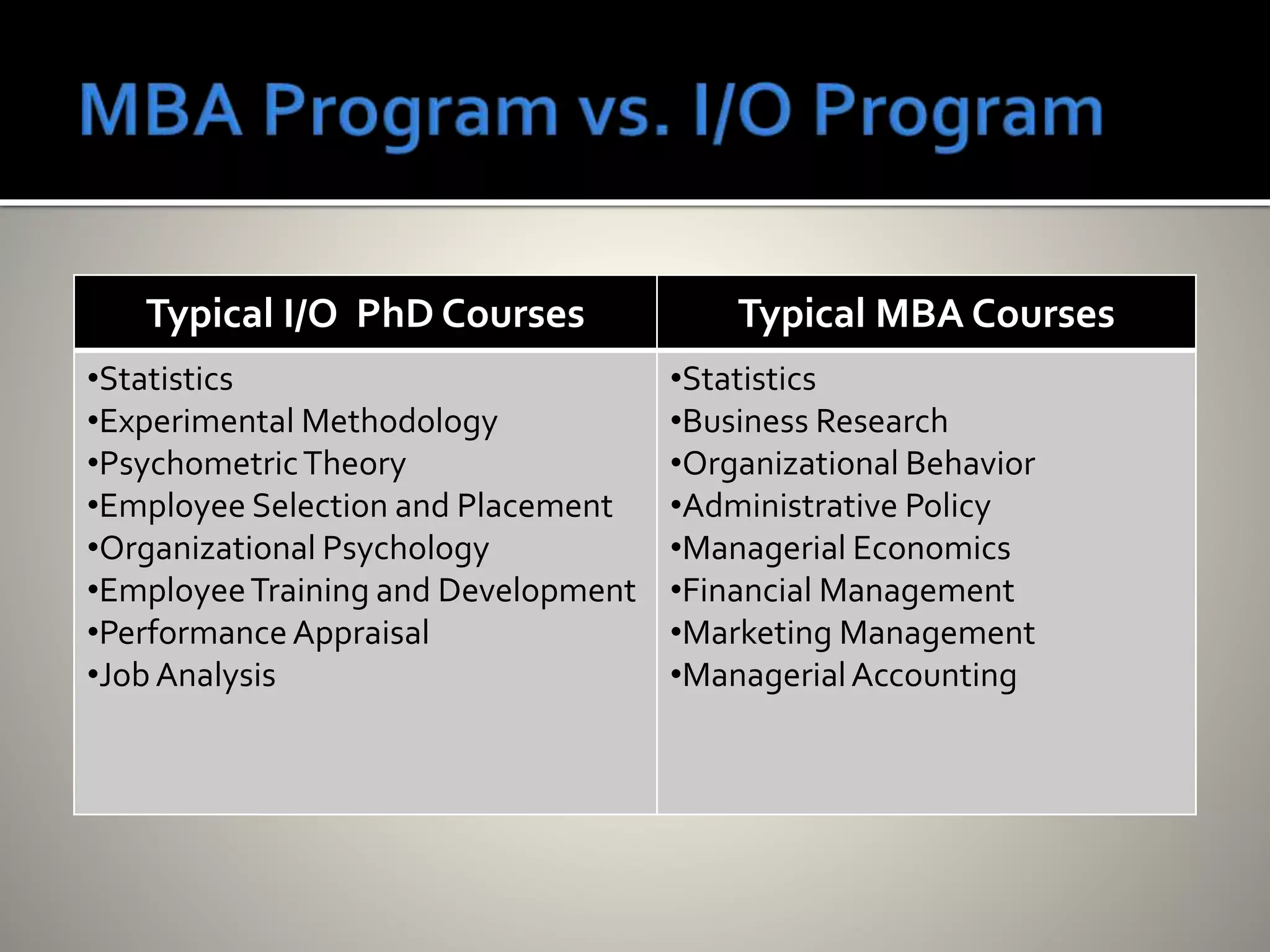
