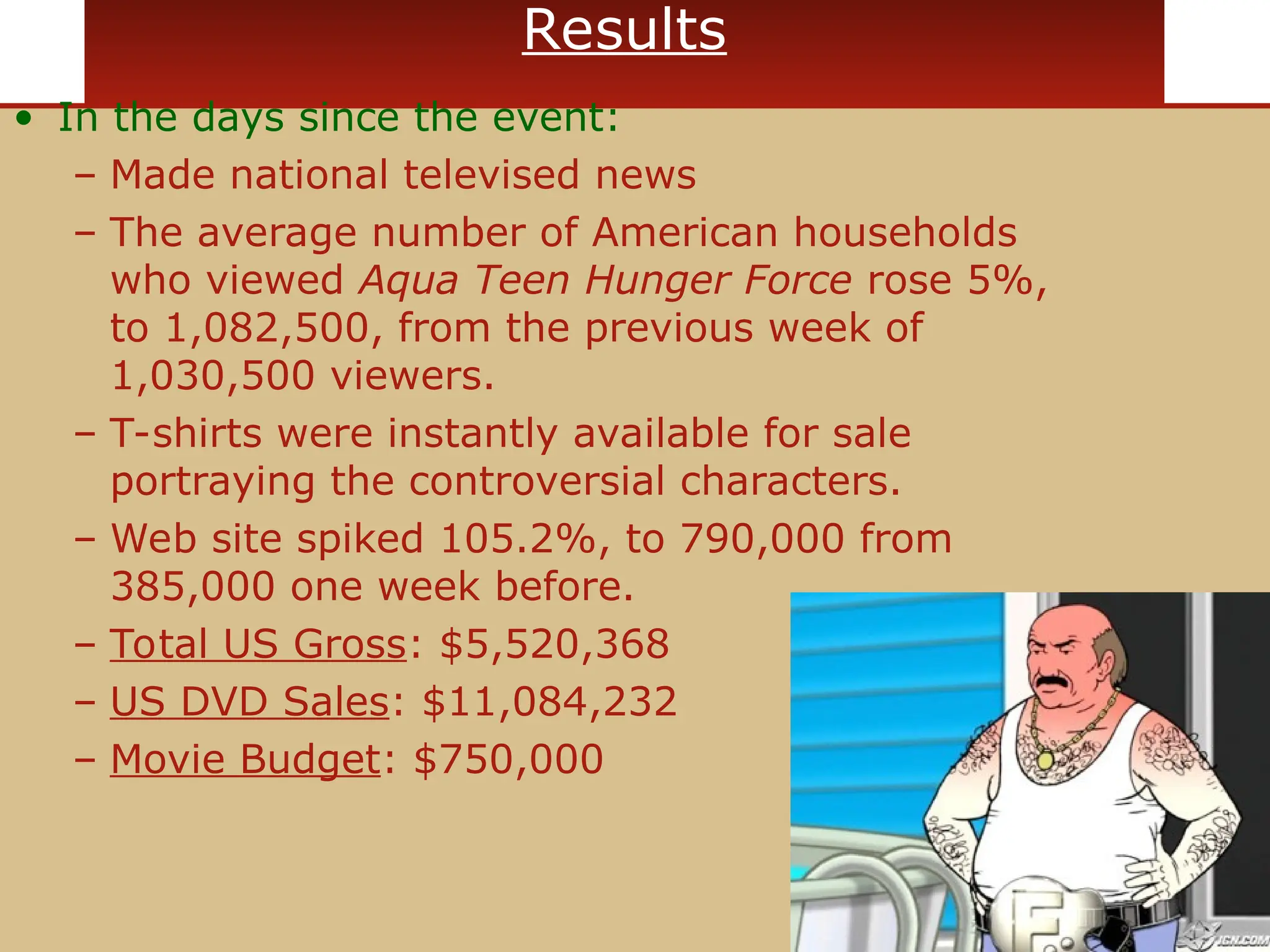
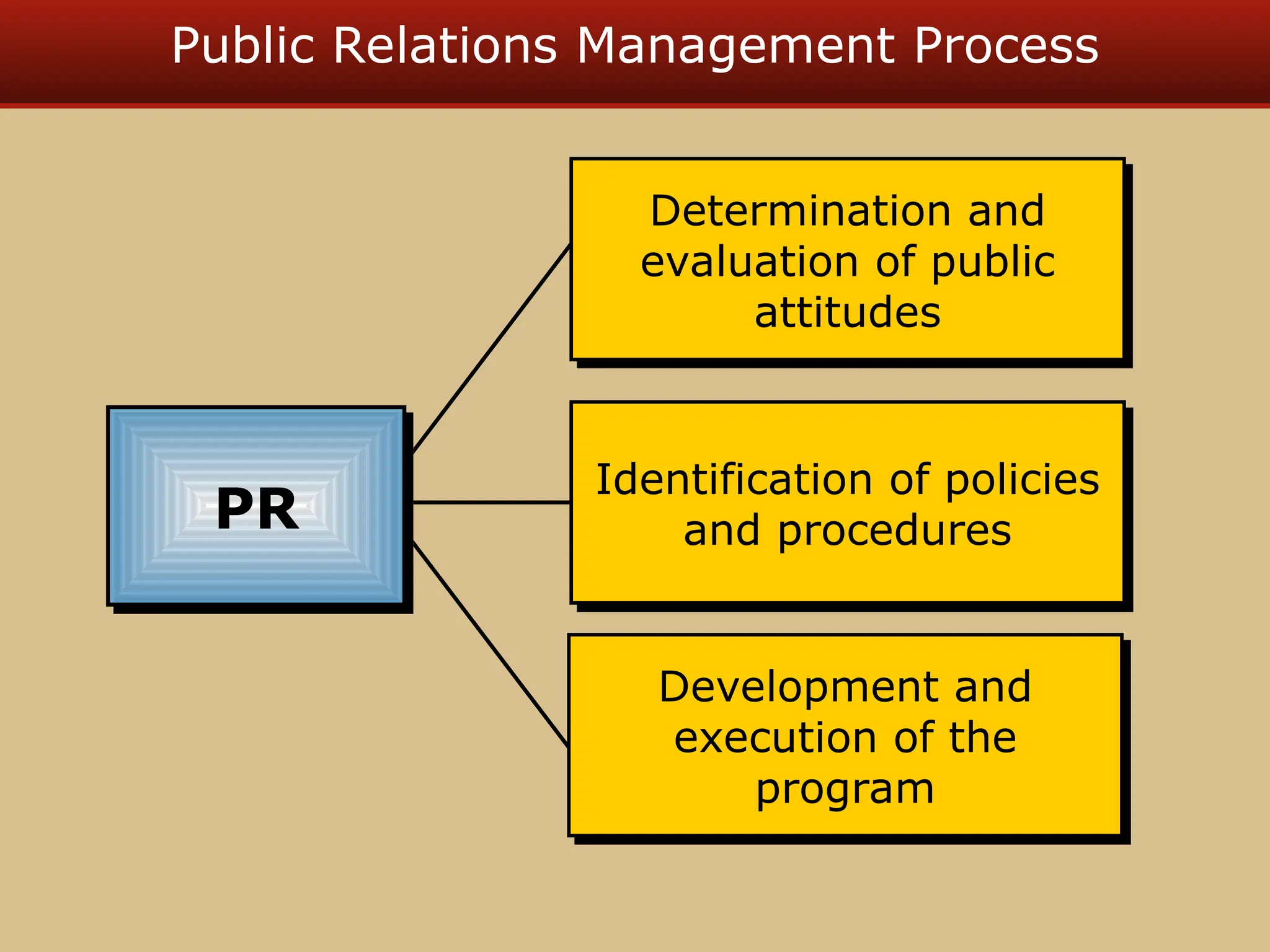
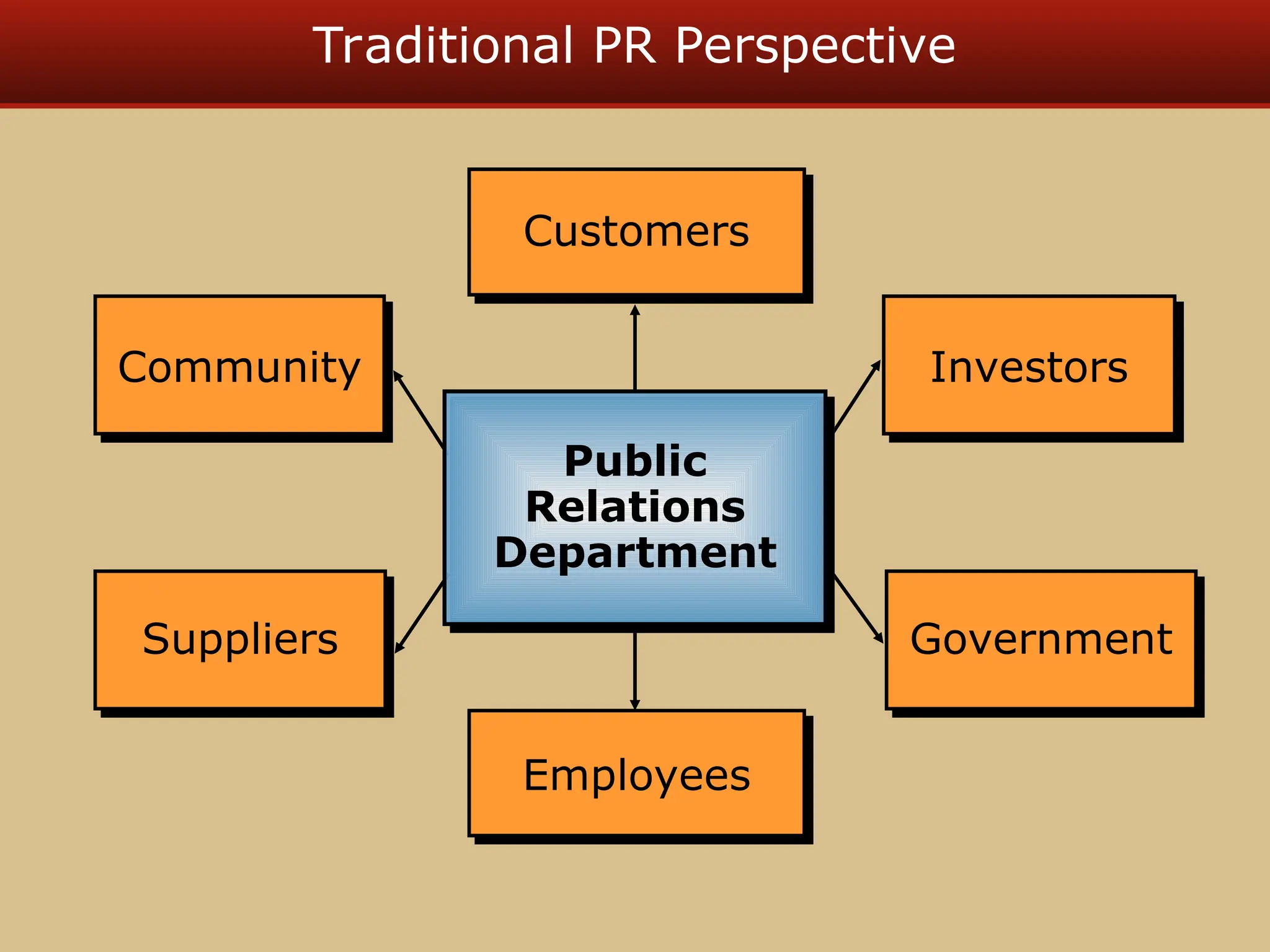
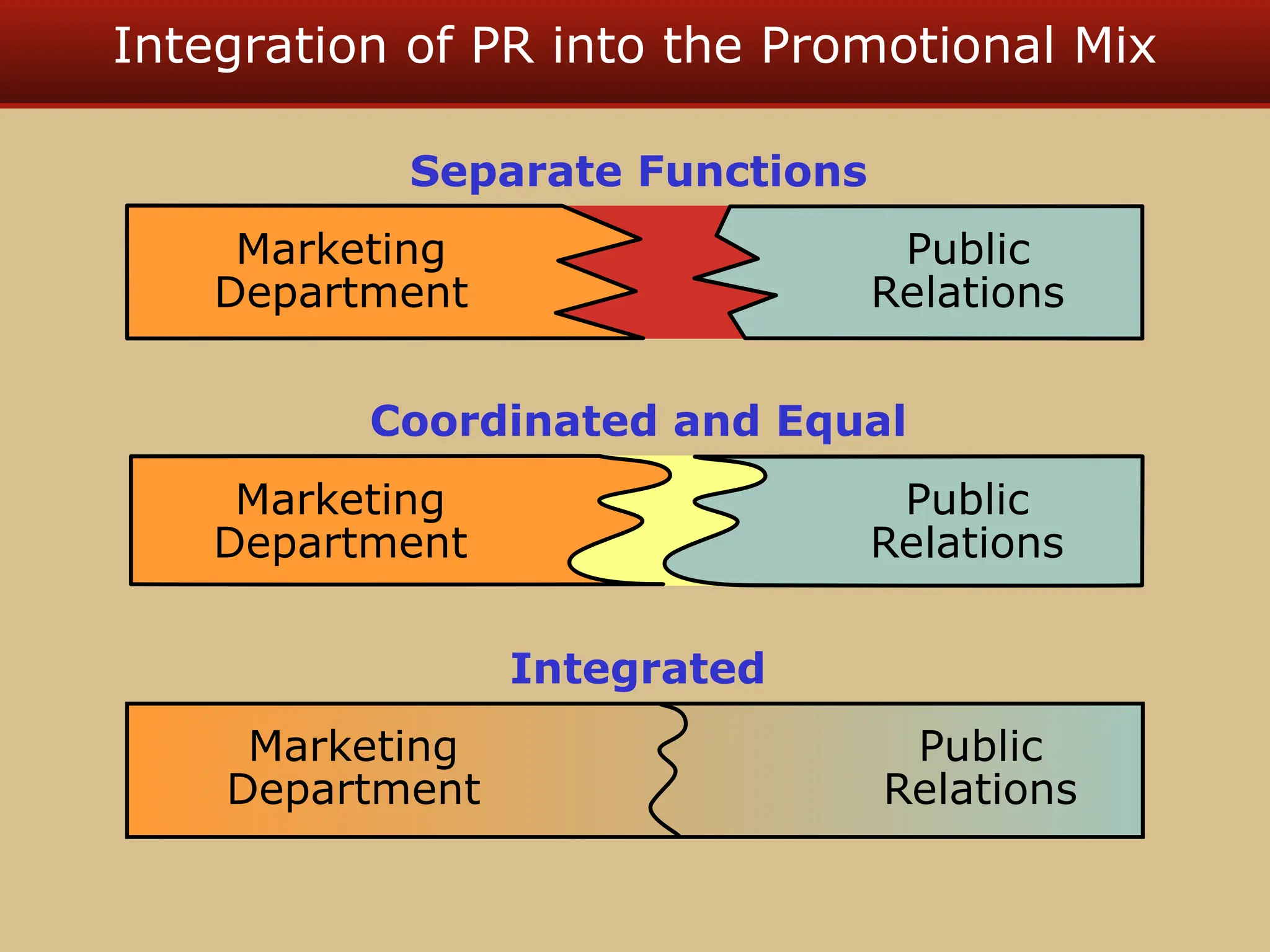
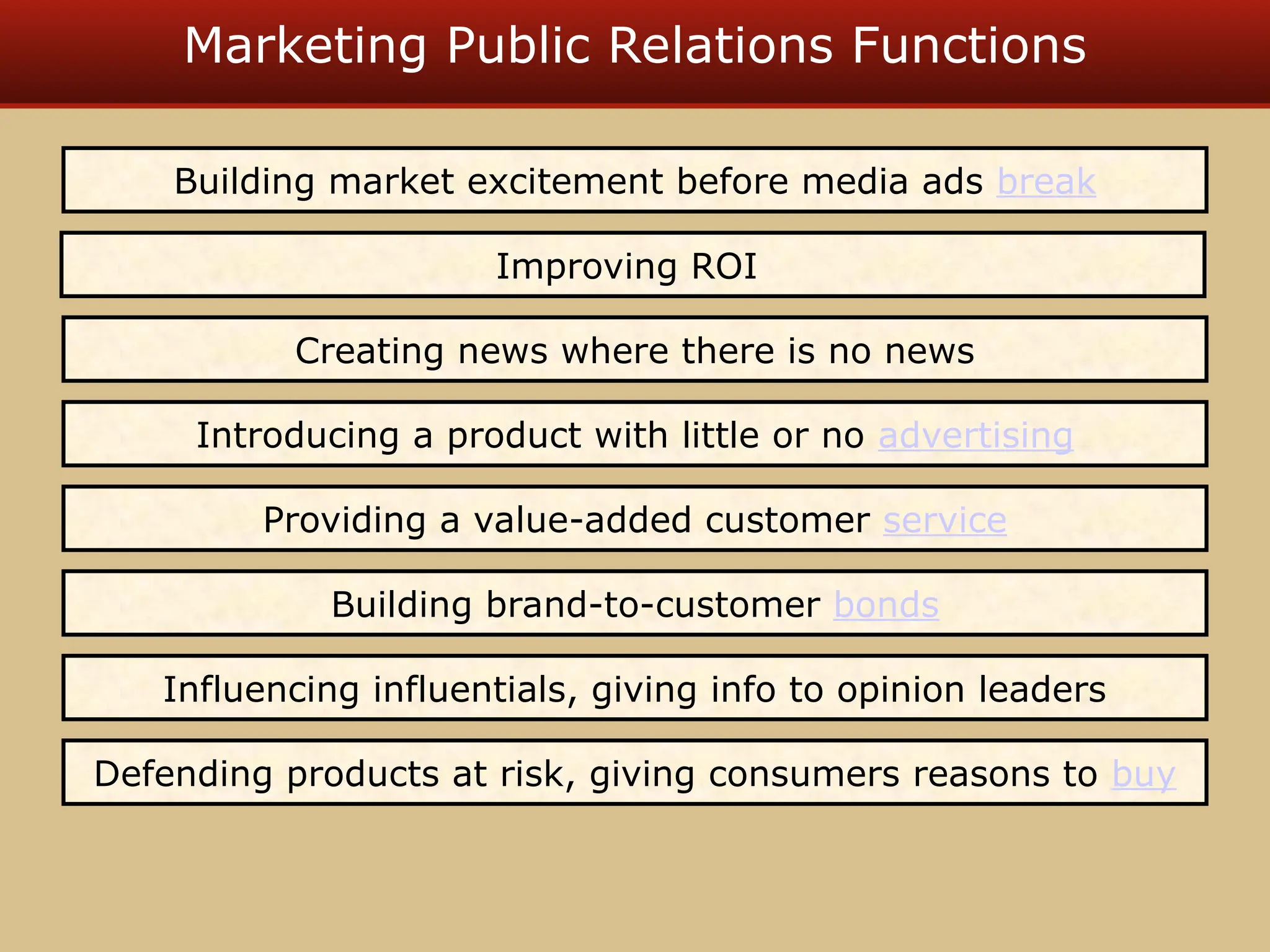
