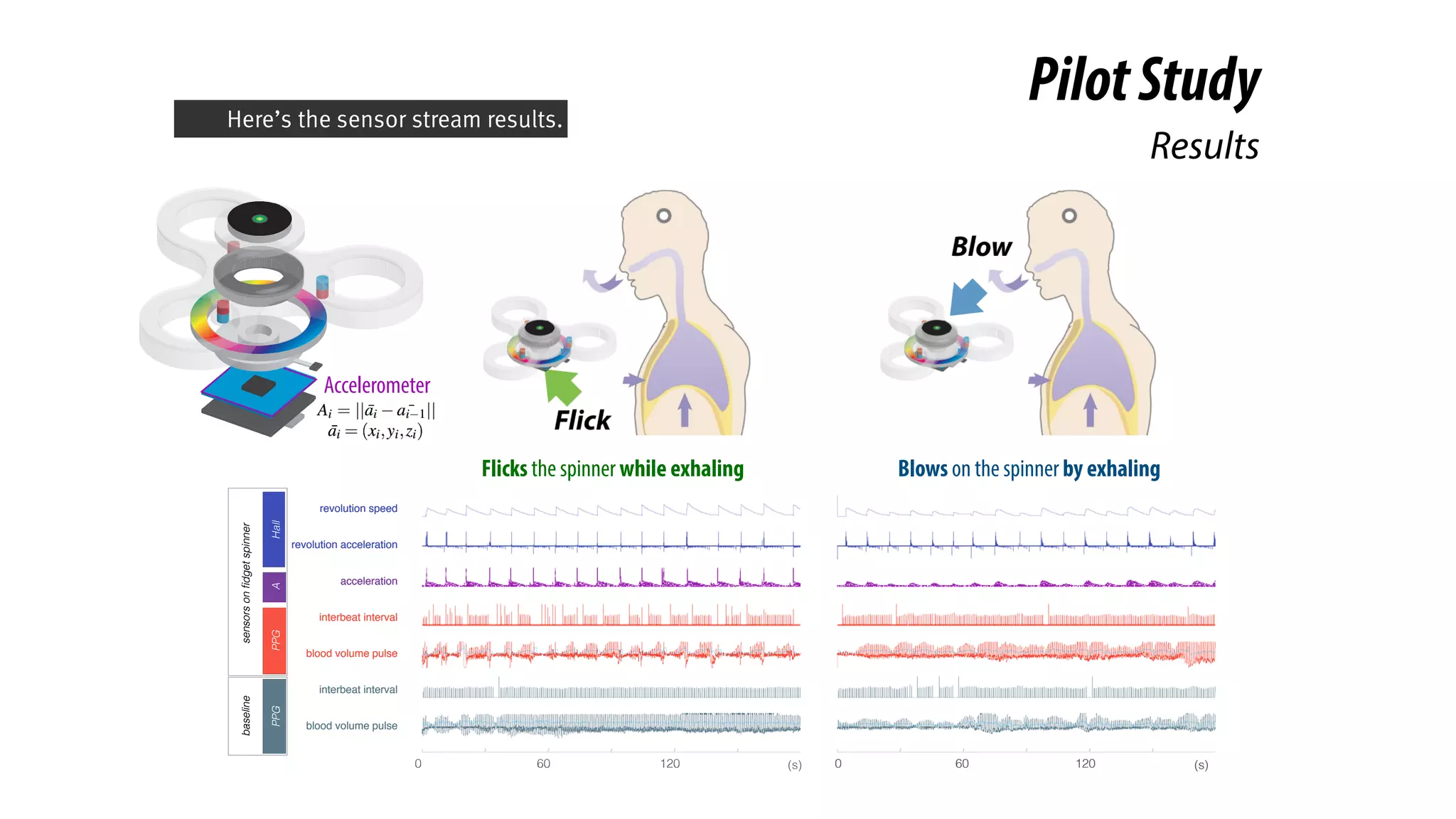
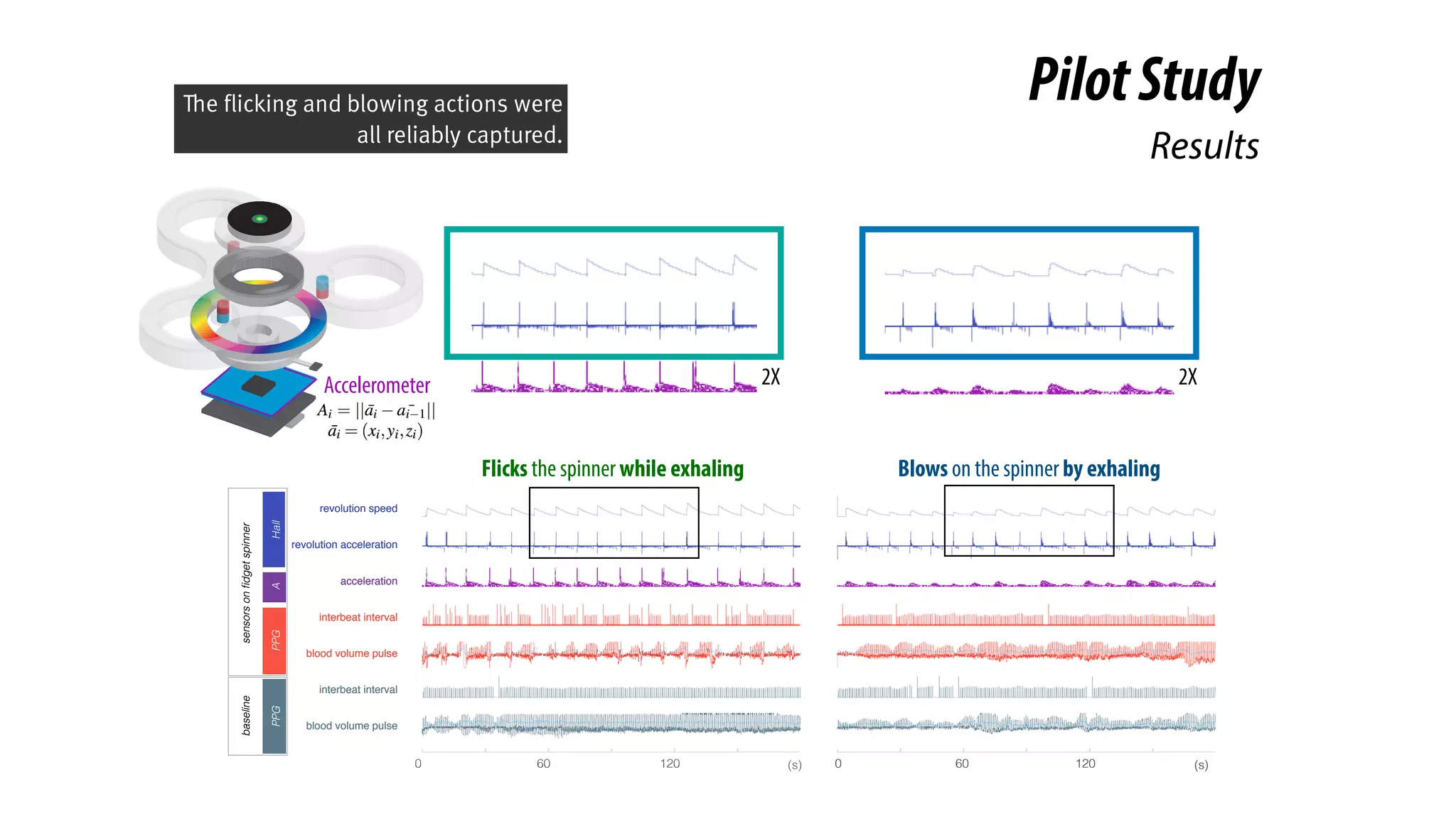
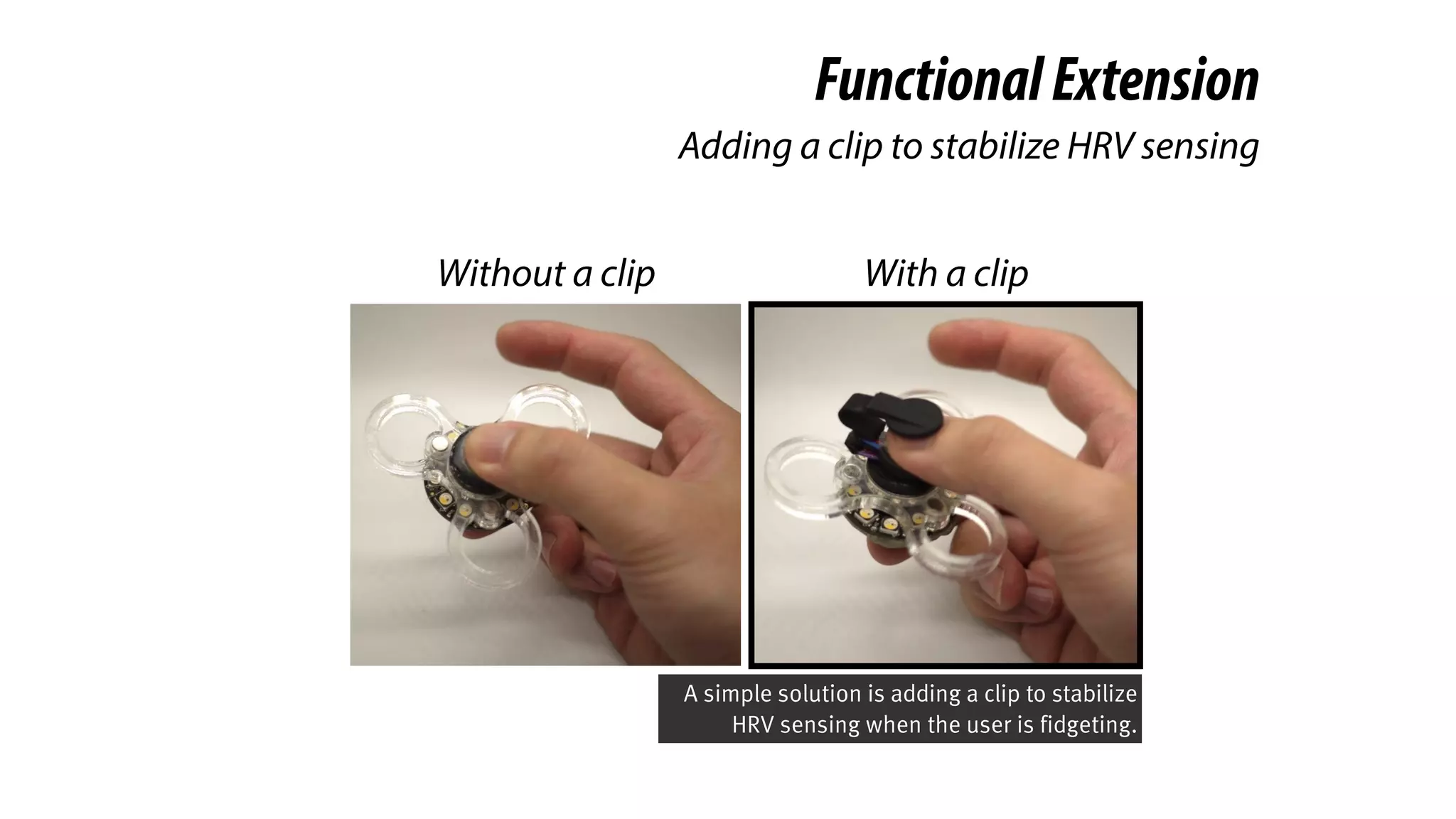
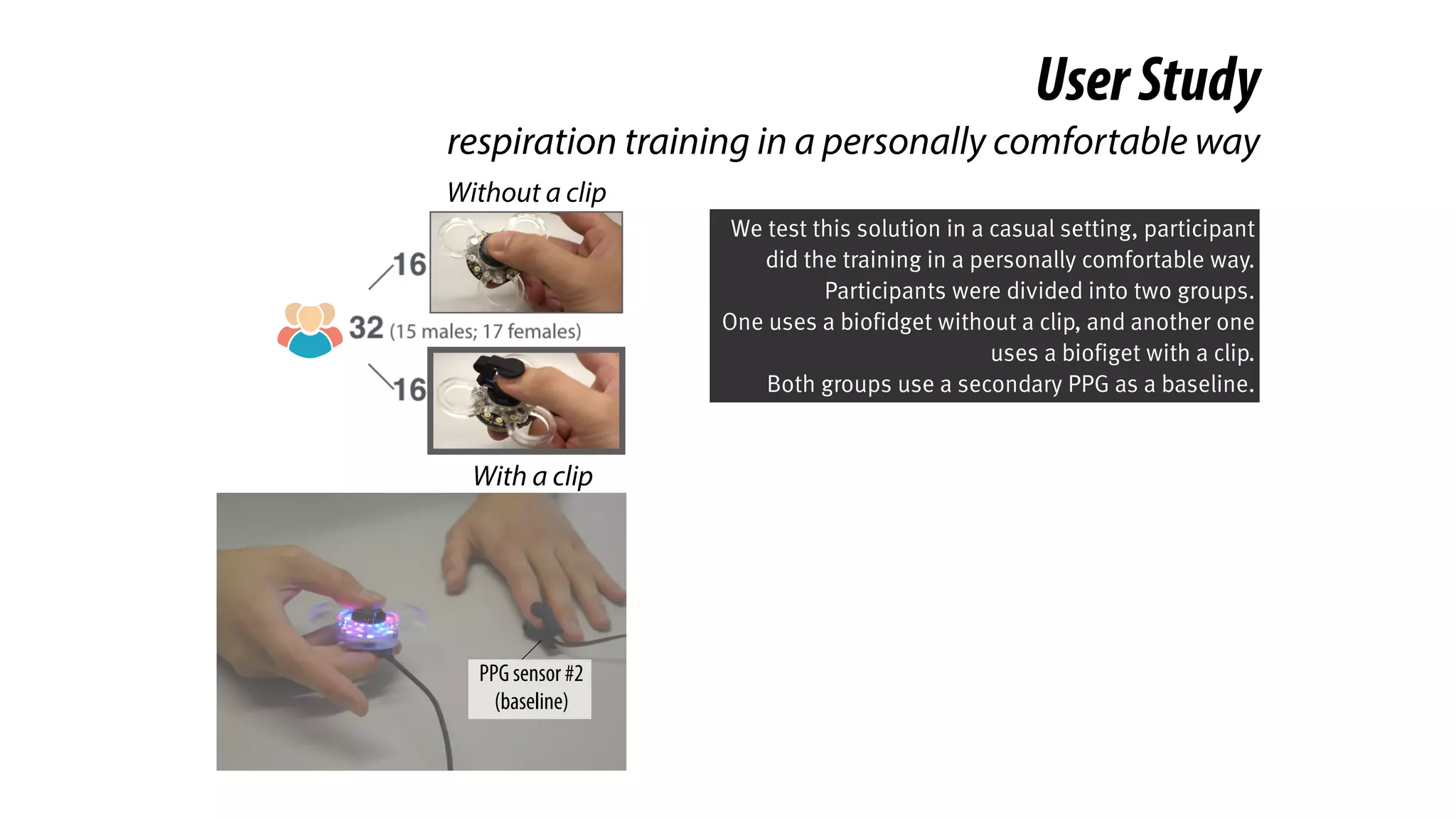
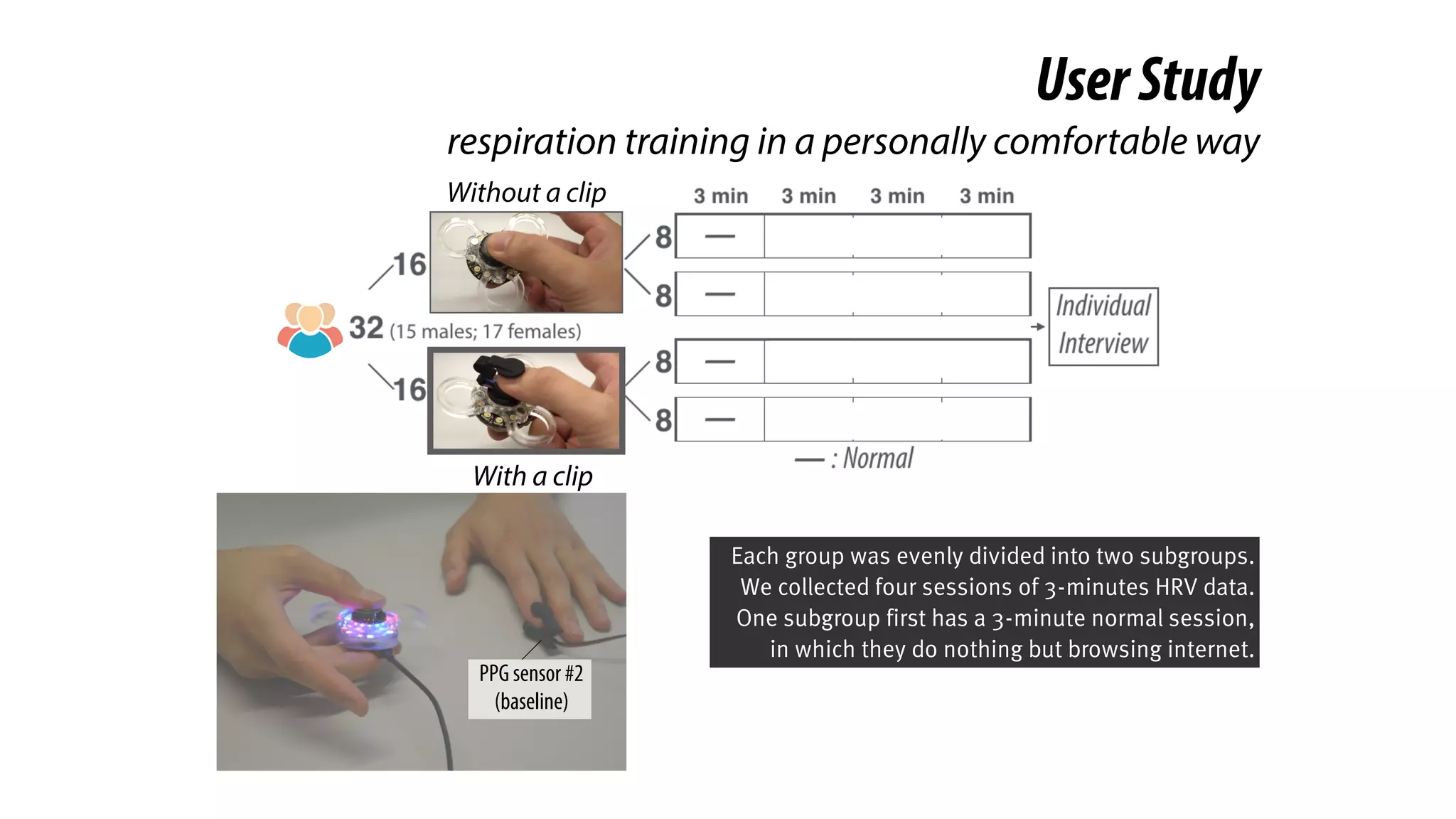
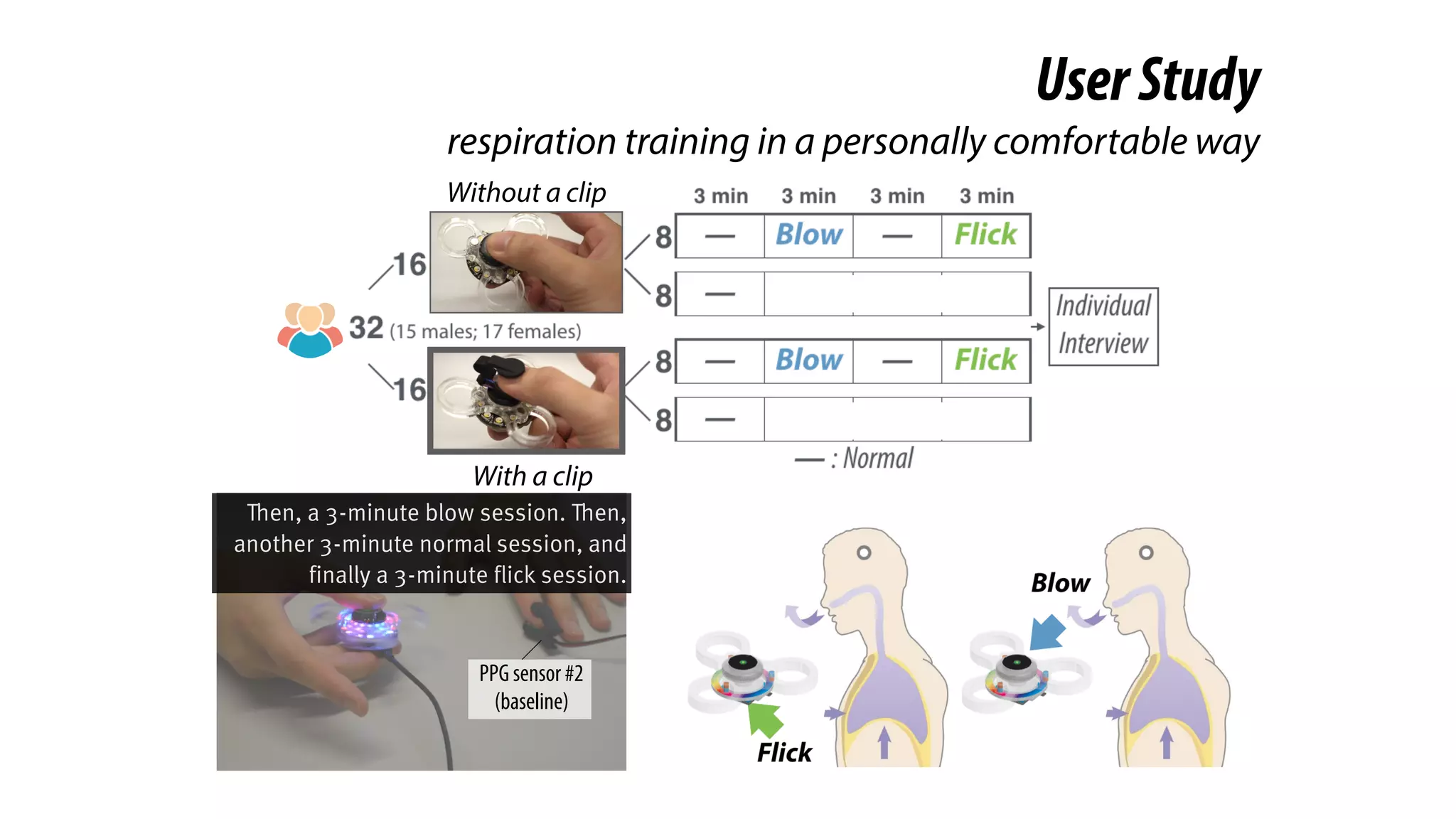
