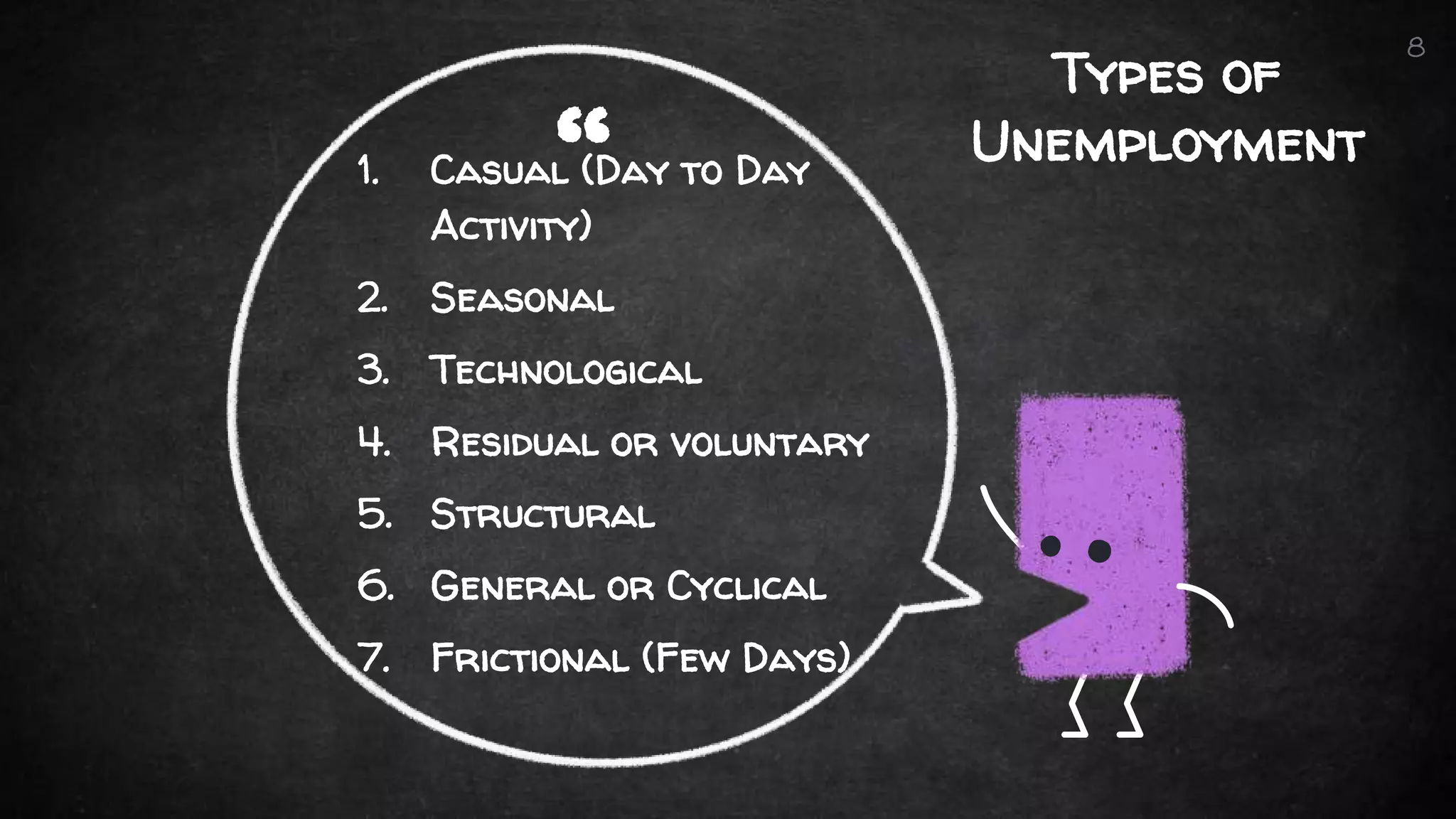
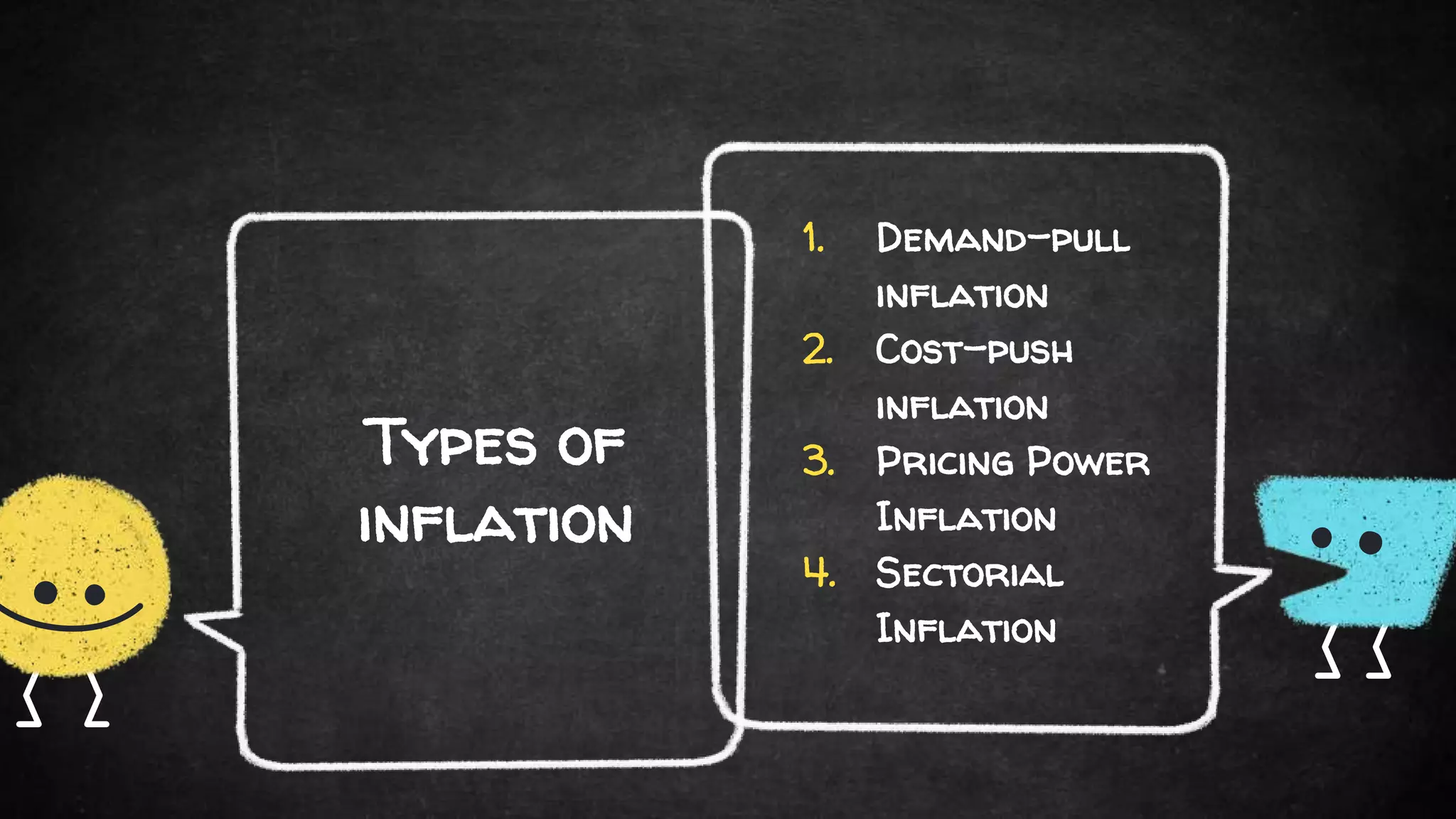
The document discusses the basic economic problem, which highlights the imbalance between unlimited human wants and limited resources, leading to key issues such as poverty, unemployment, and inflation. It categorizes poverty and its causes, outlines types and causes of unemployment, and defines inflation along with its types and remedies. Additionally, it presents measures to alleviate these economic issues.