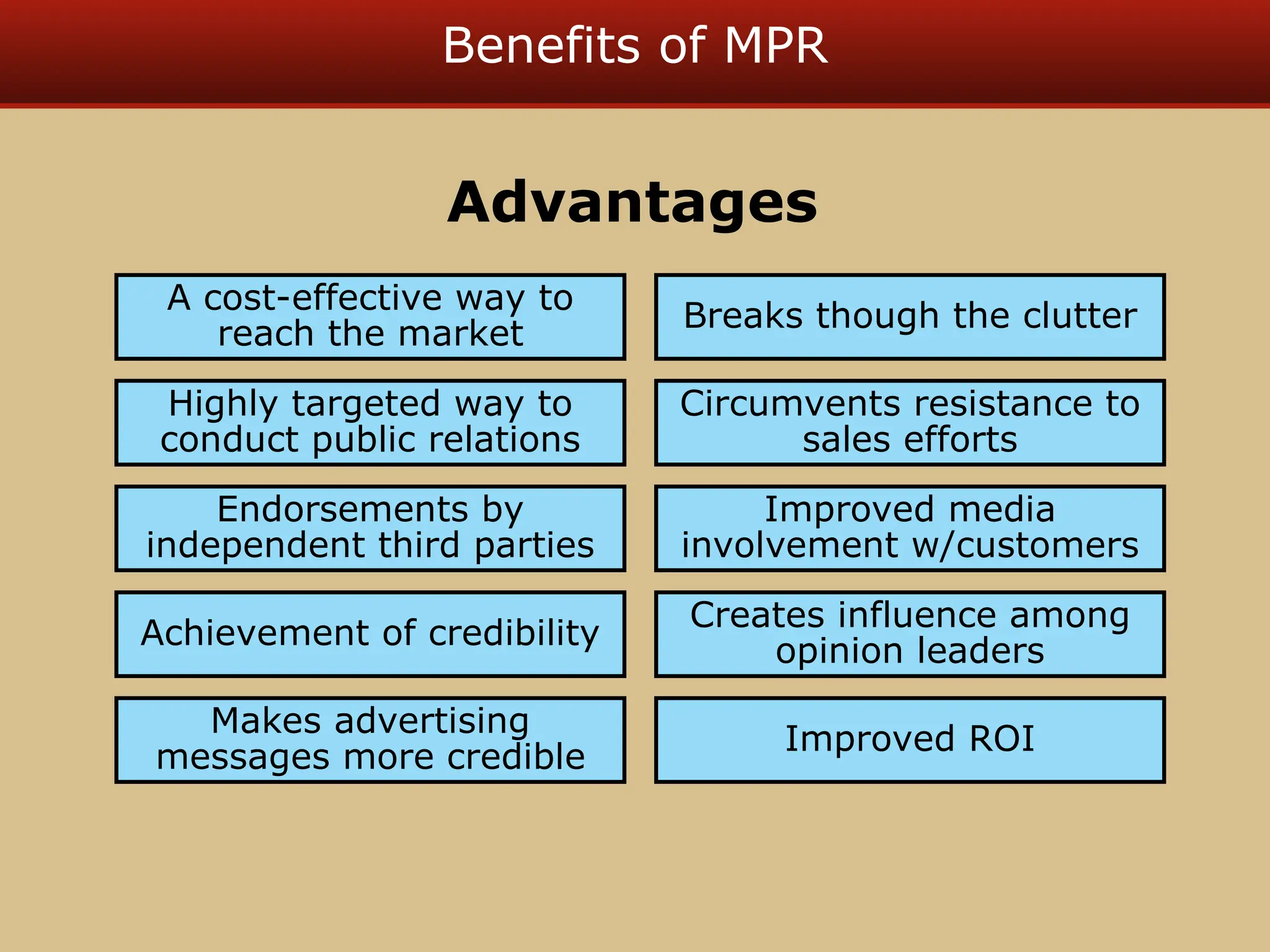
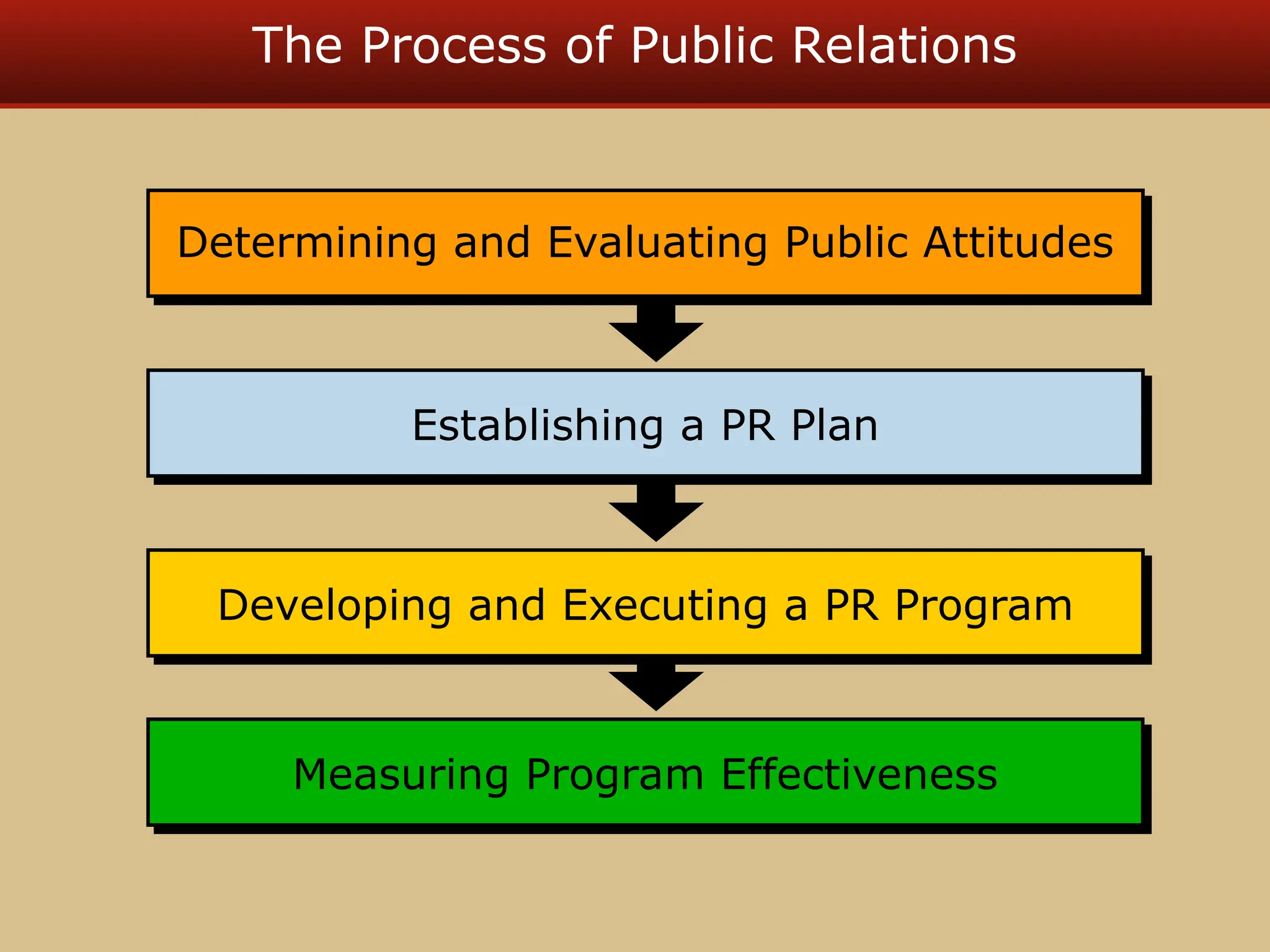
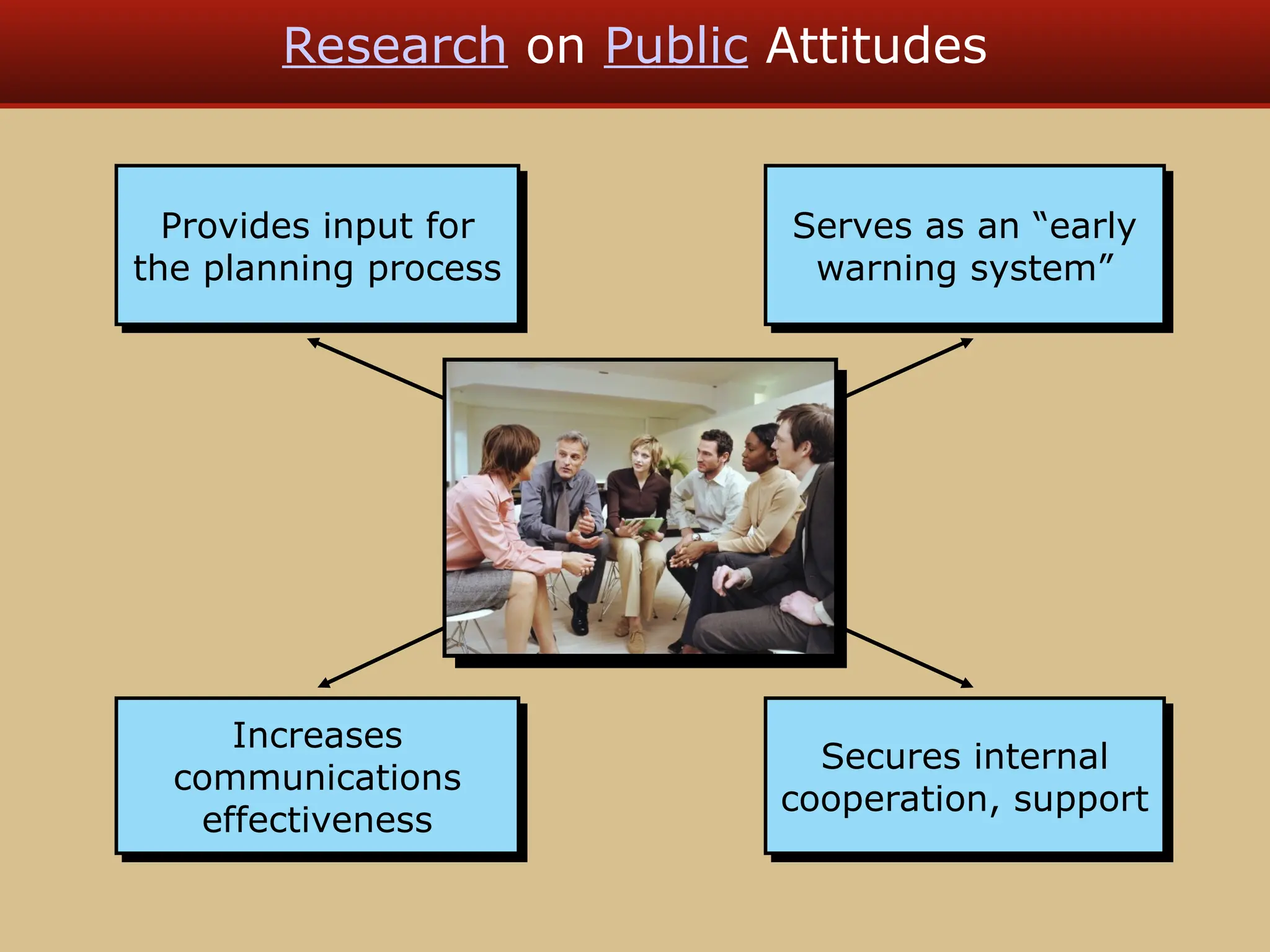
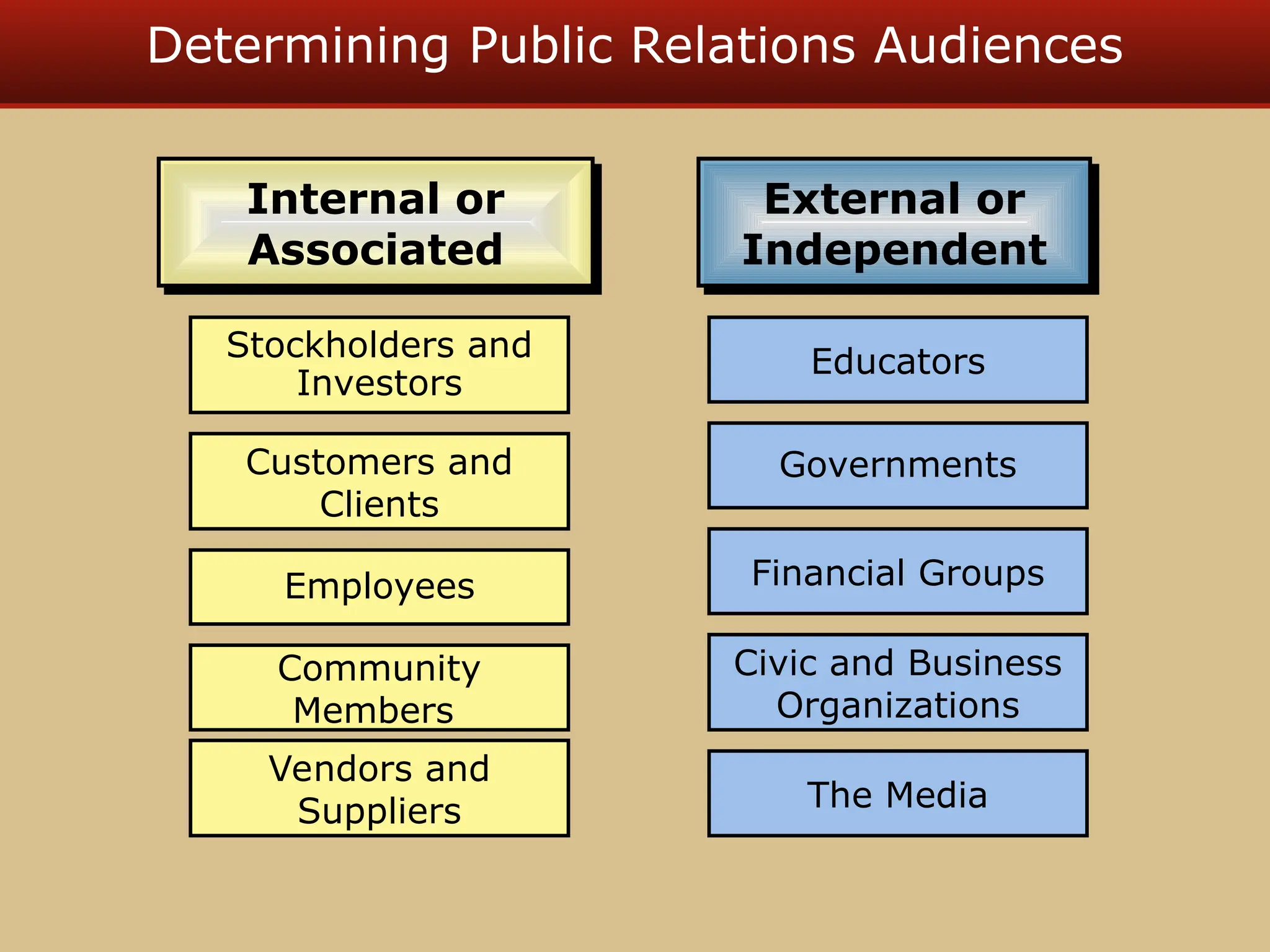