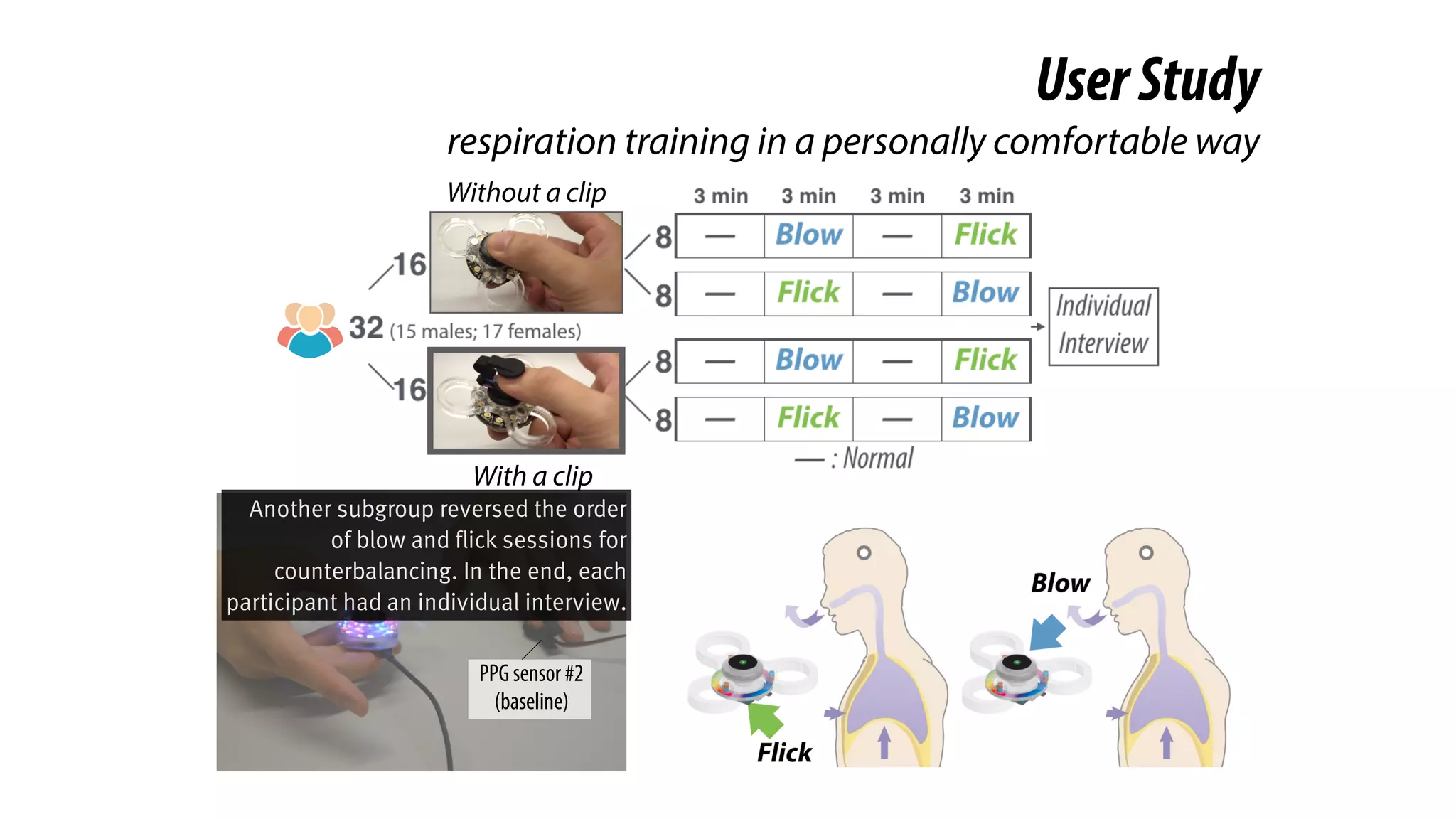
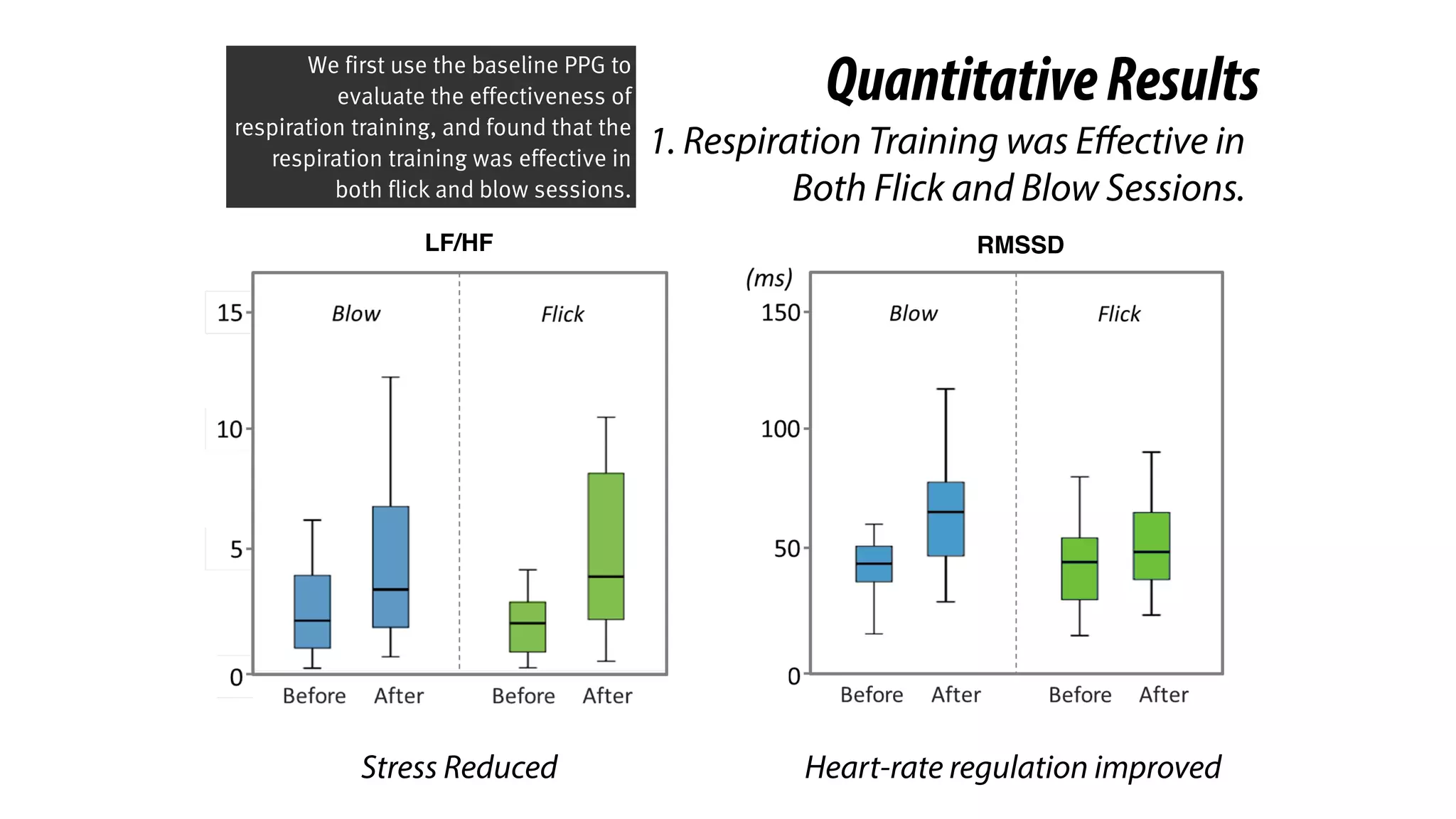
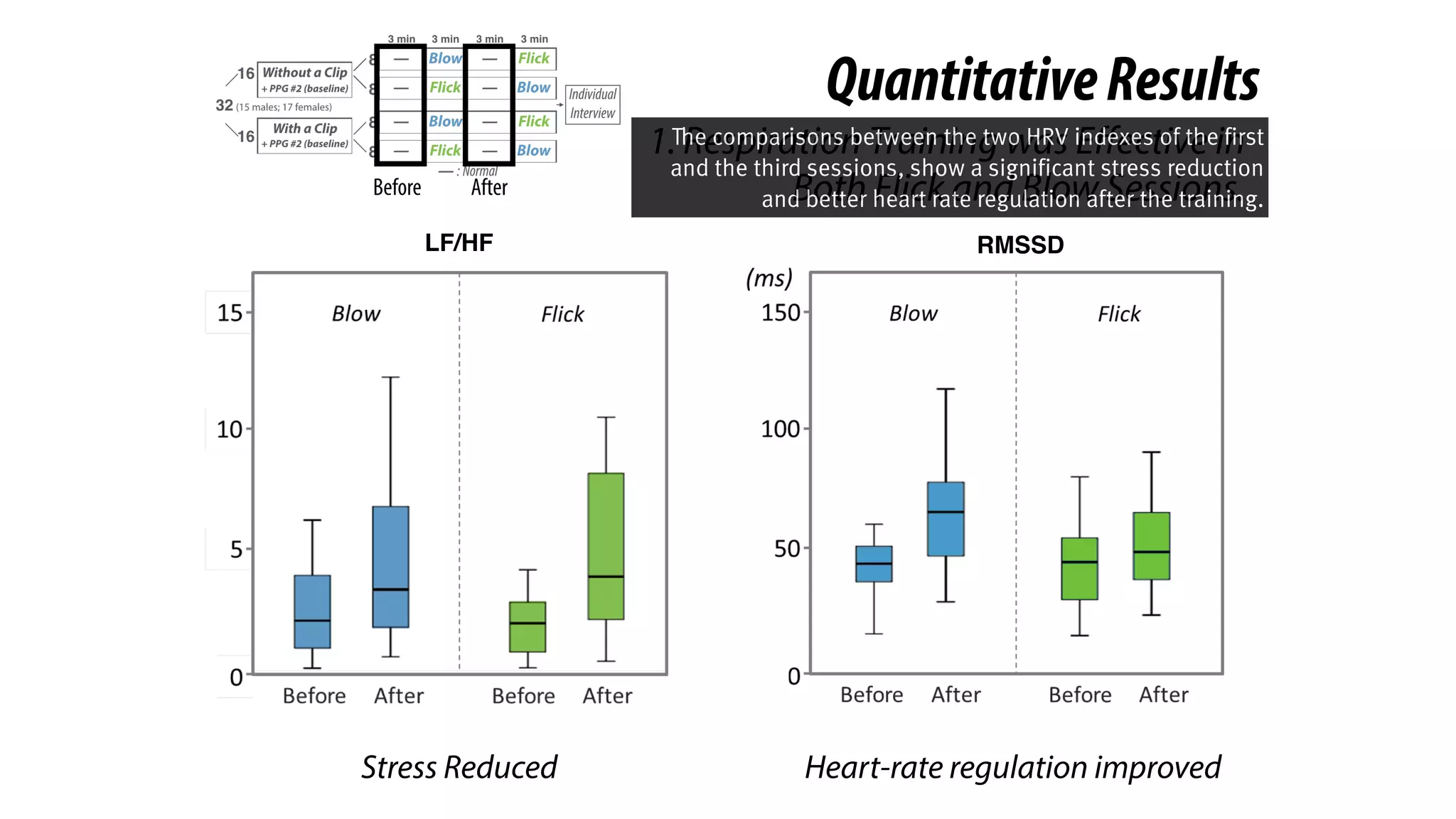
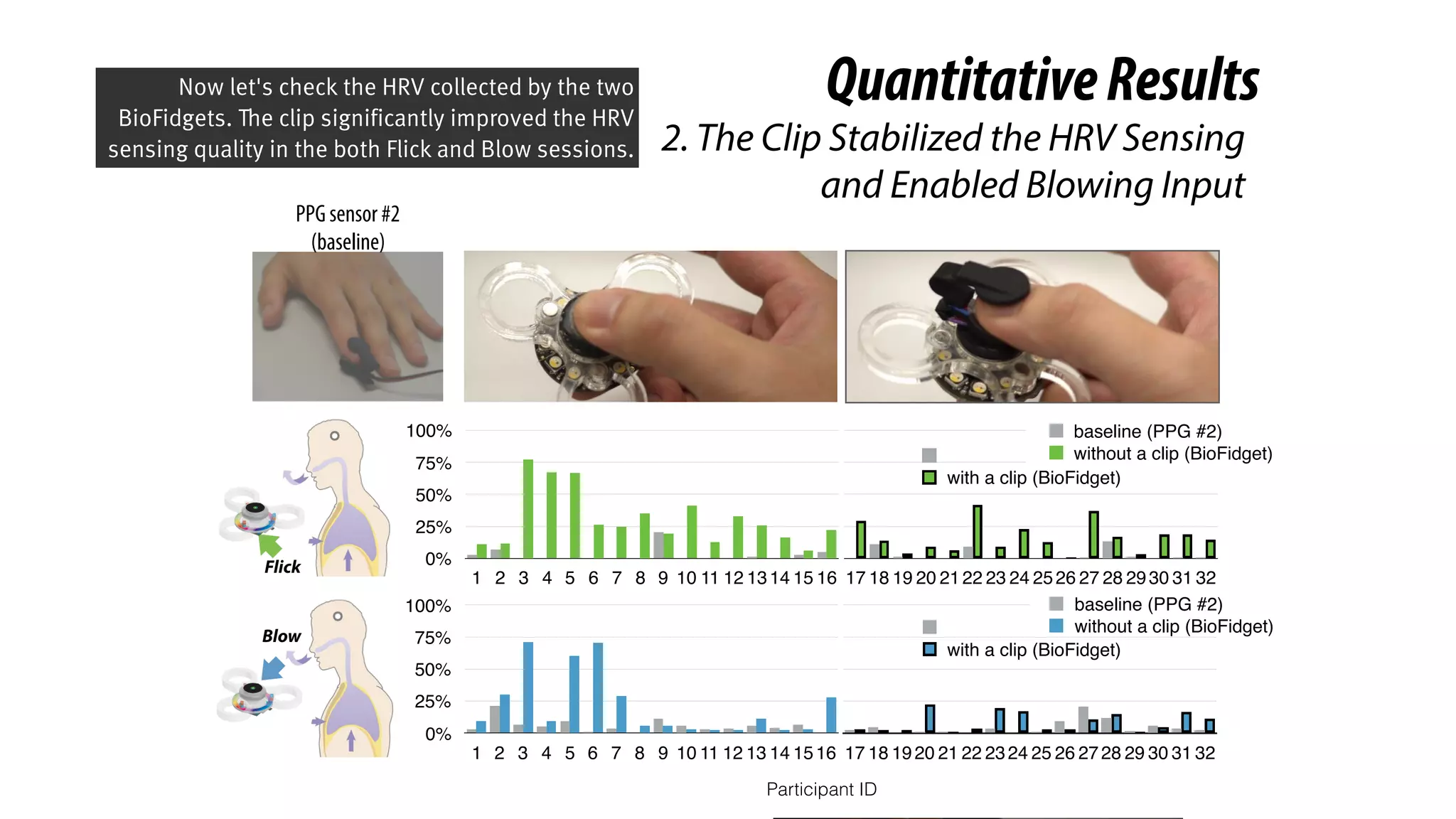
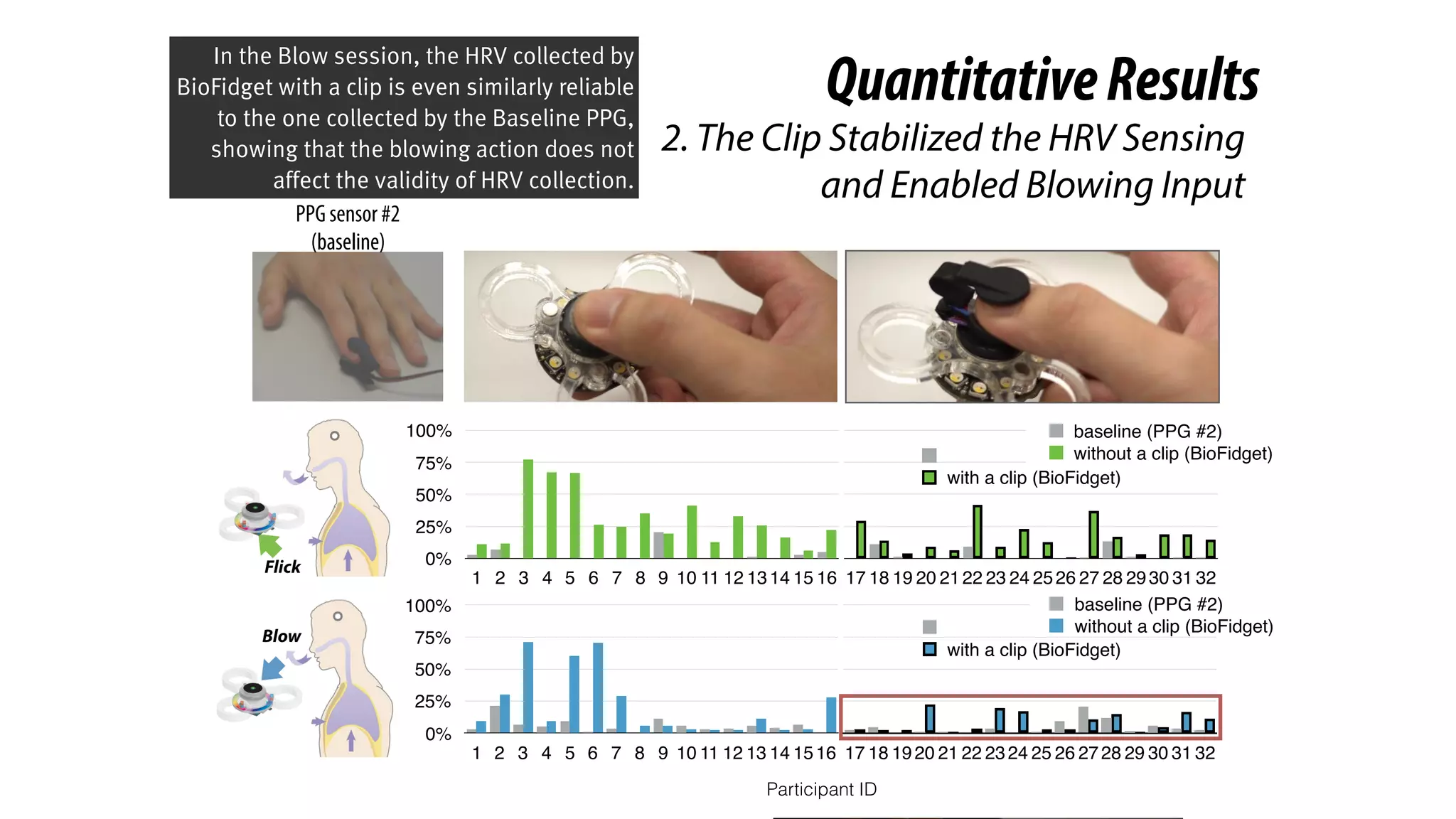
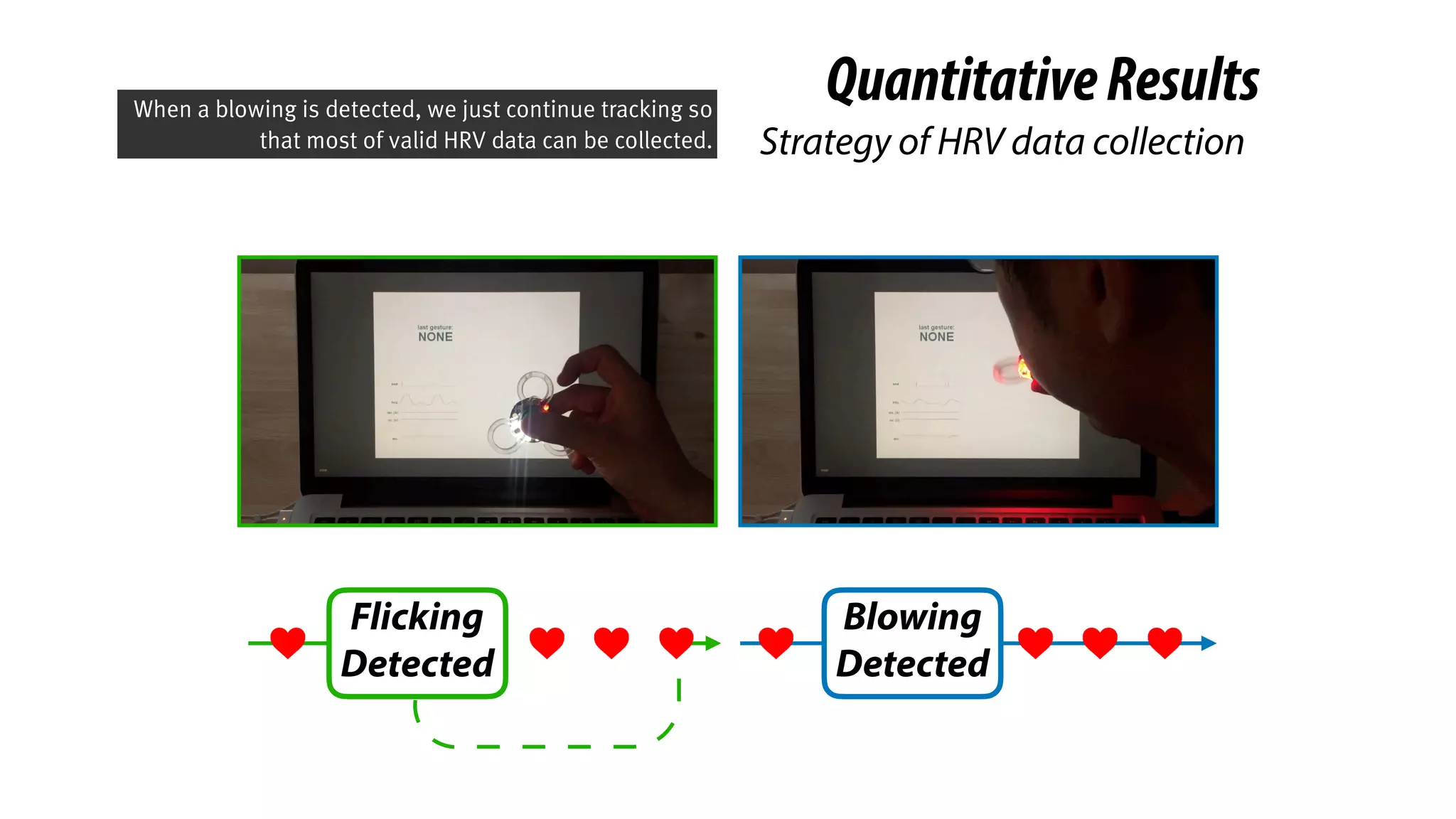
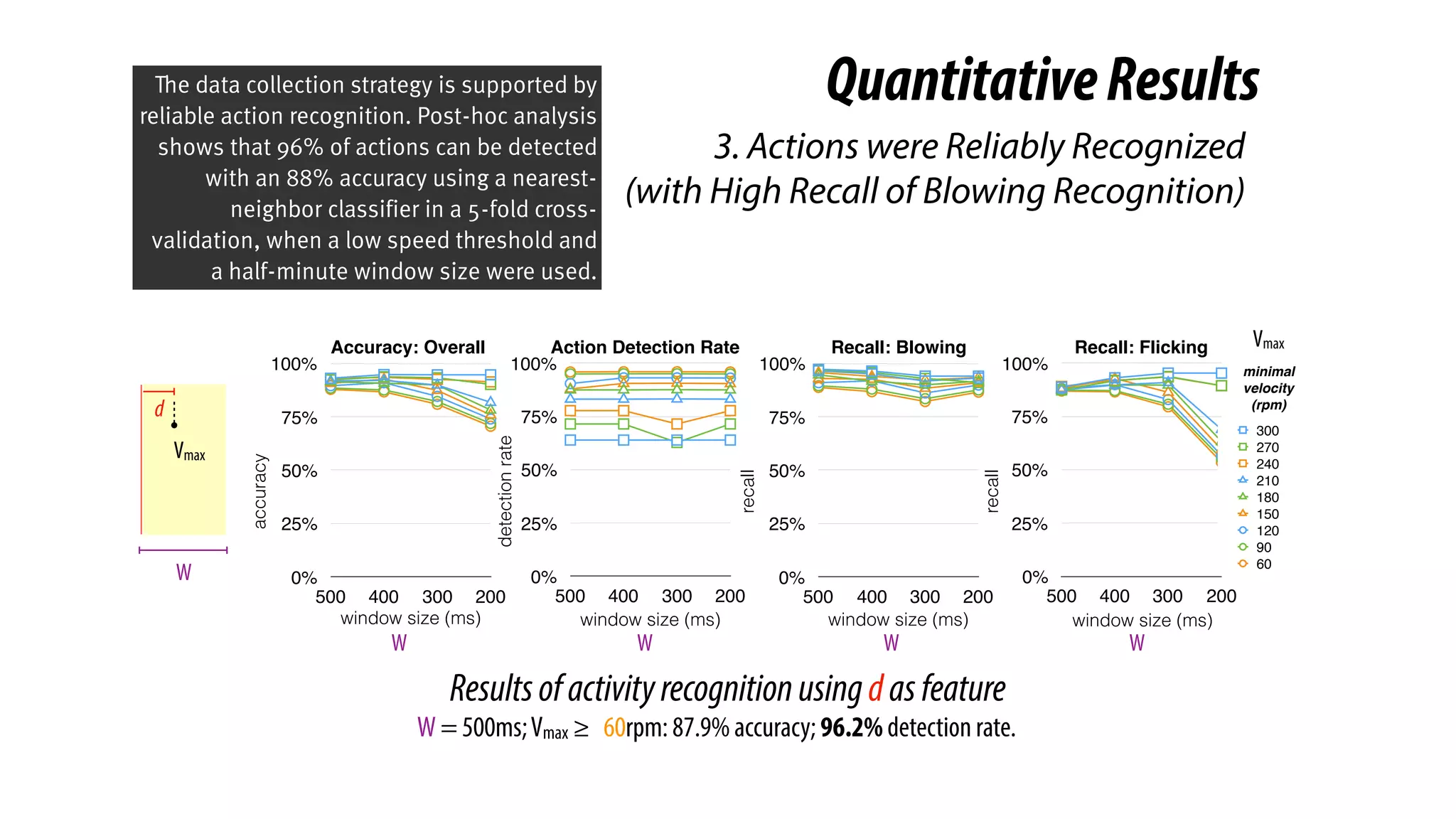
