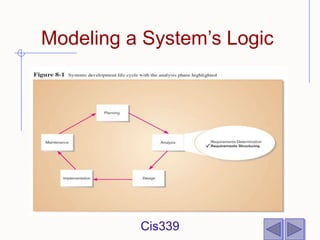
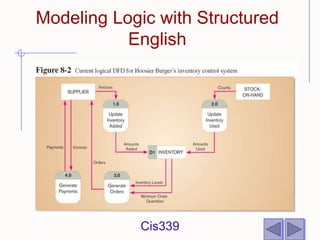
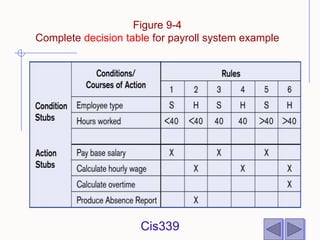
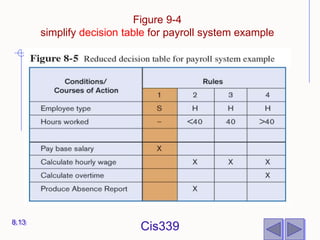
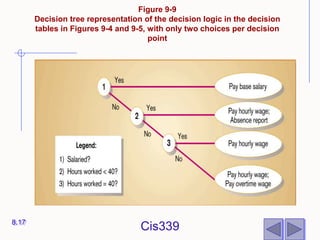
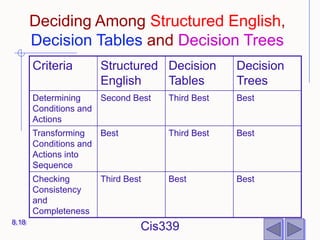
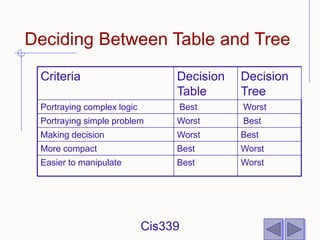
The document discusses different techniques for modeling system logic, including structured English, decision tables, and decision trees. It provides examples of how to represent logic using each technique and the benefits and drawbacks of each. Specifically, decision tables are best for representing complex decision logic as a matrix, while decision trees are more intuitive for simple problems with sequential decisions. Structured English modifies standard English to formally specify process steps.