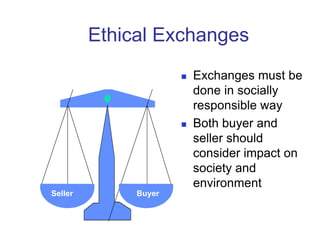
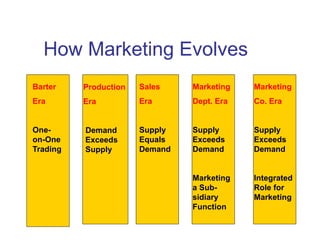
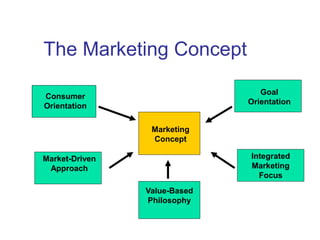
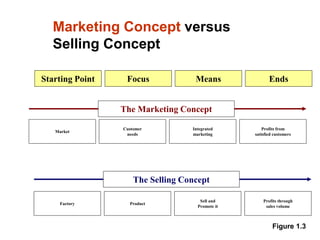
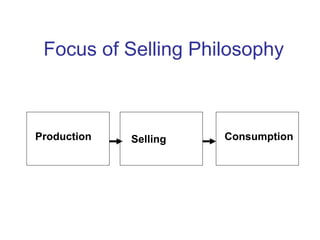
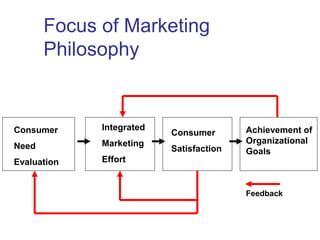
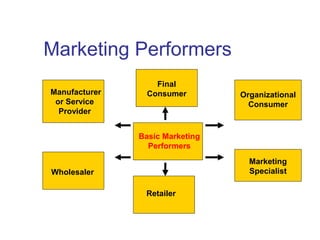
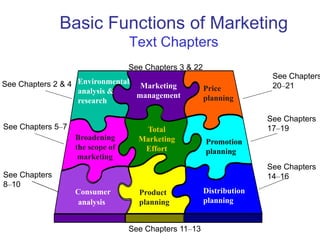
This document provides an overview of marketing concepts and functions. It defines marketing as anticipating, managing, and satisfying customer demand through exchange. The marketing concept focuses on customer needs rather than production and aims to profit through customer satisfaction. Relationship marketing builds loyalty through satisfaction. The 8 marketing functions include environmental analysis, product planning, distribution, promotion, pricing, and management of the overall marketing effort.