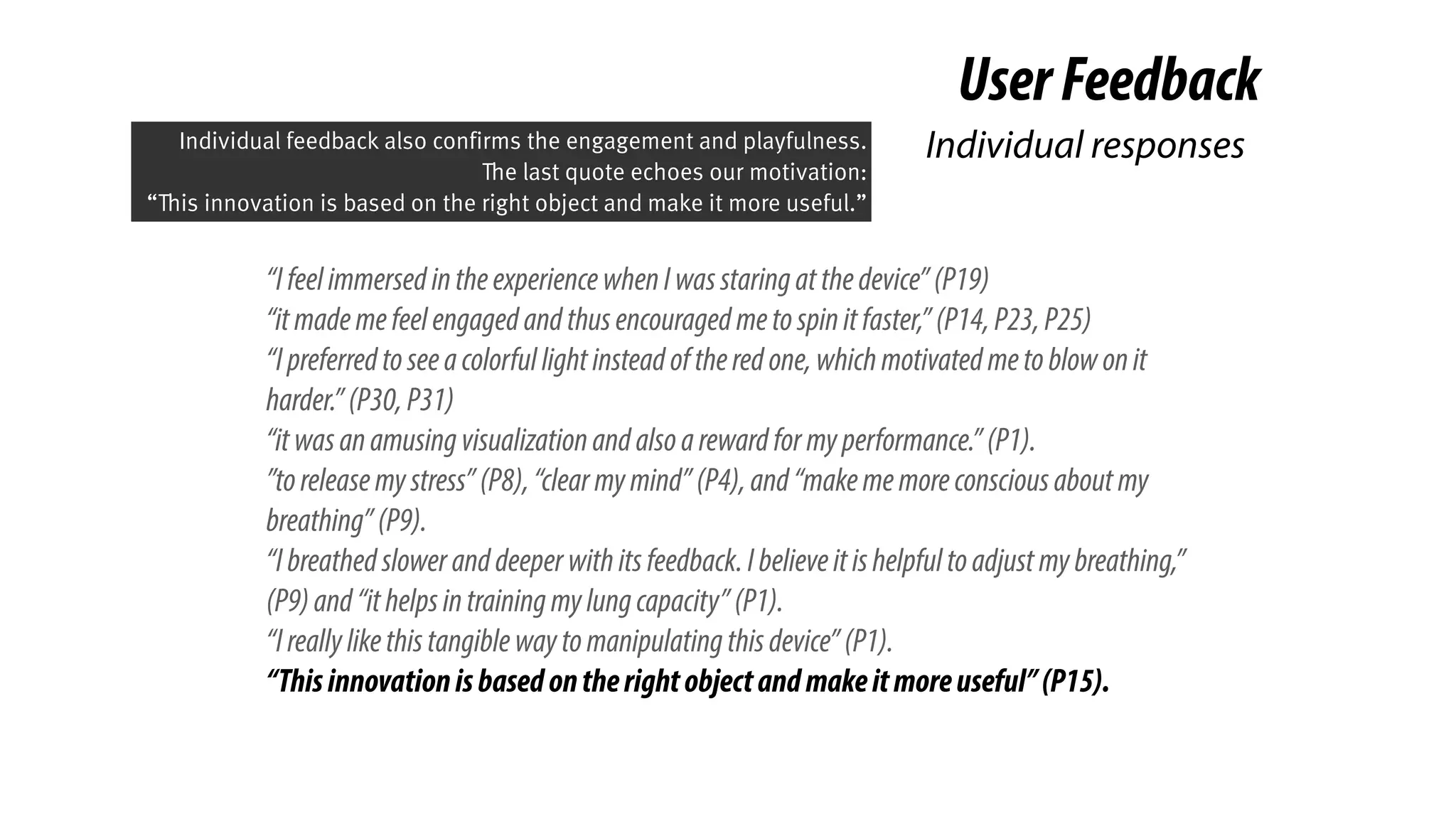
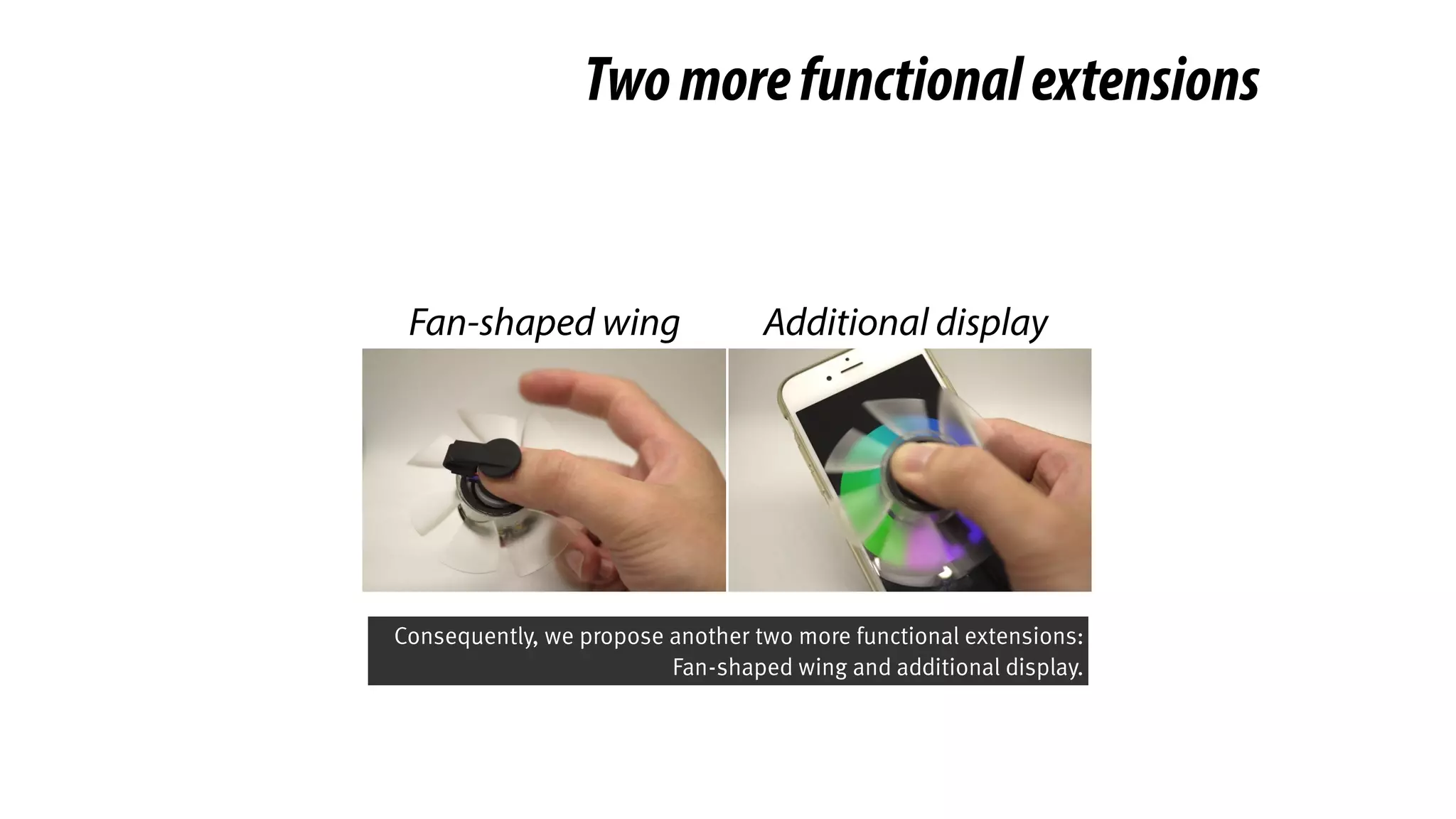
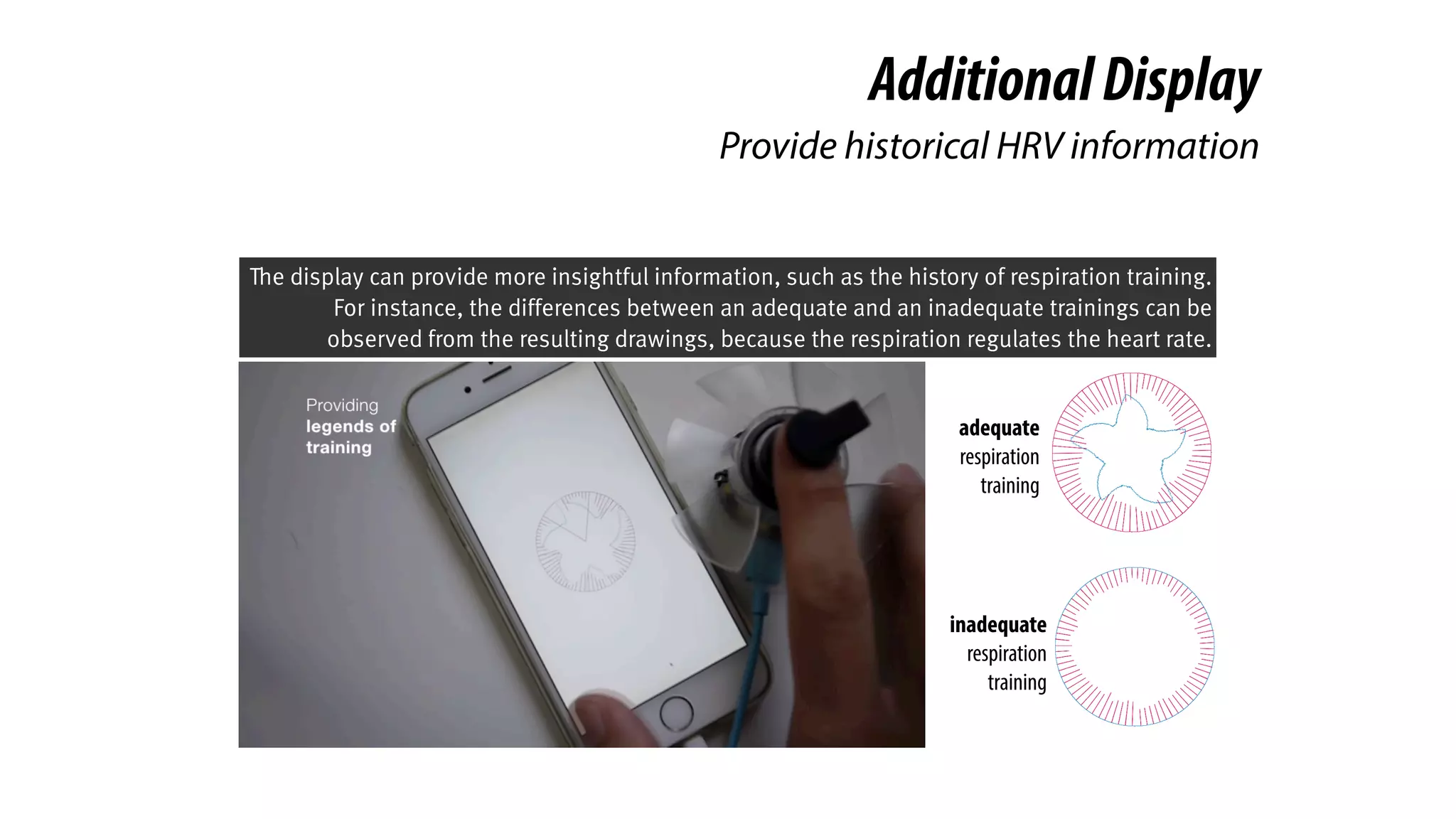
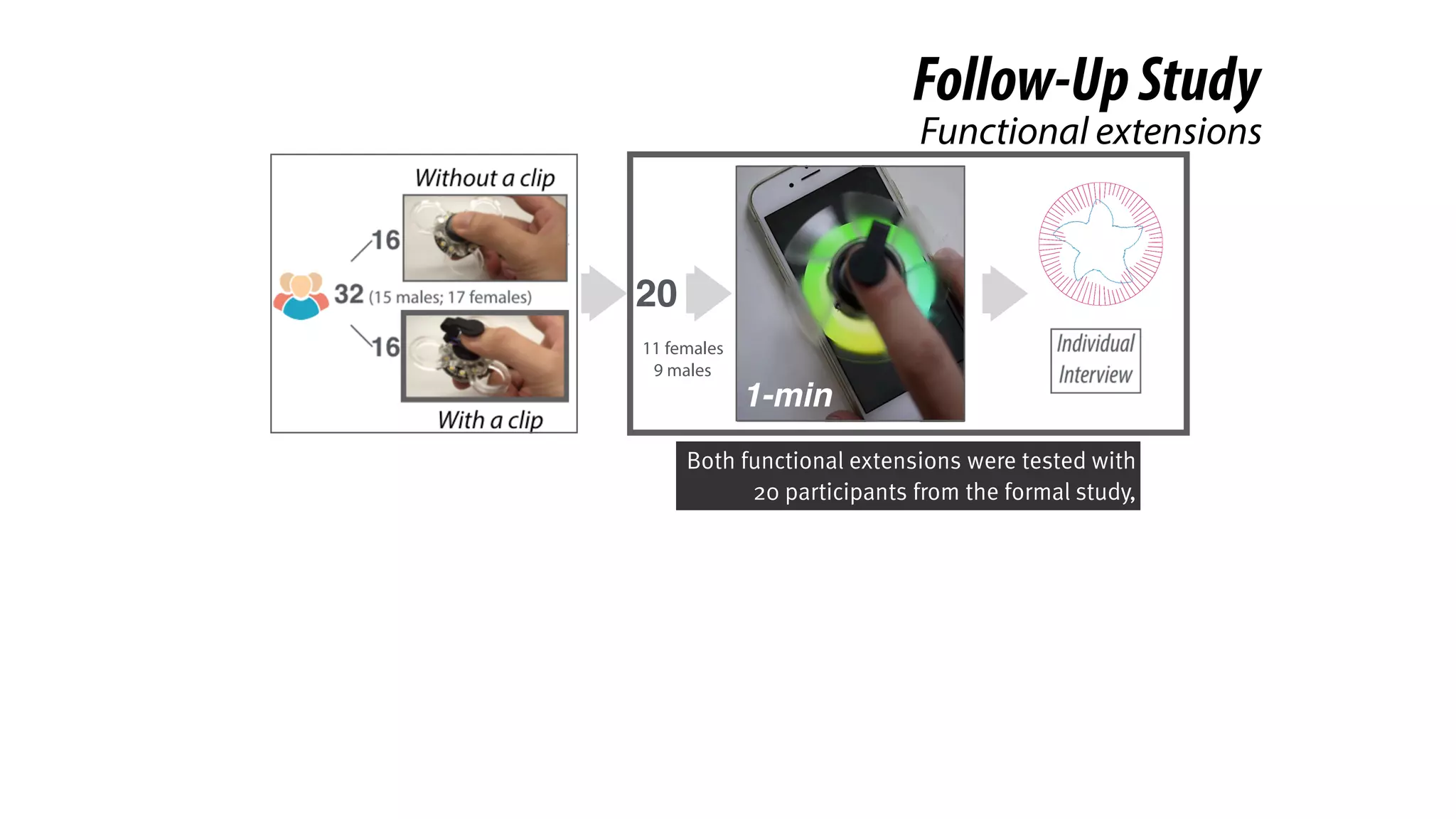
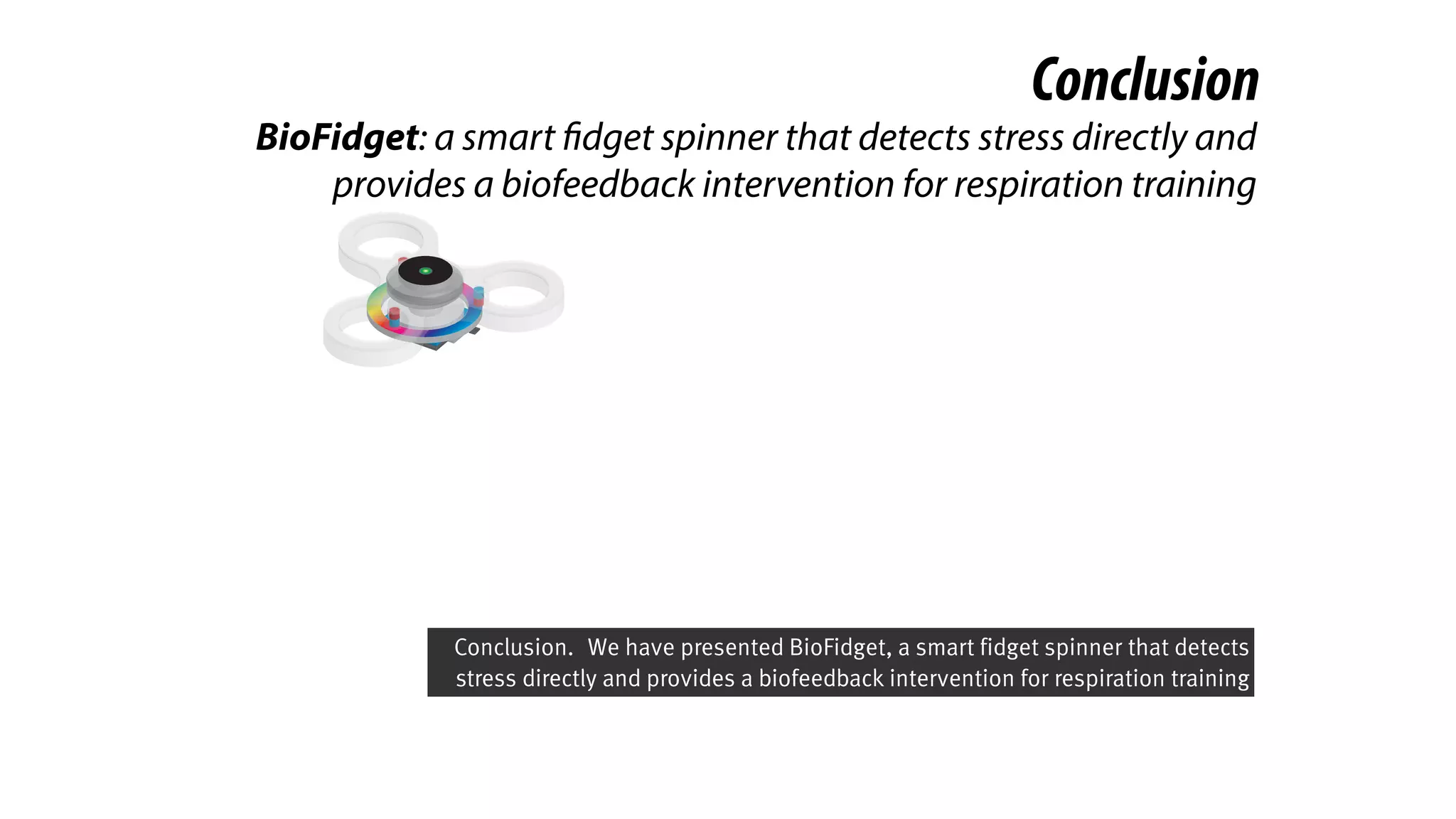
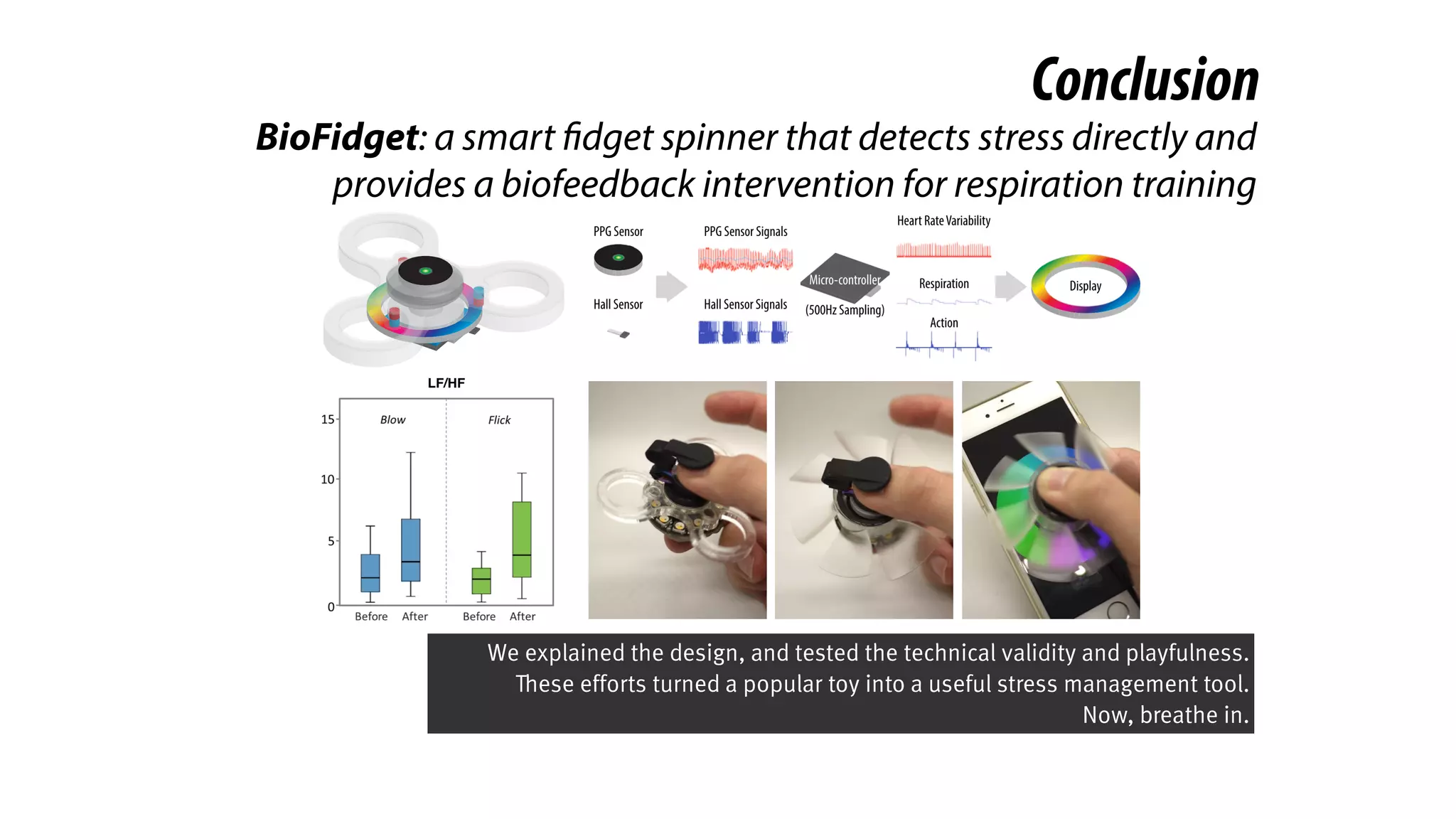
The document presents a project called Biofidget that integrates biofeedback into an augmented fidget spinner for respiration training and stress management. It highlights the benefits of respiration training, the challenges of user engagement, and the design of the device that senses heart rate variability and respiration without requiring additional sensors. The Biofidget aims to provide a playful yet effective tool for users to manage stress through deep breathing exercises, combining technology with the engaging action of fidget spinning.