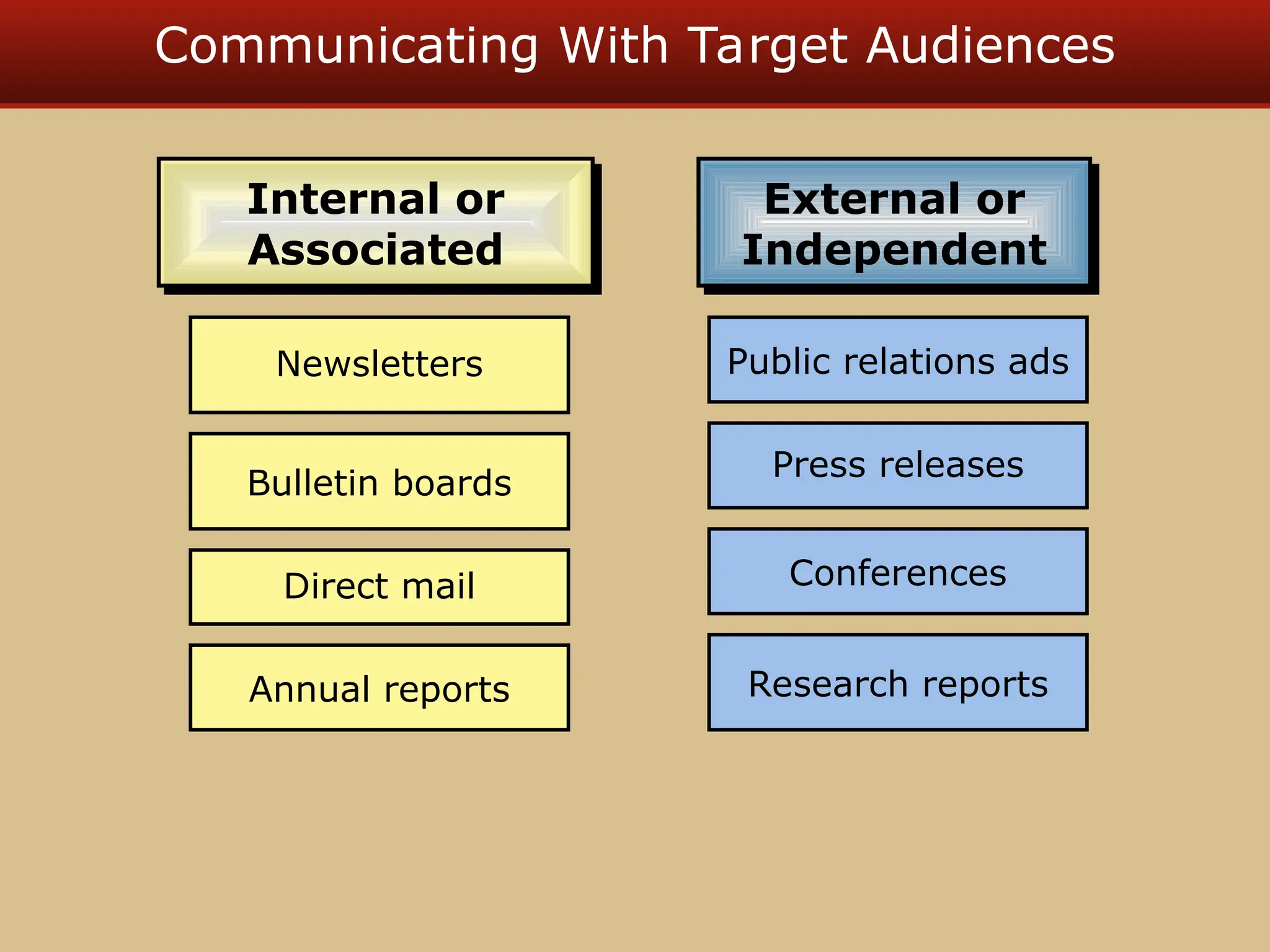
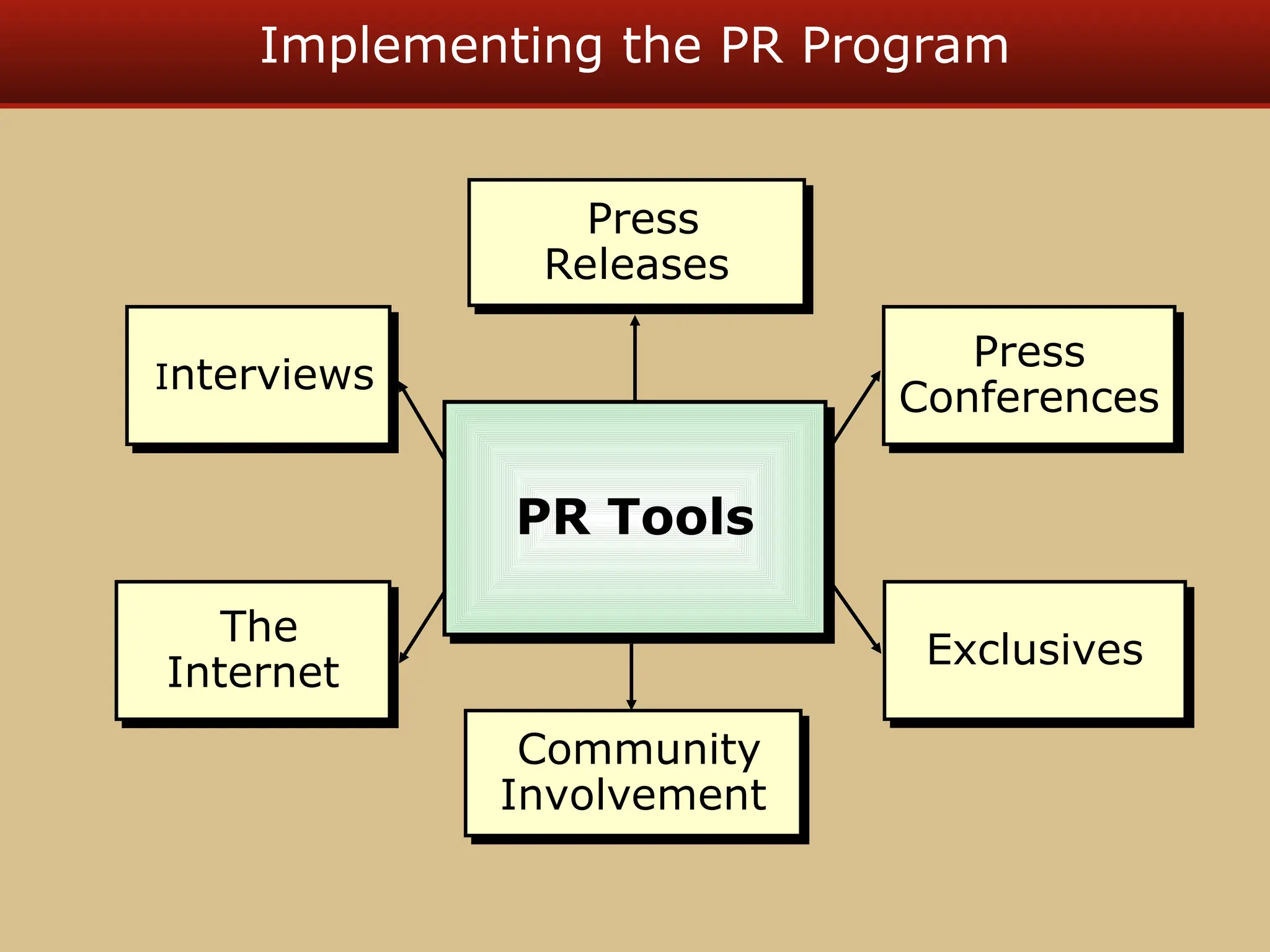
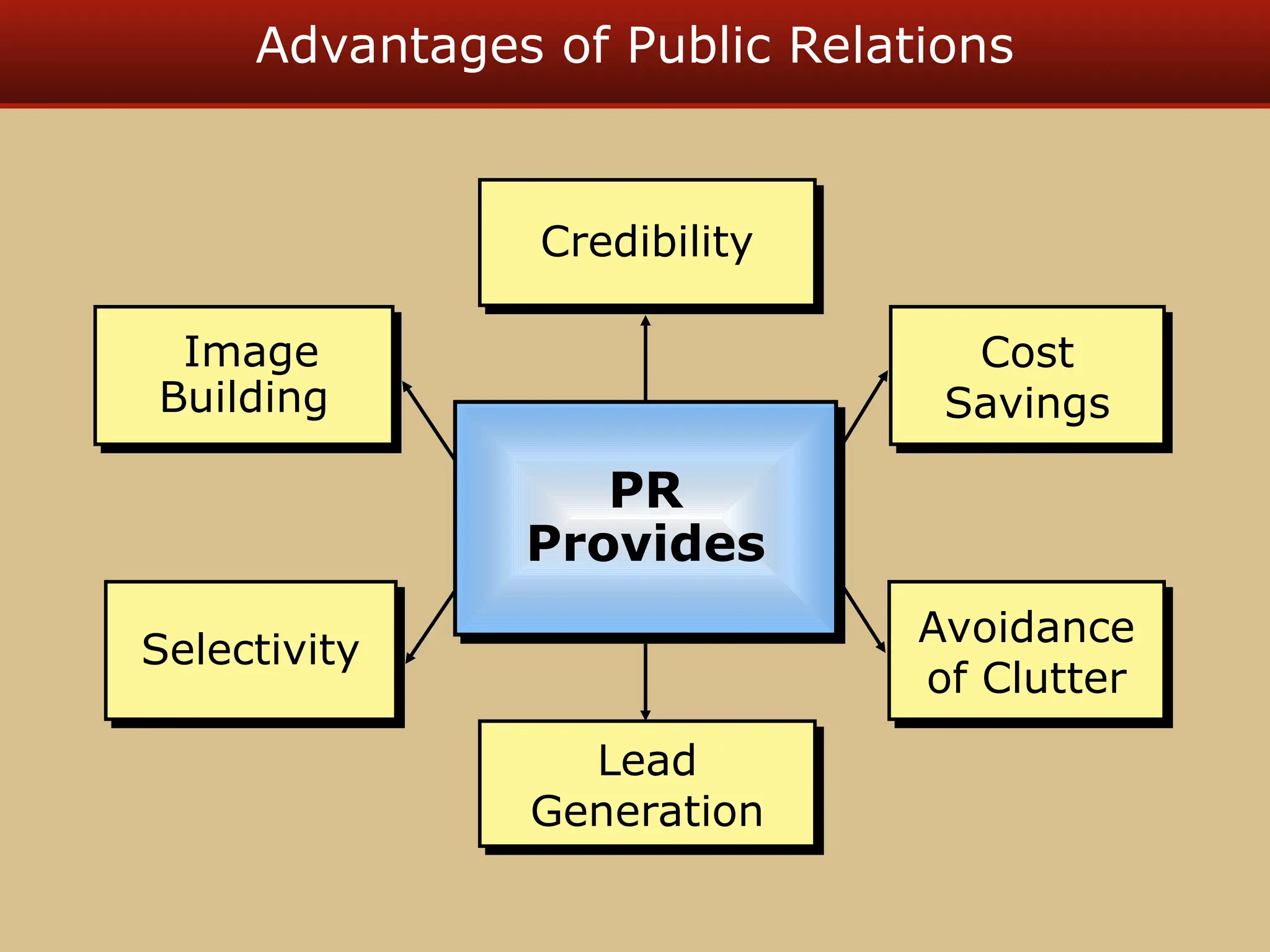
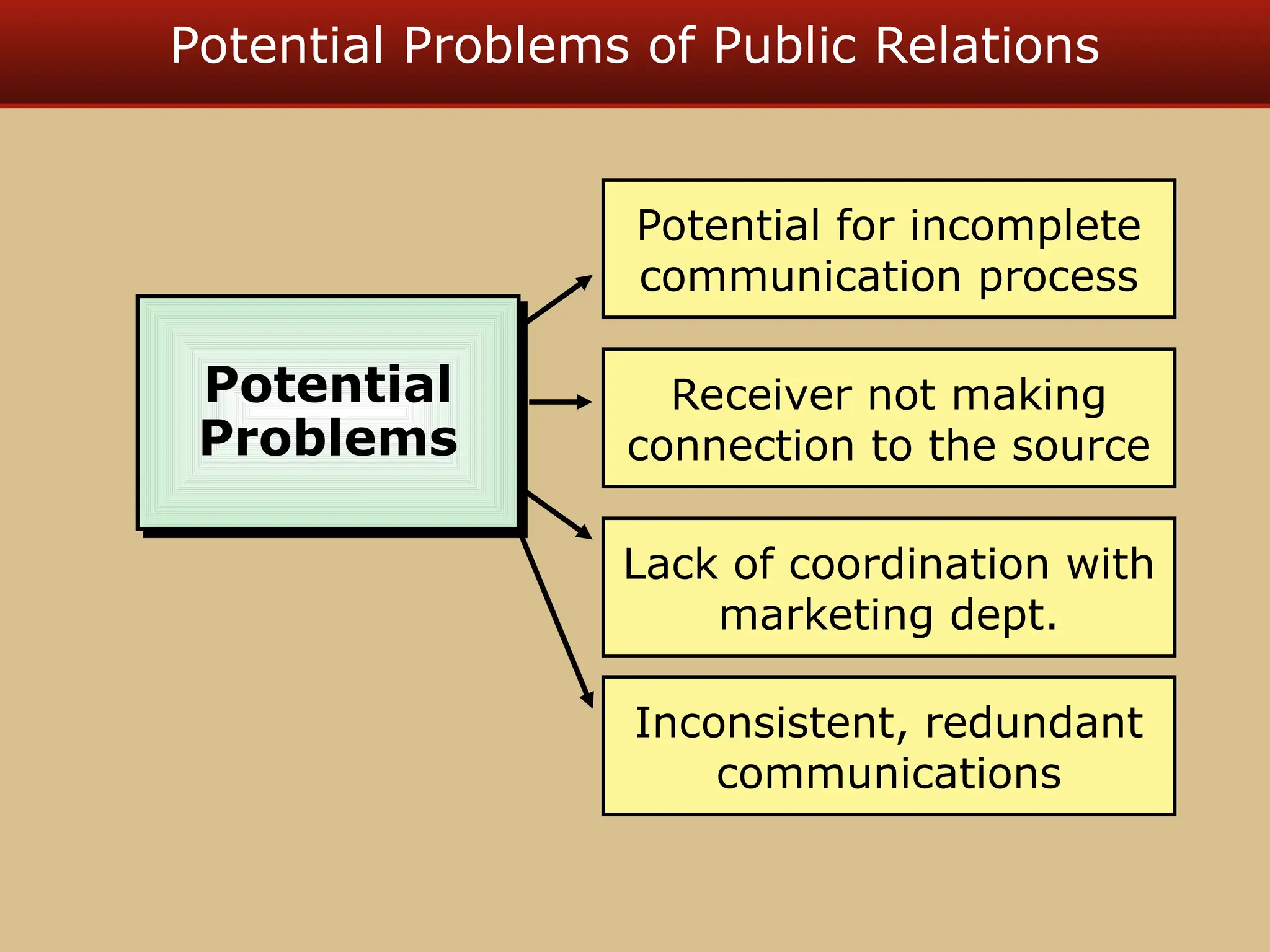
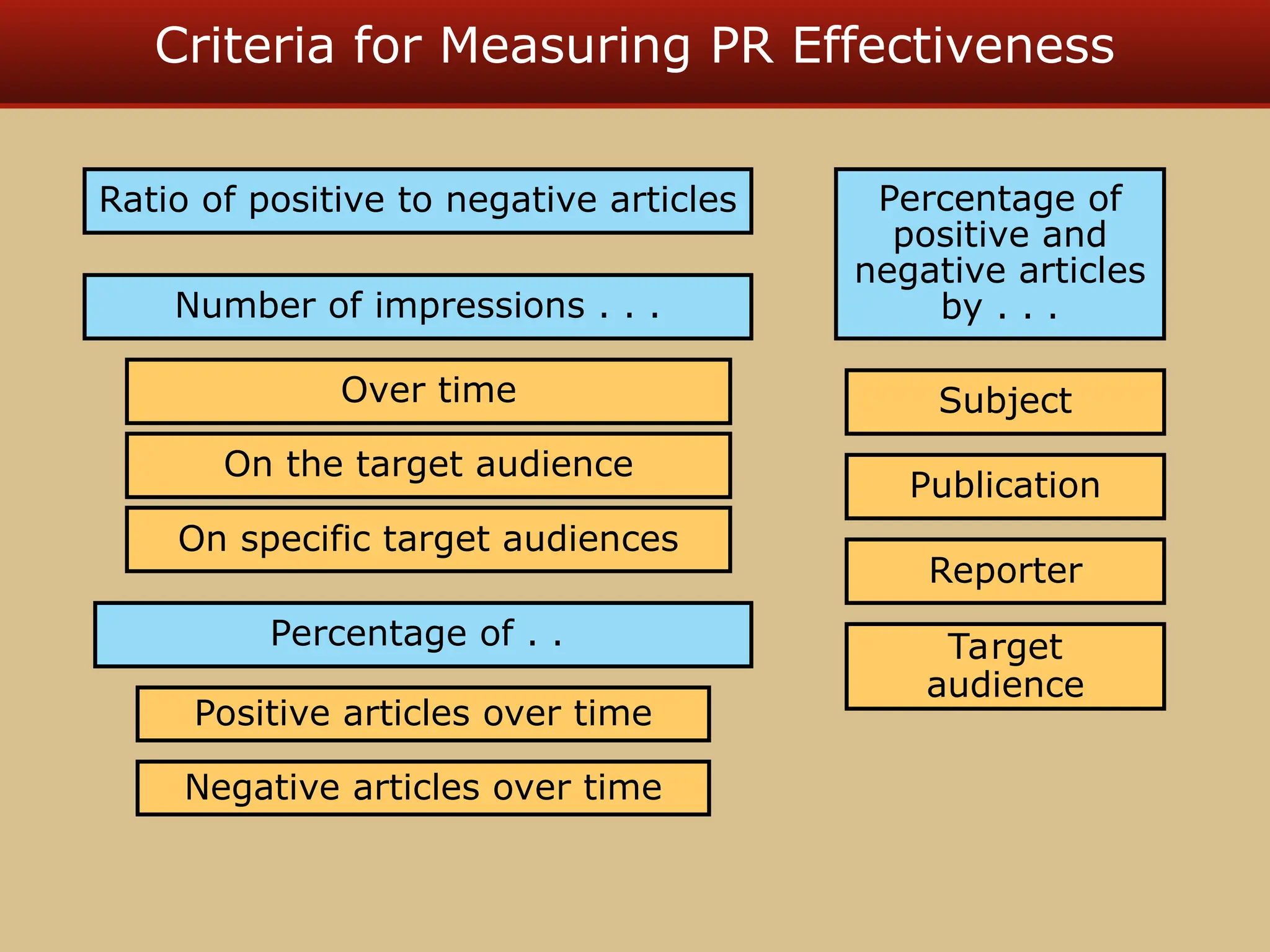
