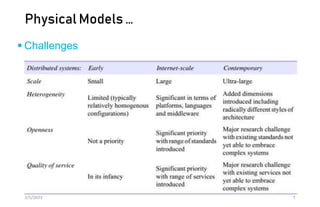
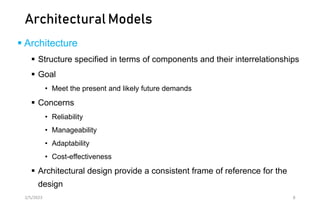
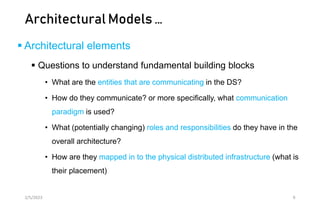
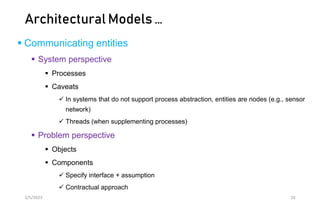
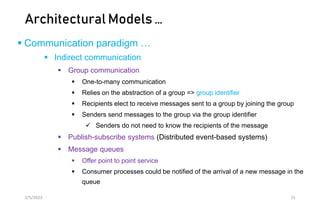
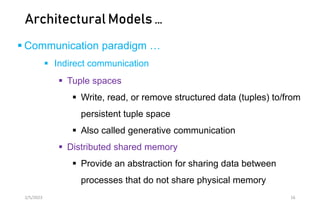
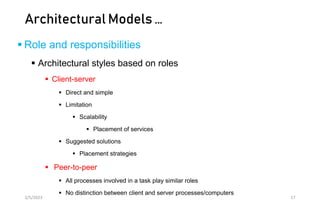
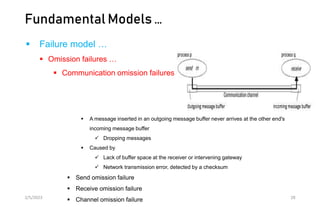
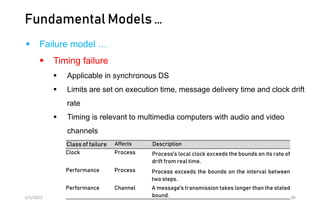
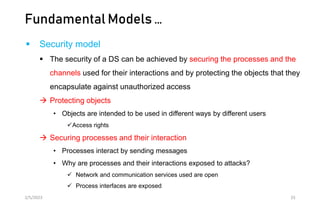
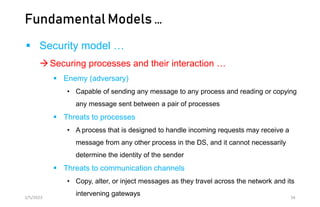
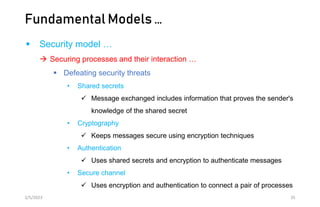
This document discusses different models of distributed systems including physical, architectural, and fundamental models. The physical model represents the underlying hardware elements like networked computers. The architectural model defines the structure and components of a distributed system and their relationships. Fundamental models capture key aspects like interaction, failure, and security. Interaction models consider factors like timing and clocks. Failure models classify failures as omissions, arbitrary, or timing. The security model defines threats from adversaries and techniques to secure processes and communication.