![]
Lehrer, P. M., Vaschillo, E., and Vaschillo,
B. Resonant frequency biofeedback training to increase cardiac variability: Rationale and manual for training. Applied
psychophysiology and biofeedback 25, 3 (2000), 177–191.
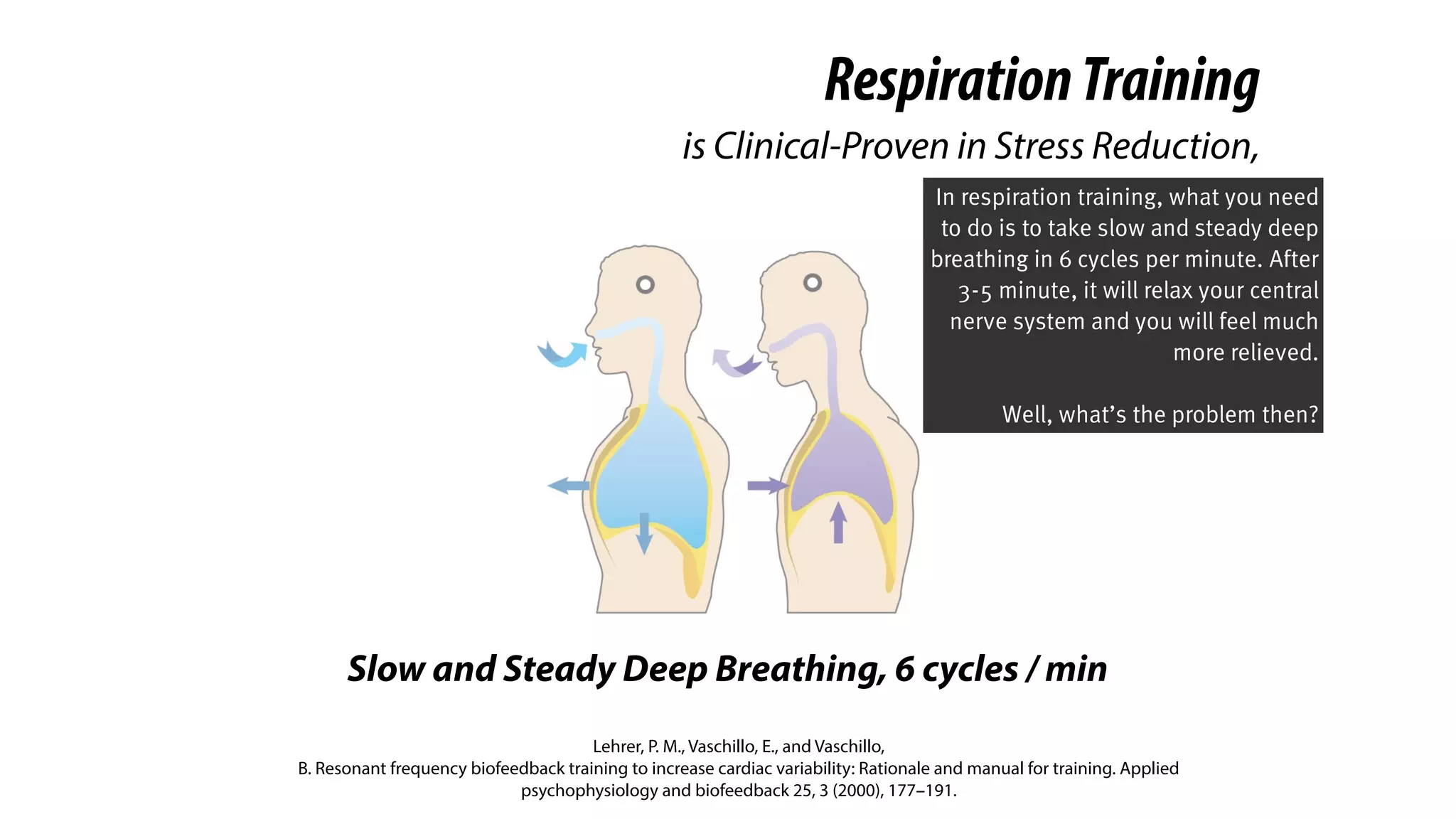
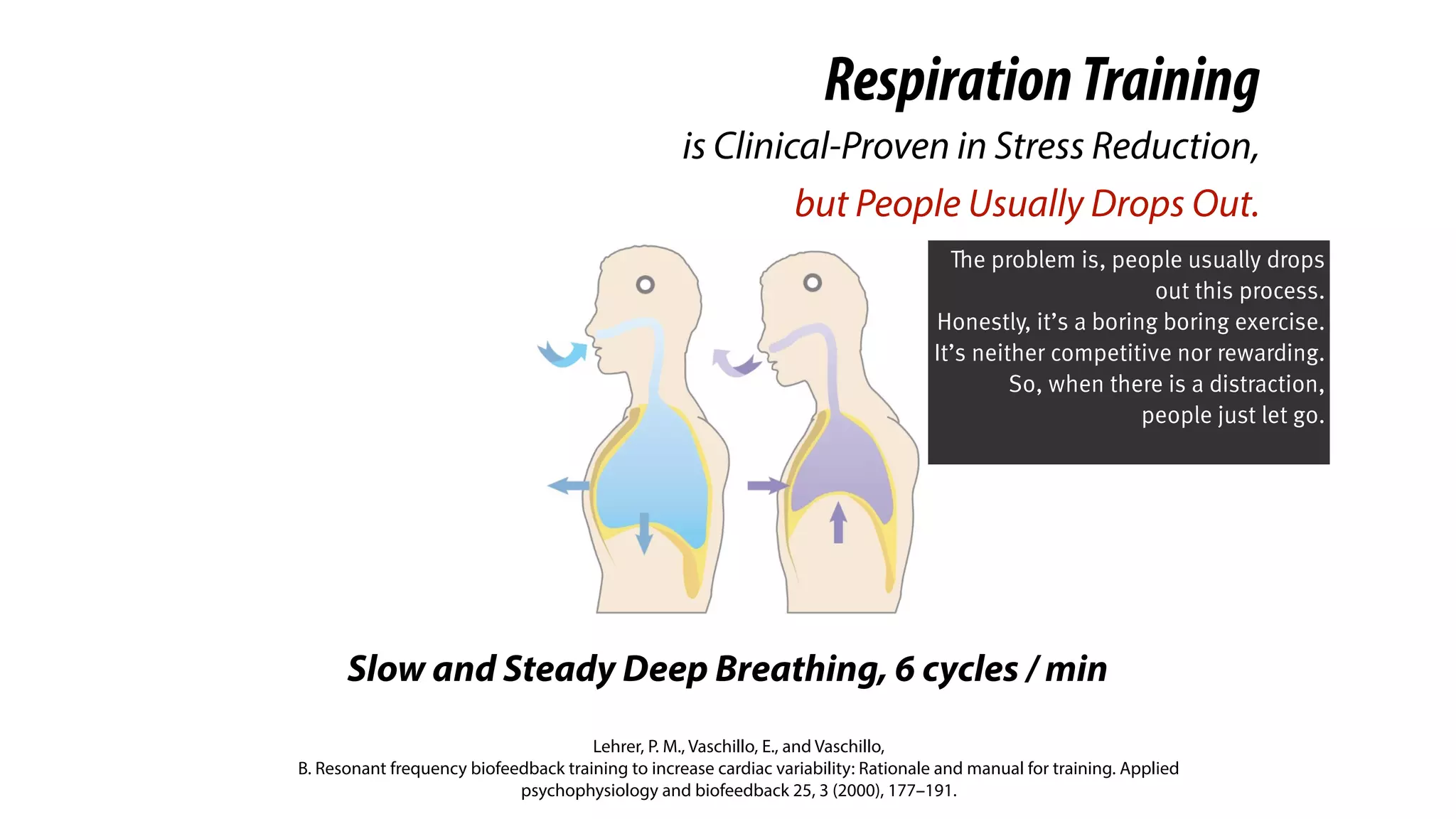
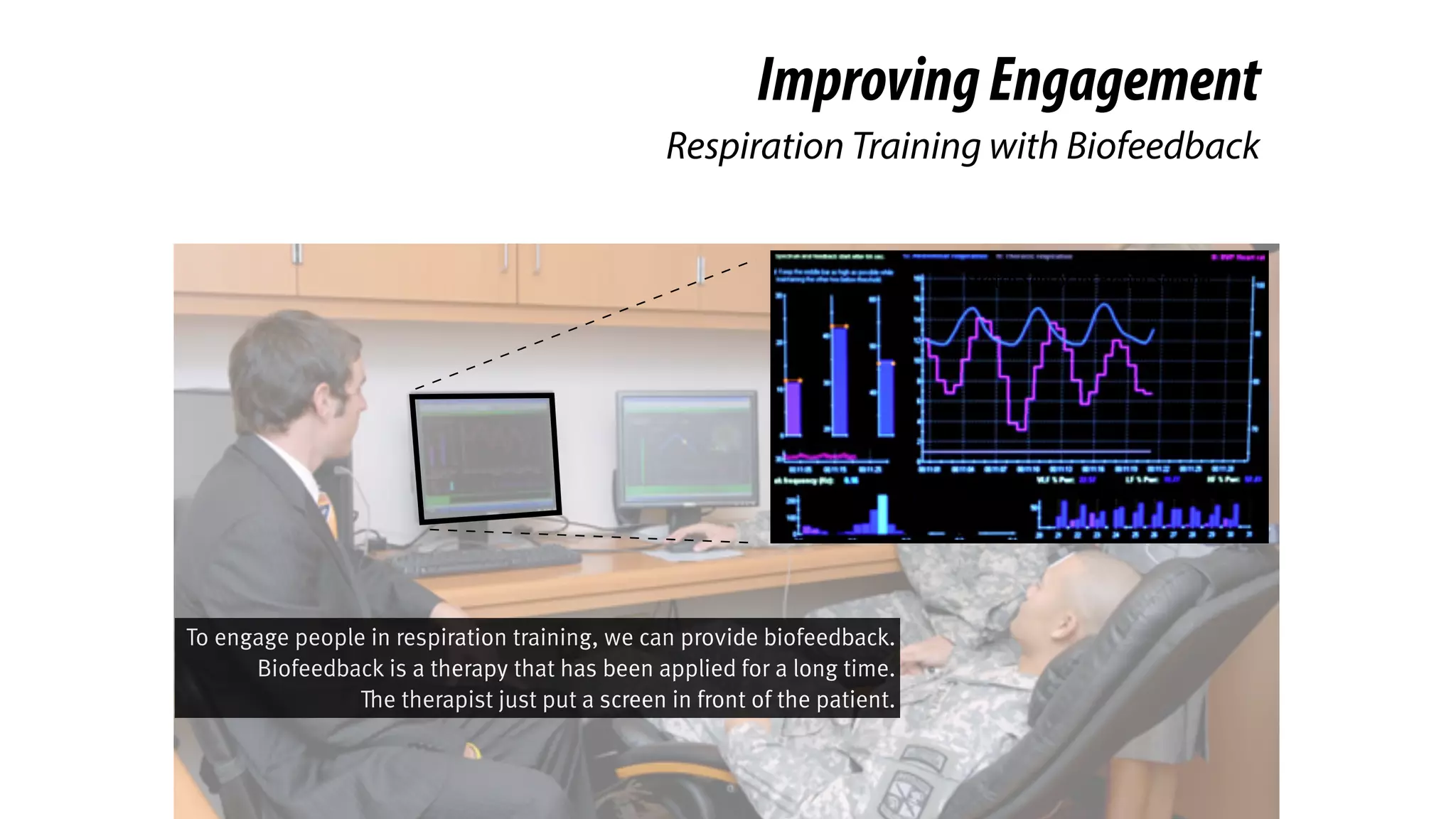