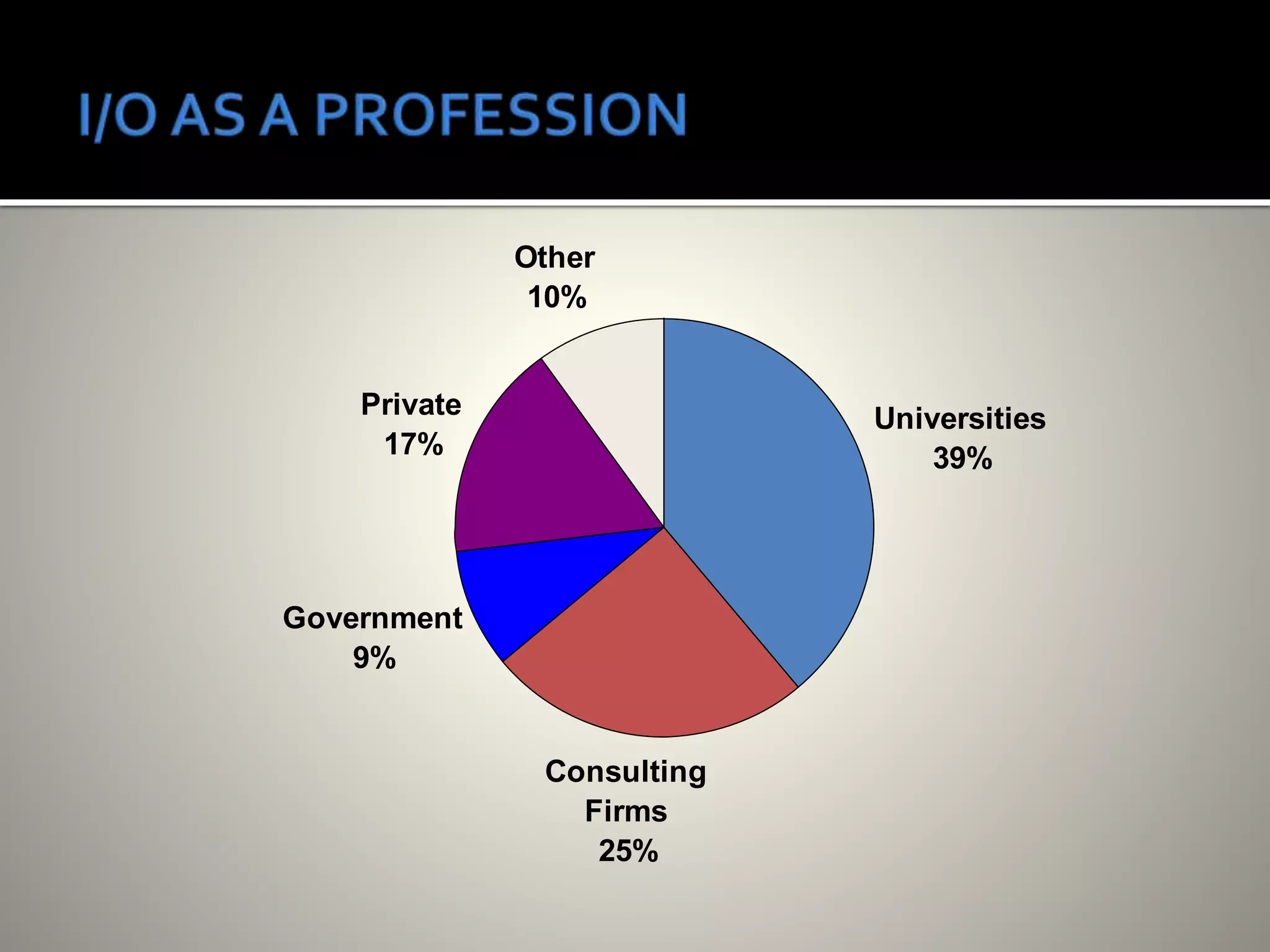
