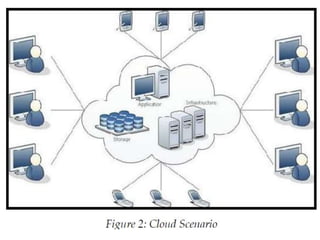
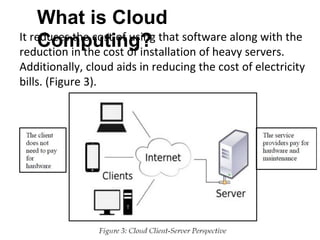
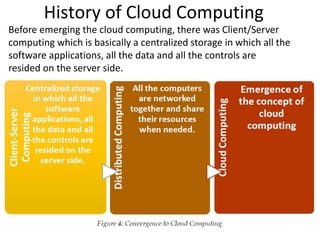
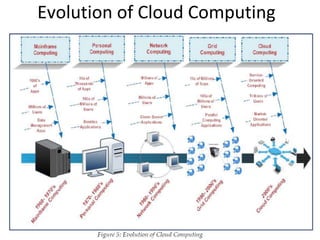
Cloud computing refers to remote network services that provide users with access to shared computing resources such as servers, storage, and applications over the internet or private networks. It has transformed the ICT industry by allowing easy access, scalable resources, and reduced costs. The evolution of cloud computing has progressed through various stages since its inception in the 1960s, leading to current services offered by major companies like Amazon and Google.