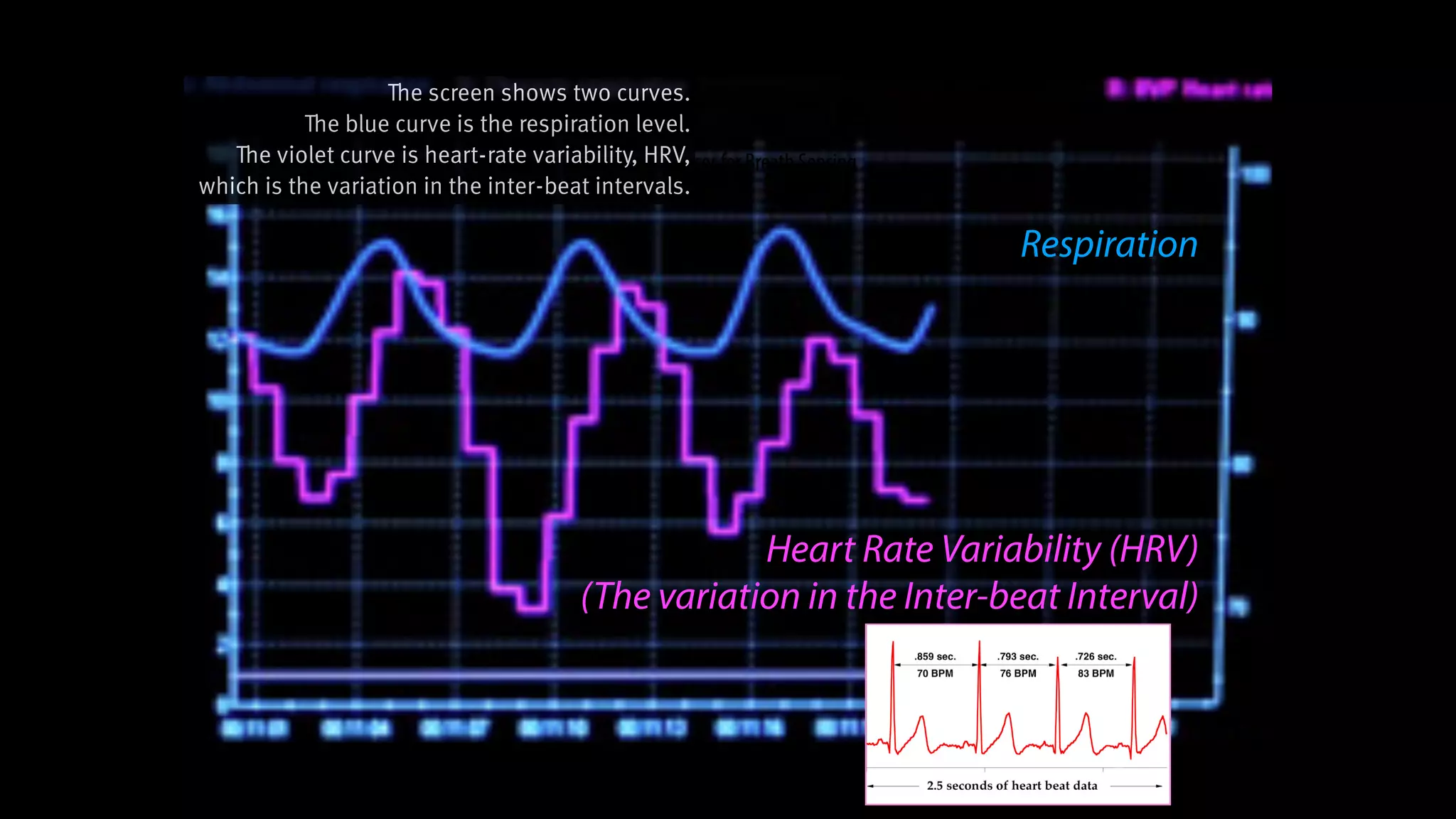
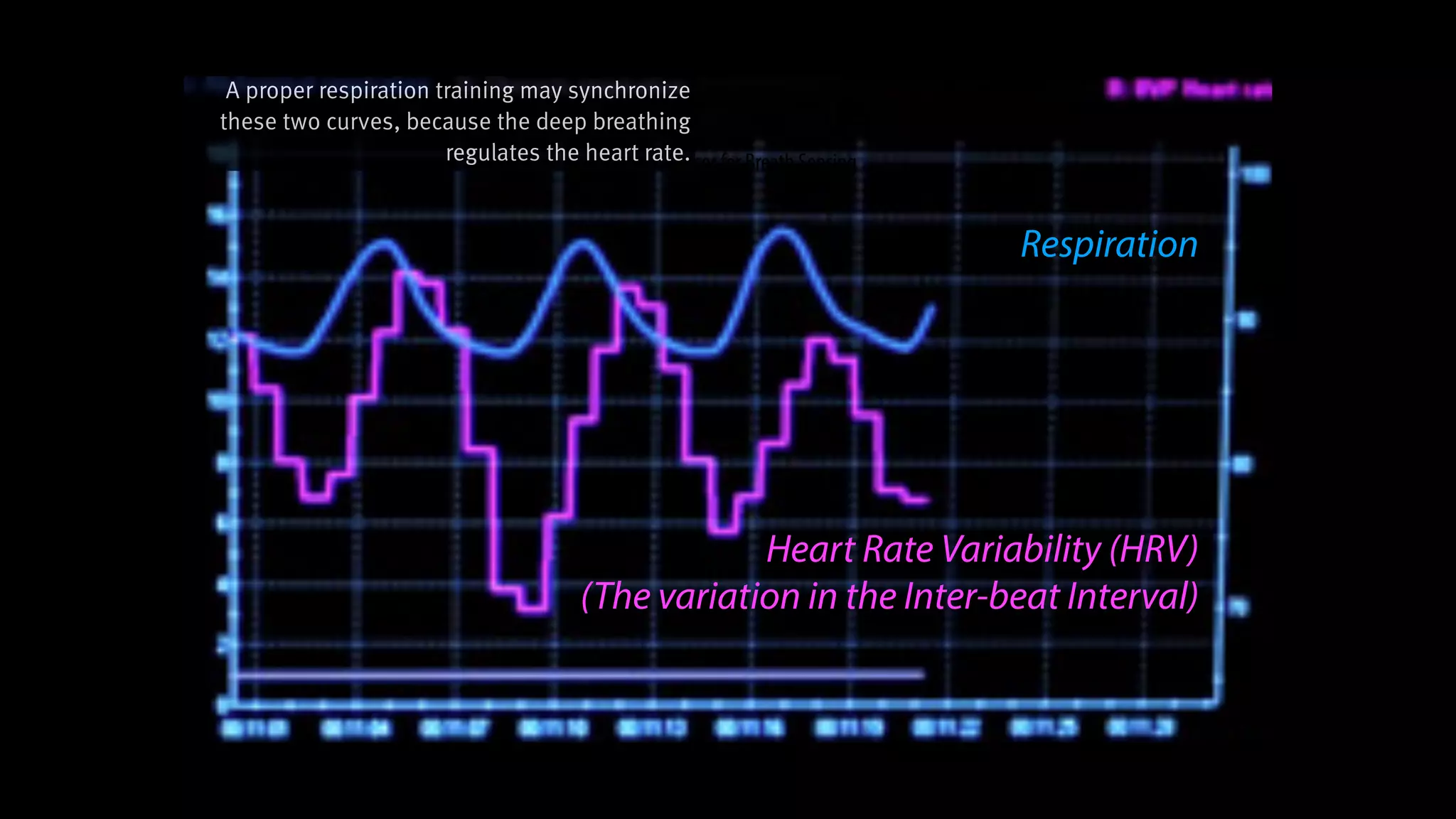
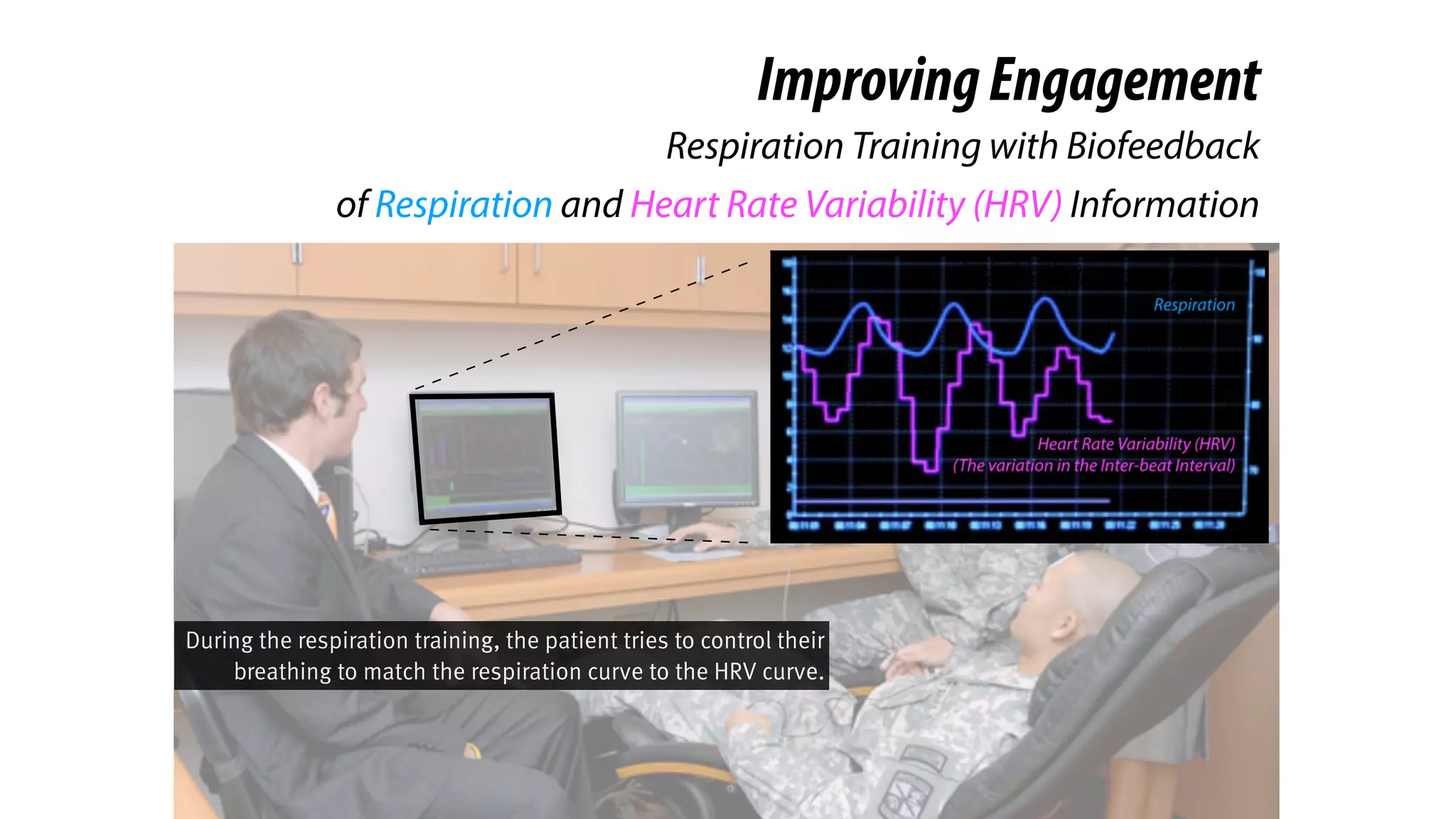
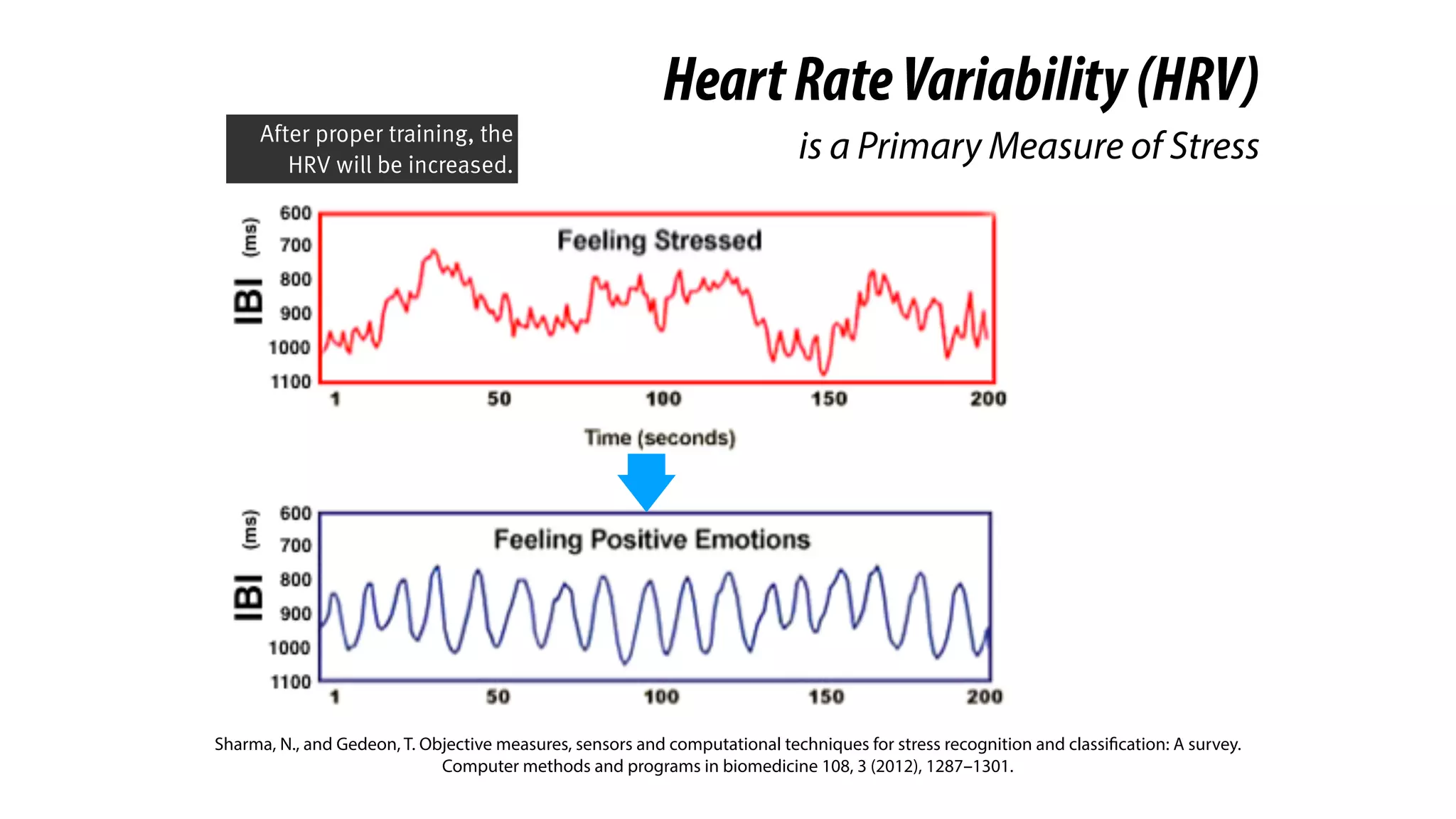
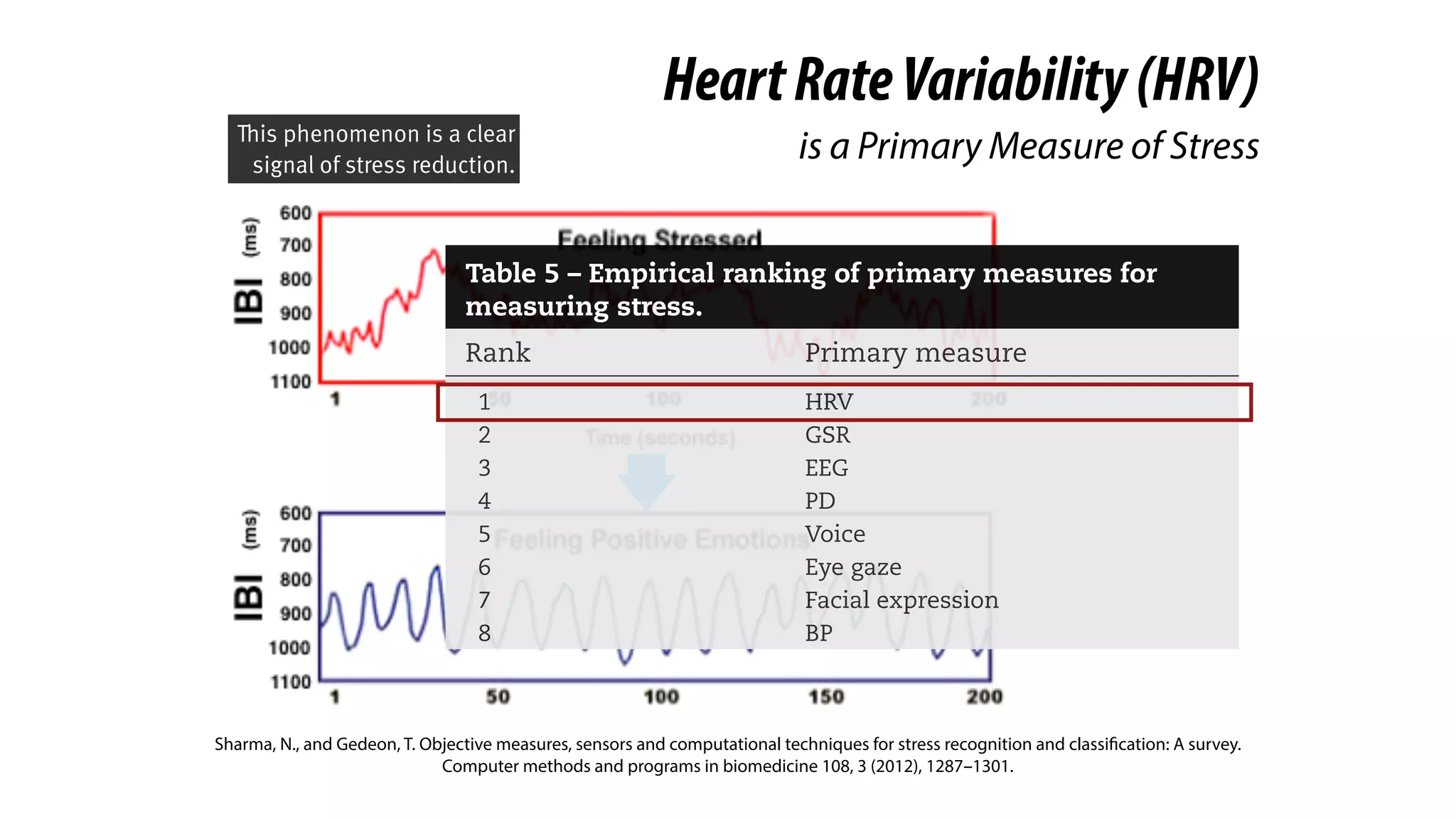
RespirationTraining
is Clinical-Proven in Stress Reduction,
Here we introduce a clinical-
proven method in stress
management.
