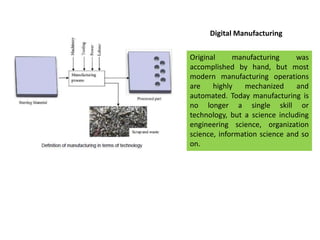
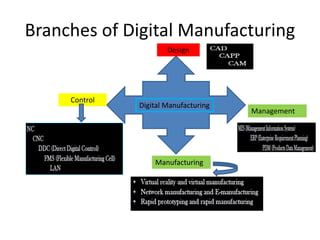
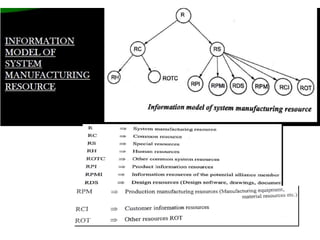
The document discusses digital manufacturing, including:
1. Digital manufacturing uses computer-based systems including simulation, 3D visualization, analytics, and collaboration tools to simultaneously create product and manufacturing process definitions.
2. Key technologies for digital manufacturing systems include product description, manufacturing process expression and control, manufacturing data handling, network/grid technologies, and virtual/simulation technologies.
3. Modeling is an important part of digital manufacturing and includes modeling products, resources, information, organizations, production processes, and the network environment using appropriate modeling methods and theories.