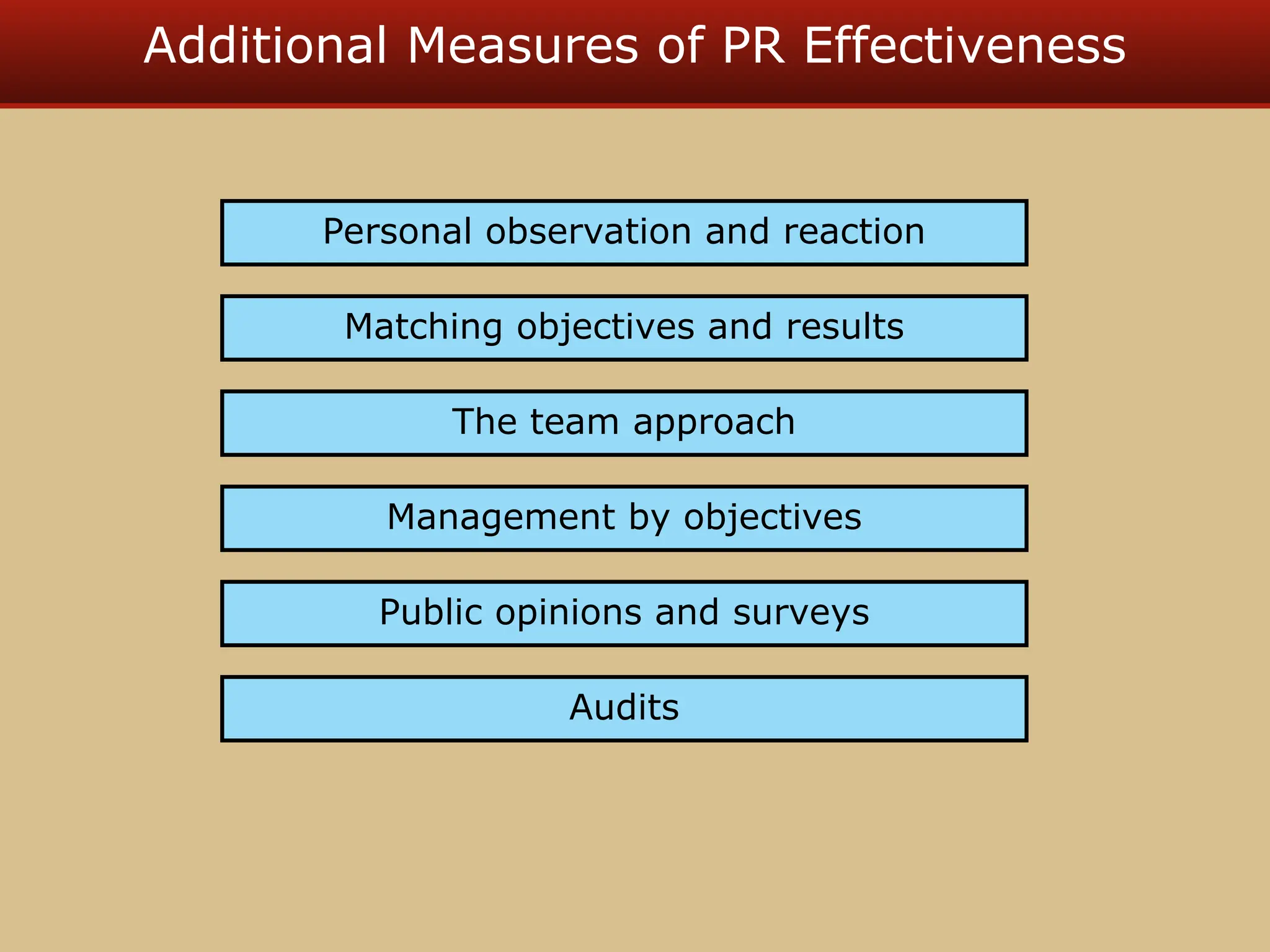
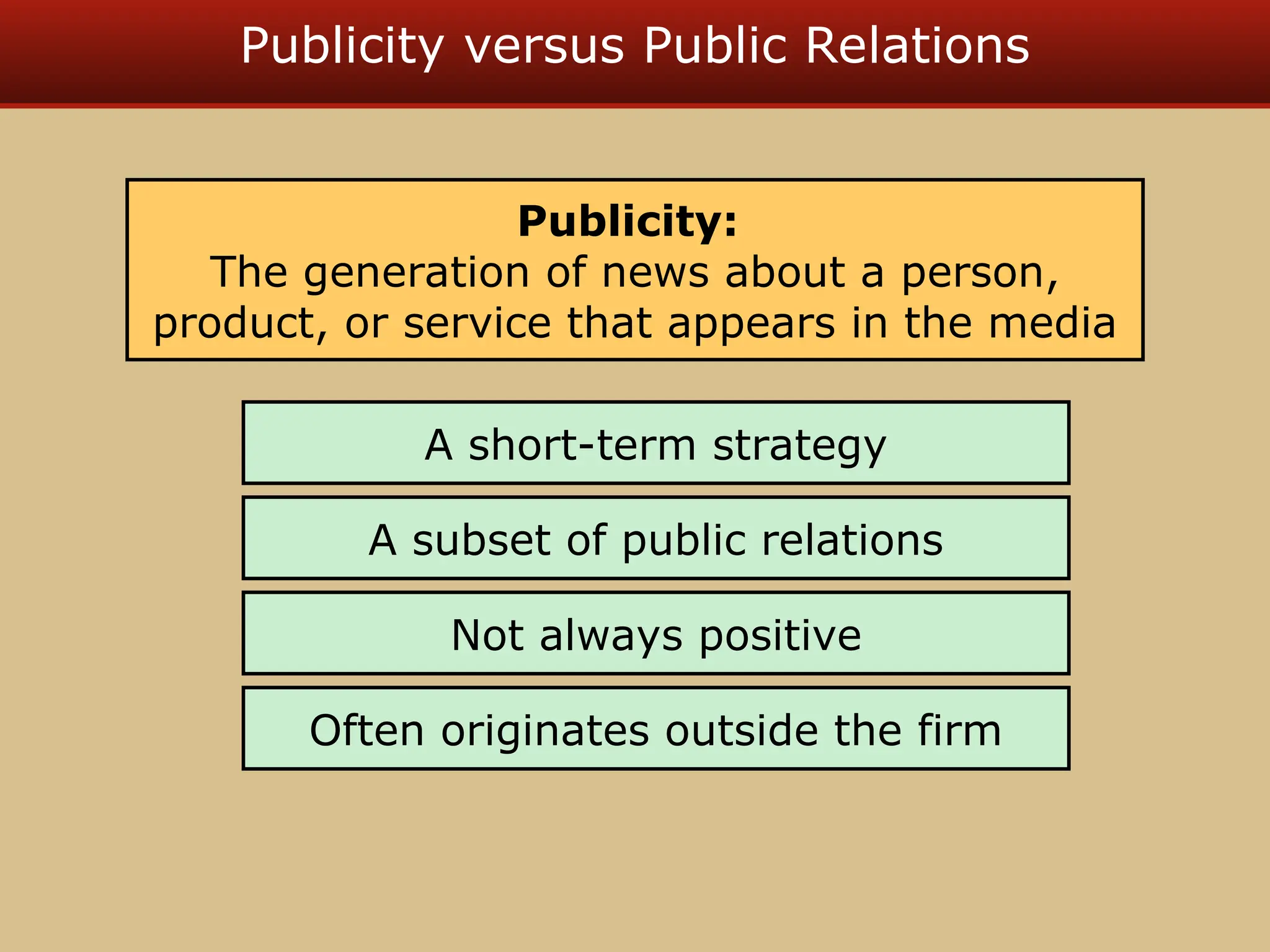
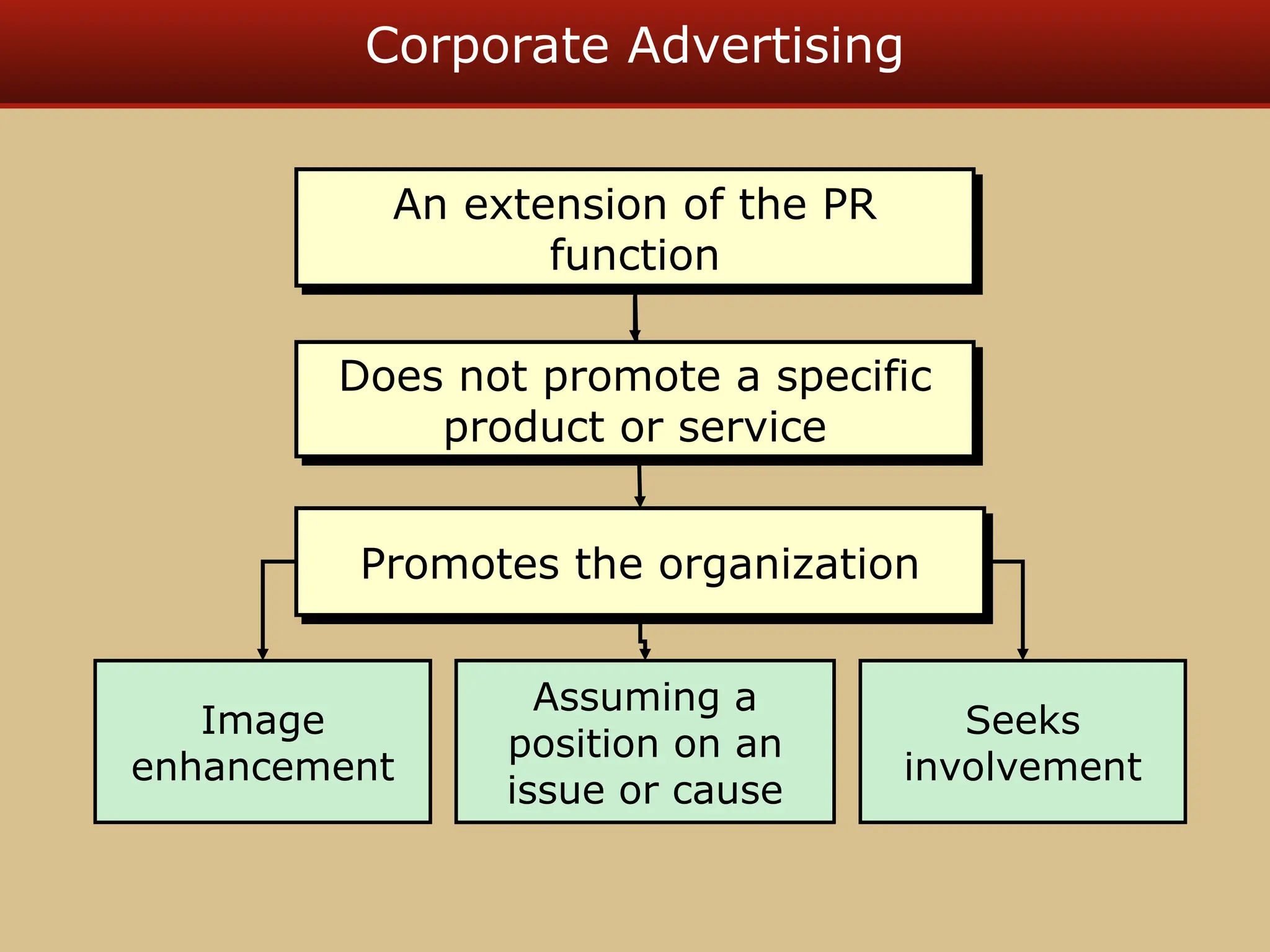
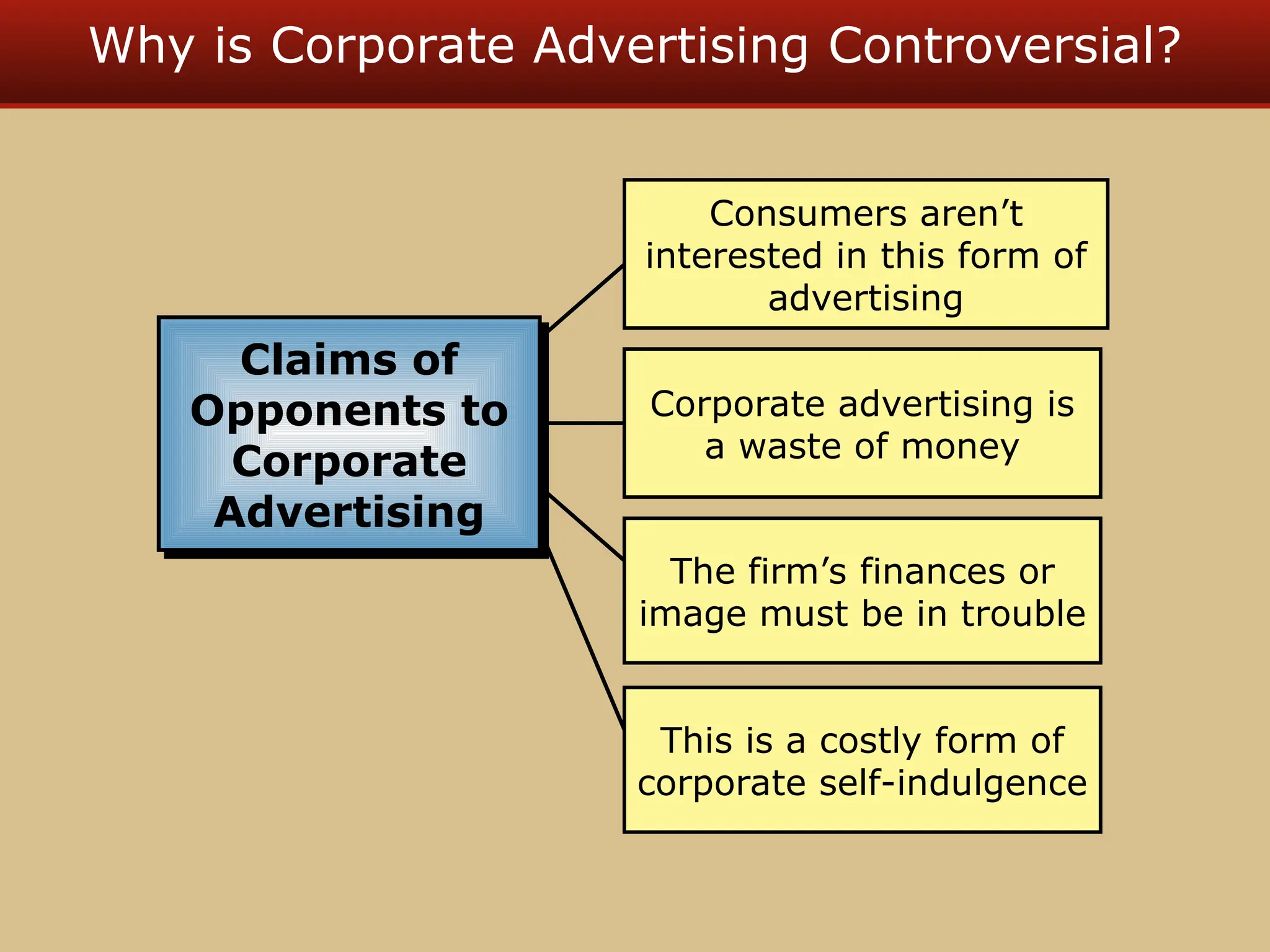