And you probably knew it. It’s
respiration training.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chi2018biofidgetsswithscript-180429203948/75/CHI-18-Paper-BioFidget-Biofeedback-for-Respiration-Training-Using-an-Augmented-Fidget-Spinner-with-script-5-2048.jpg)
![HR via Music [Yokoyama 2002]SQUID [Farjadian et al. 2013]BreathTray [Moraveji et al. 2012]
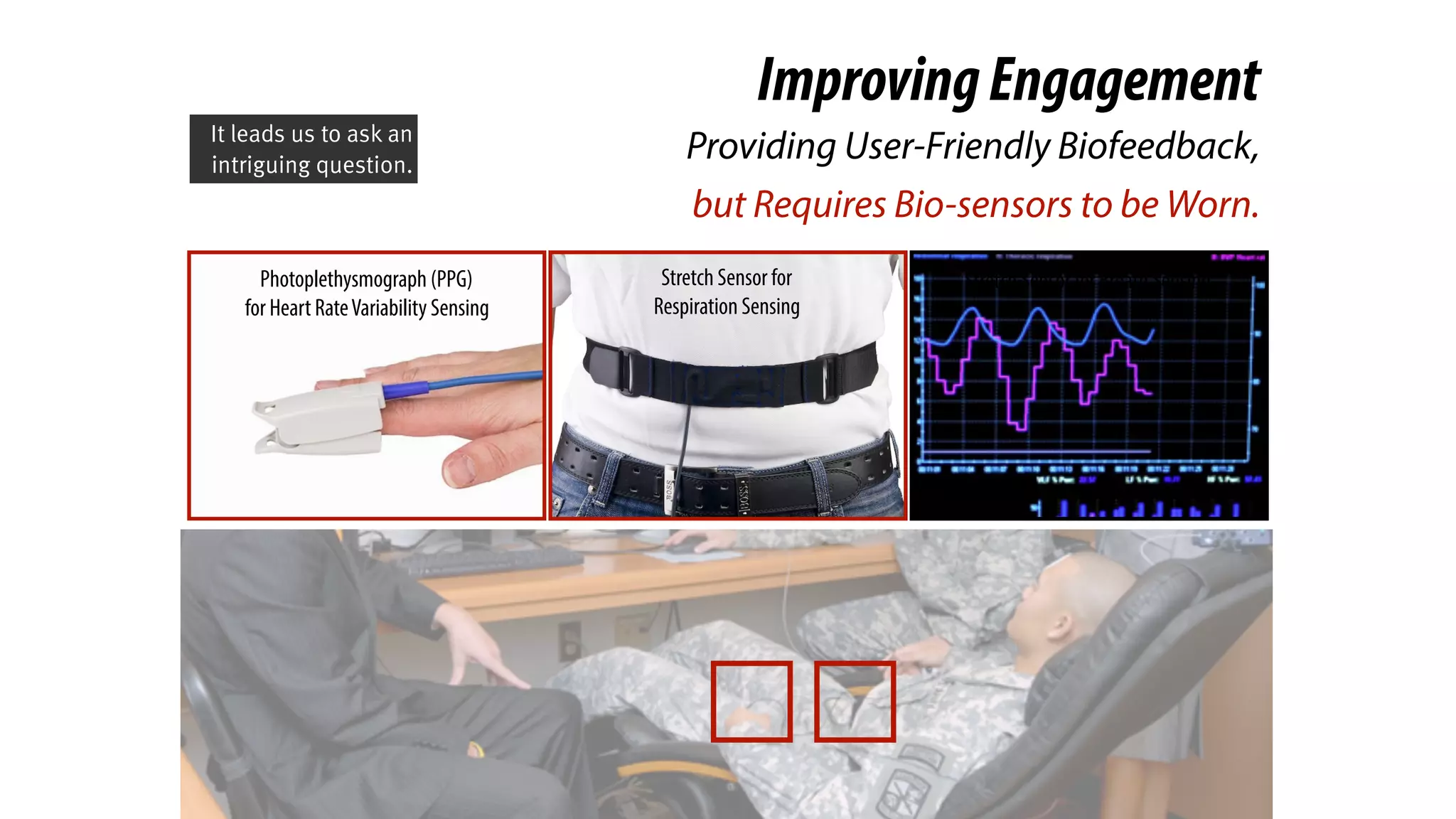
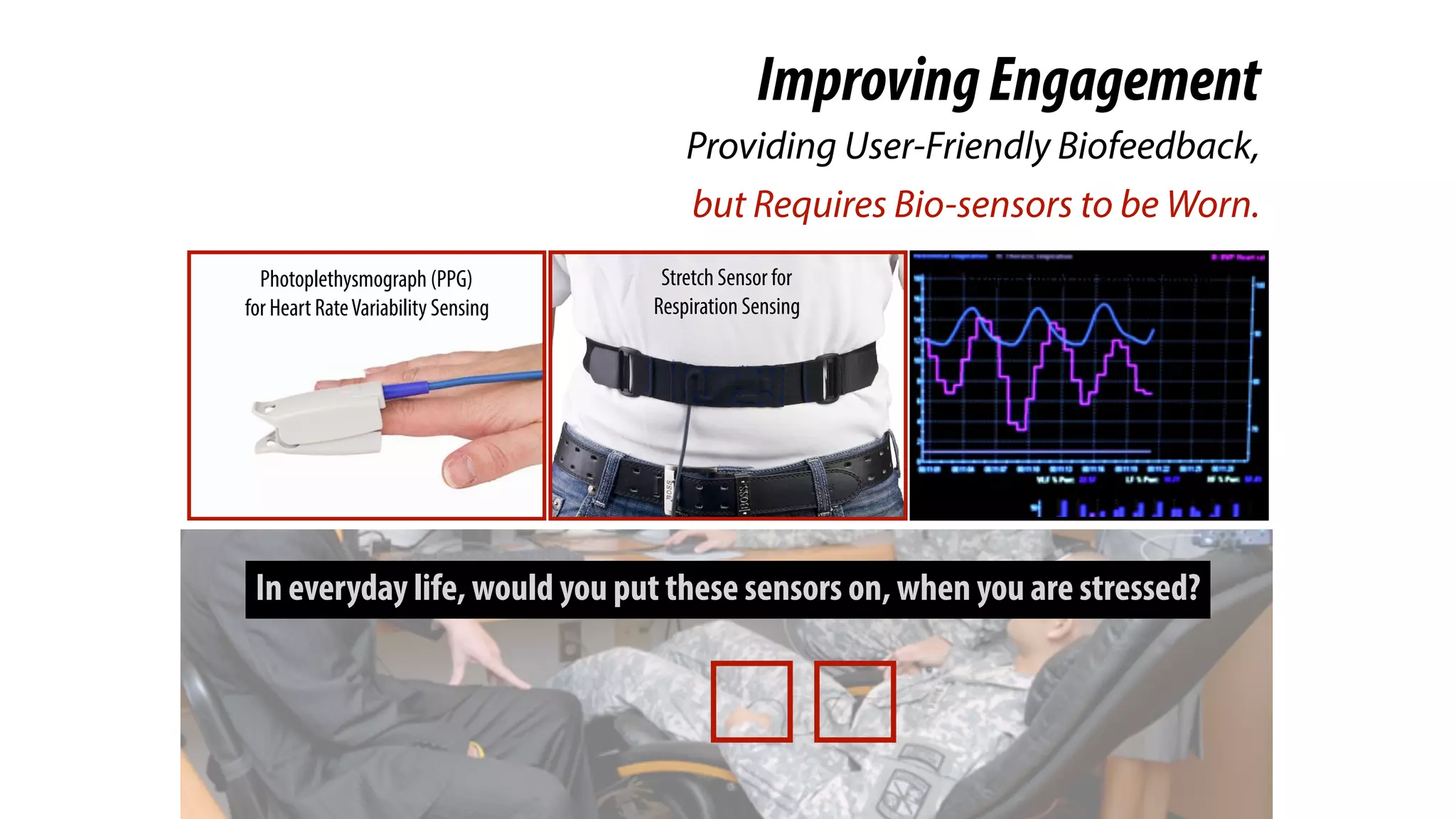
ImprovingEngagement
Providing User-Friendly Biofeedback,
Previous work tried to improve
the experiences by providing
user-friendly biofeedback in
visual, haptic, and audio
channels.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chi2018biofidgetsswithscript-180429203948/75/CHI-18-Paper-BioFidget-Biofeedback-for-Respiration-Training-Using-an-Augmented-Fidget-Spinner-with-script-14-2048.jpg)
![HR via Music [Yokoyama 2002]SQUID [Farjadian et al. 2013]
Living Surface [Yu et al. 2016]
BreathTray [Moraveji et al. 2012]
InnerGarden [Roo et al. 2017]
ImprovingEngagement
Providing User-Friendly Biofeedback,
Some further use shape
changing interfaces and virtual
reality to increase the
immersion.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chi2018biofidgetsswithscript-180429203948/75/CHI-18-Paper-BioFidget-Biofeedback-for-Respiration-Training-Using-an-Augmented-Fidget-Spinner-with-script-15-2048.jpg)
![SQUID [Farjadian et al. 2013]
Living Surface [Yu et al. 2016]
BreathTray [Moraveji et al. 2012]
InnerGarden [Roo et al. 2017]
ImprovingEngagement
Providing User-Friendly Biofeedback,
but Requires Bio-sensors to be Worn.
HR via Music [Yokoyama 2002]
However, these systems all
require the users to wear both
heart rate and respiration sensors,
before they start the training.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chi2018biofidgetsswithscript-180429203948/75/CHI-18-Paper-BioFidget-Biofeedback-for-Respiration-Training-Using-an-Augmented-Fidget-Spinner-with-script-16-2048.jpg)


![do not sense the user’s physiological data
[Wensveen et al. 2012] Mind Sphere, PhilipsFidgetWidget [Karlesky et al. 2014] Relax! Pen [Bruns 2010]
FidgetDevicesforSelf-Regulation
Same as fidget spinners, previous work uses tangible
user interfaces as fidgets to help the users in doing
self-regulation. They also did not provide
biofeedback based on stress-related biosignal.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chi2018biofidgetsswithscript-180429203948/75/CHI-18-Paper-BioFidget-Biofeedback-for-Respiration-Training-Using-an-Augmented-Fidget-Spinner-with-script-21-2048.jpg)
![FidgetDevicesforSelf-Regulation
[Wensveen et al. 2012] Mind Sphere, PhilipsFidgetWidget [Karlesky et al. 2014] Relax! Pen [Bruns 2010]
HandheldDevicesforBio-Sensing
do not support rich, engaging interaction
StressEraserHandheld Spirometer Finger-based ECG
do not sense the user’s physiological data
Some handheld physiological sensors, we call it
biosensors in short, do not require users to wear,
but they try to avoid user interactions that may
affect their technical validity of bio-sensing.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chi2018biofidgetsswithscript-180429203948/75/CHI-18-Paper-BioFidget-Biofeedback-for-Respiration-Training-Using-an-Augmented-Fidget-Spinner-with-script-22-2048.jpg)
![FidgetDevicesforSelf-Regulation
[Wensveen et al. 2012] Mind Sphere, PhilipsFidgetWidget [Karlesky et al. 2014] Relax! Pen [Bruns 2010]
HandheldDevicesforBio-Sensing
do not support rich, engaging interaction
StressEraserHandheld Spirometer Finger-based ECG
do not sense the user’s physiological data
We see a gap between
these two research
domains, and that's what
we are gonna bridge.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chi2018biofidgetsswithscript-180429203948/75/CHI-18-Paper-BioFidget-Biofeedback-for-Respiration-Training-Using-an-Augmented-Fidget-Spinner-with-script-23-2048.jpg)