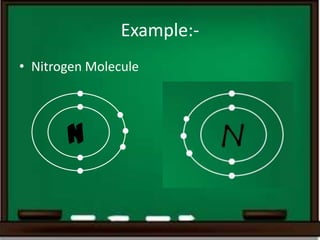
Triple covalent bonding occurs when three electron pairs are shared between two atoms, forming a stronger and shorter bond than single or double bonds. An example is the nitrogen molecule where each nitrogen atom shares three electron pairs with the other nitrogen atom. Other examples containing triple bonds include cyanides, isocyanides, dinitrogen, and carbon monoxide.