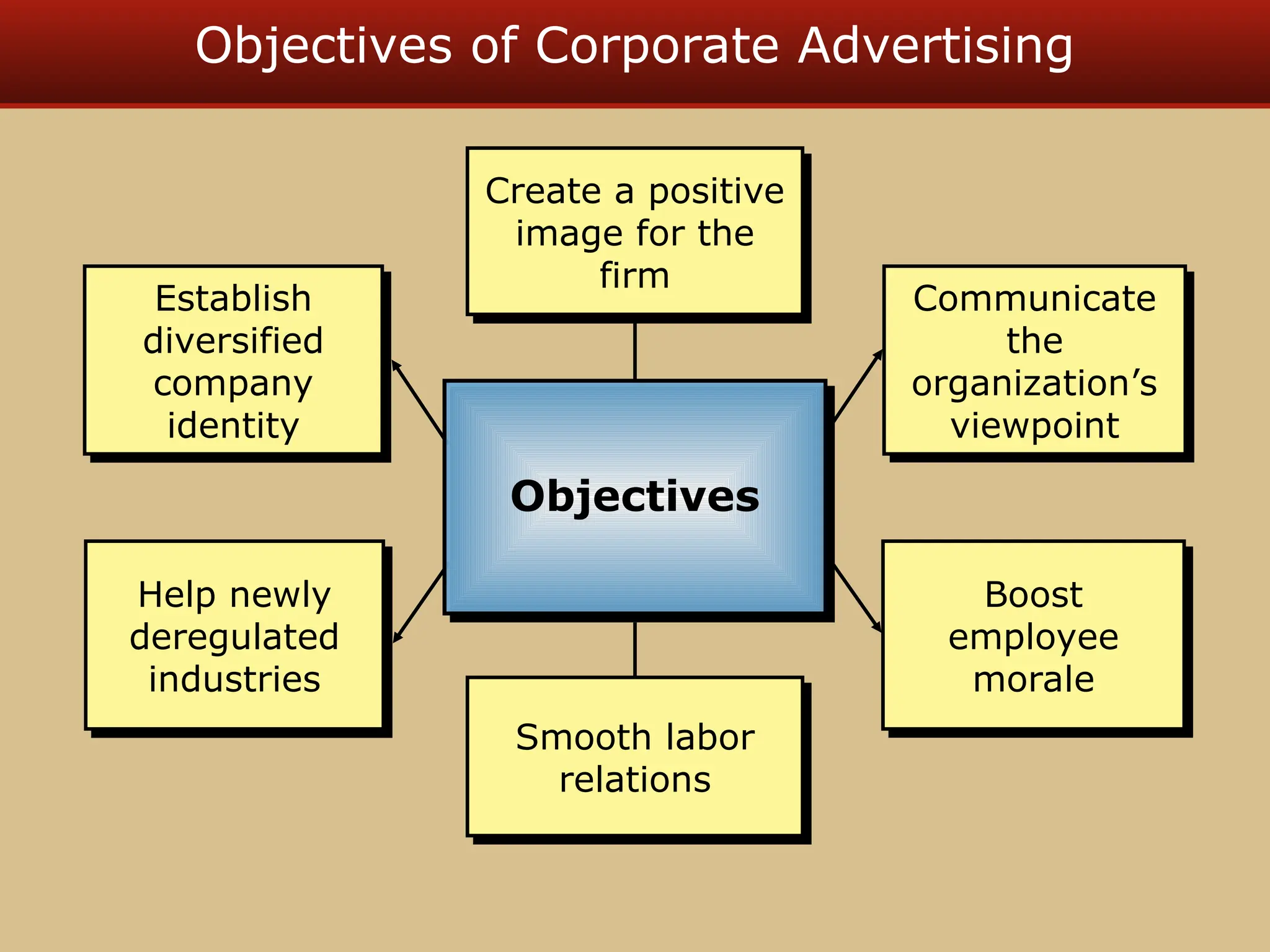
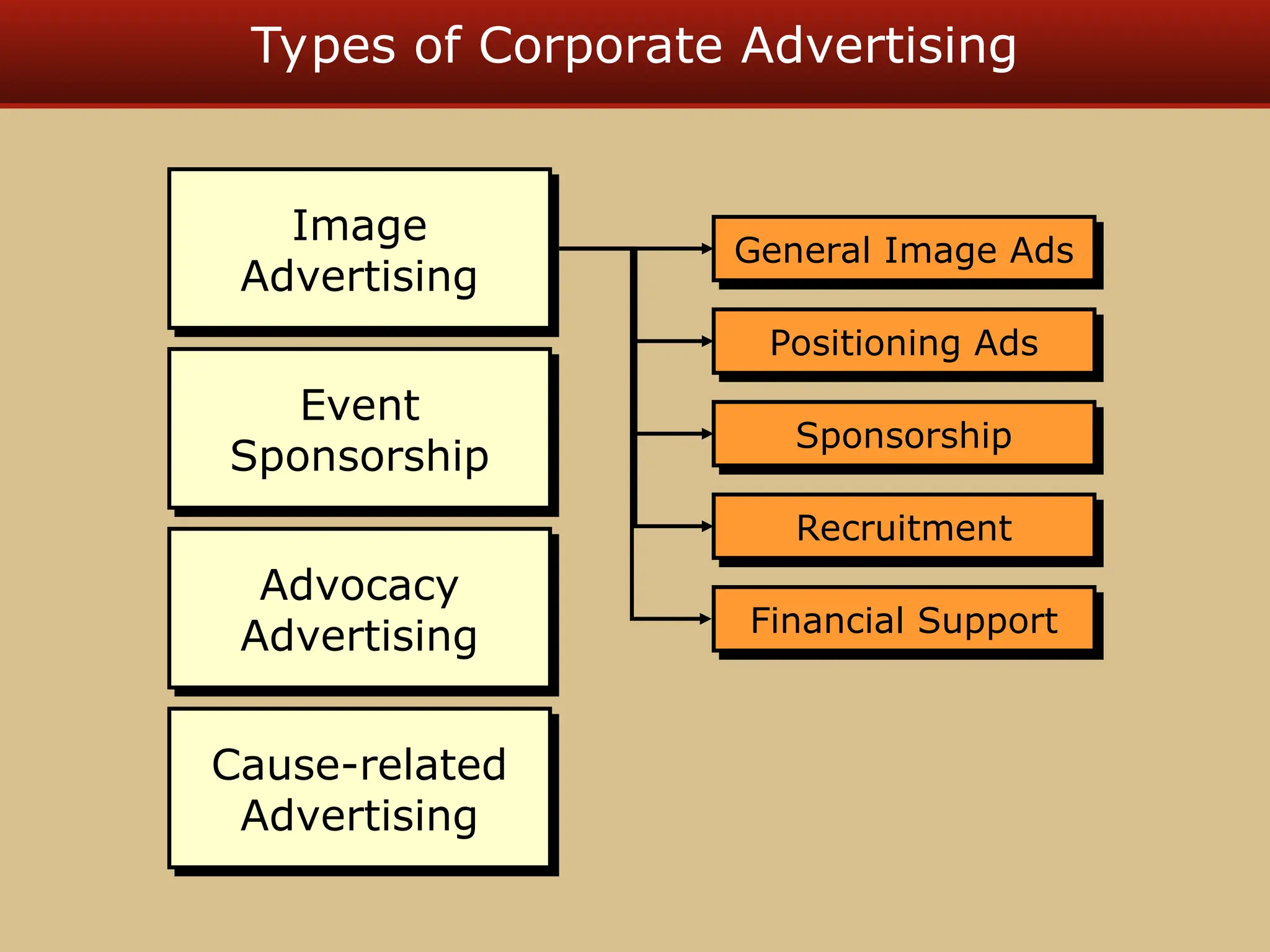
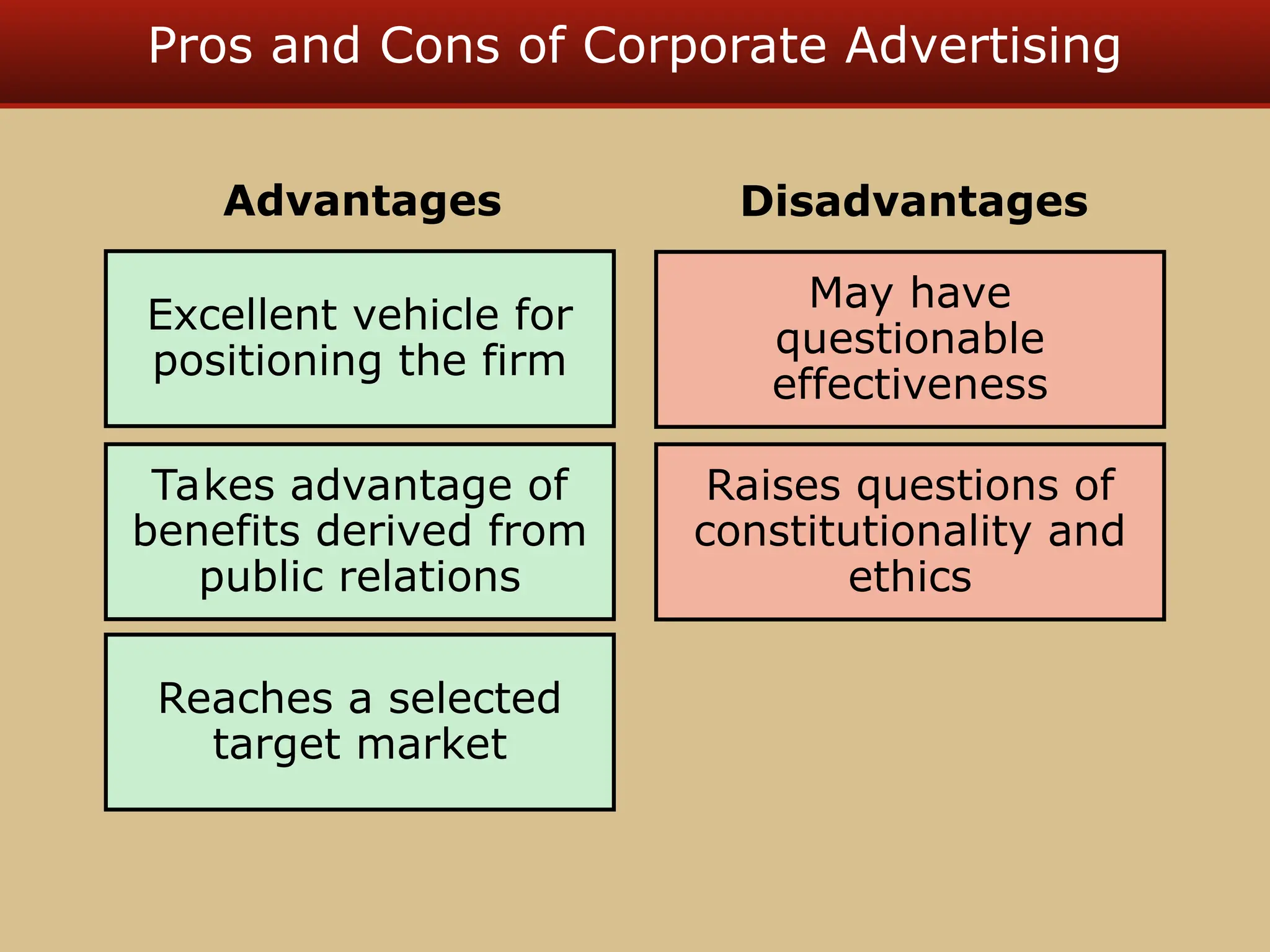
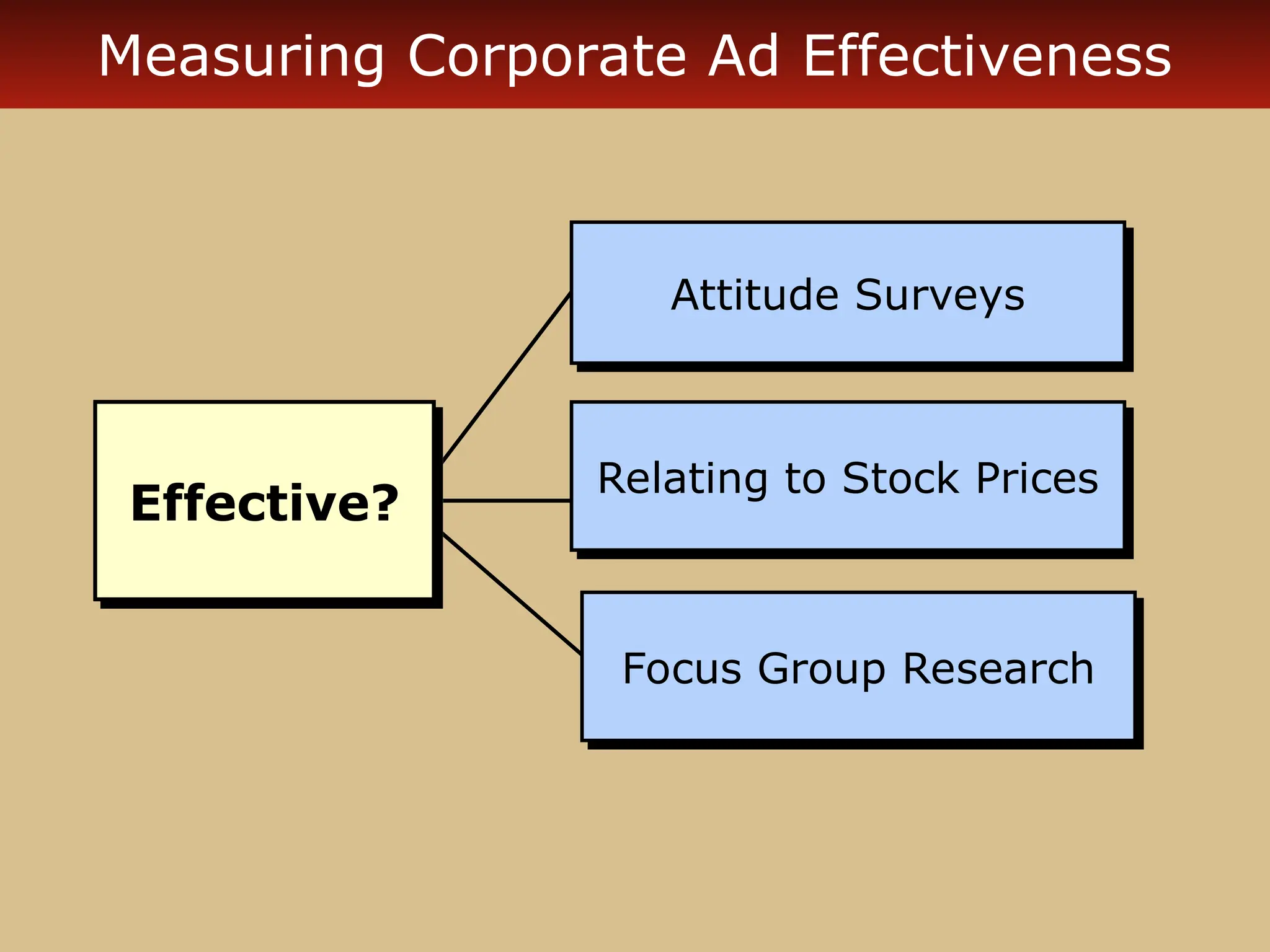
The document discusses guerilla marketing tactics used by Turner Broadcasting to promote the Aqua Teen Hunger Force movie, including a controversial campaign that resulted in a $2 million fine but increased viewer ratings and merchandise sales. It also explores public relations management, its integration into marketing strategies, and the distinctions between publicity and corporate advertising as well as their objectives, advantages, and challenges. Lastly, it emphasizes the importance of understanding public attitudes, program effectiveness, and communication strategies in building brand reputation.