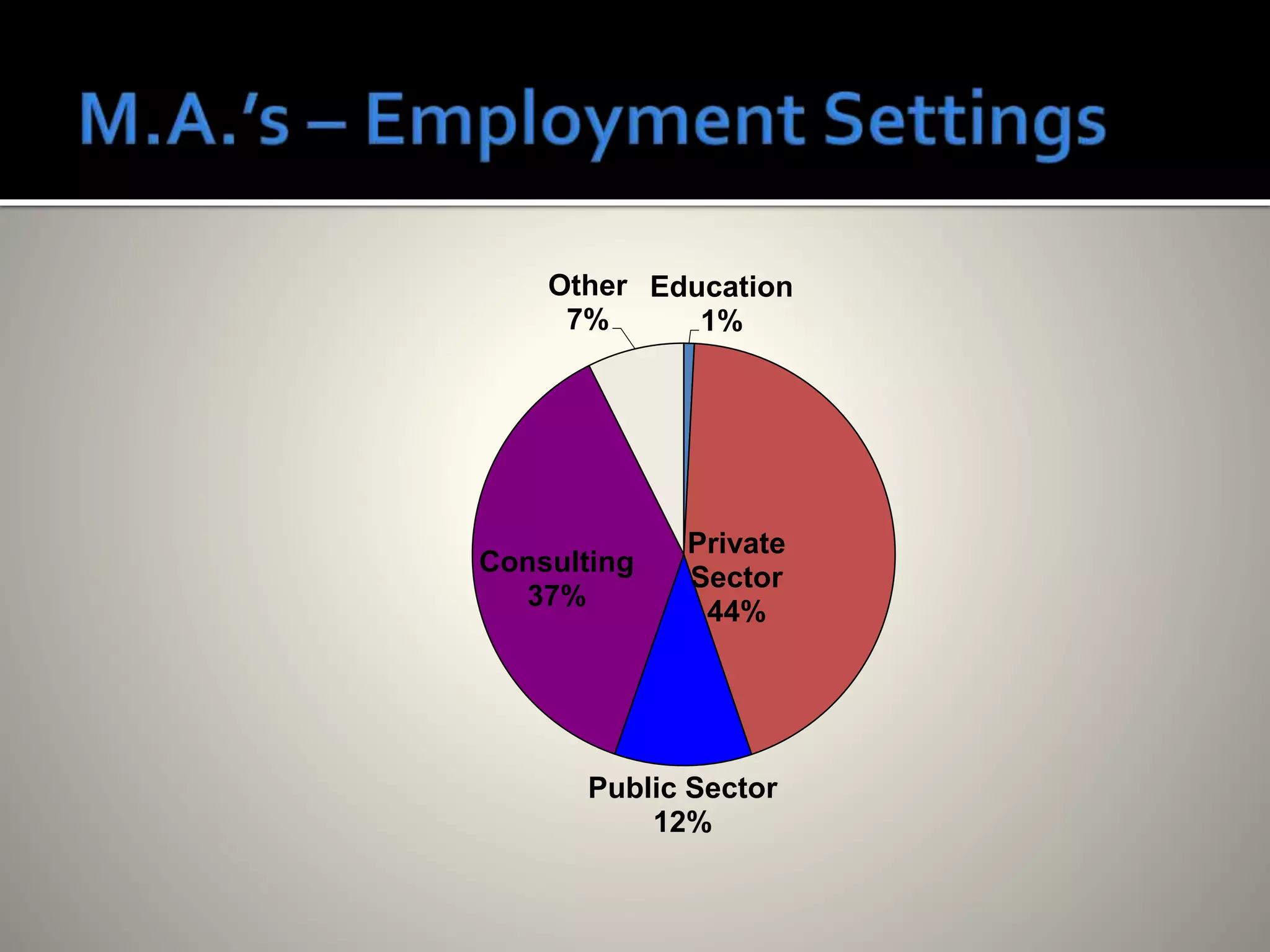
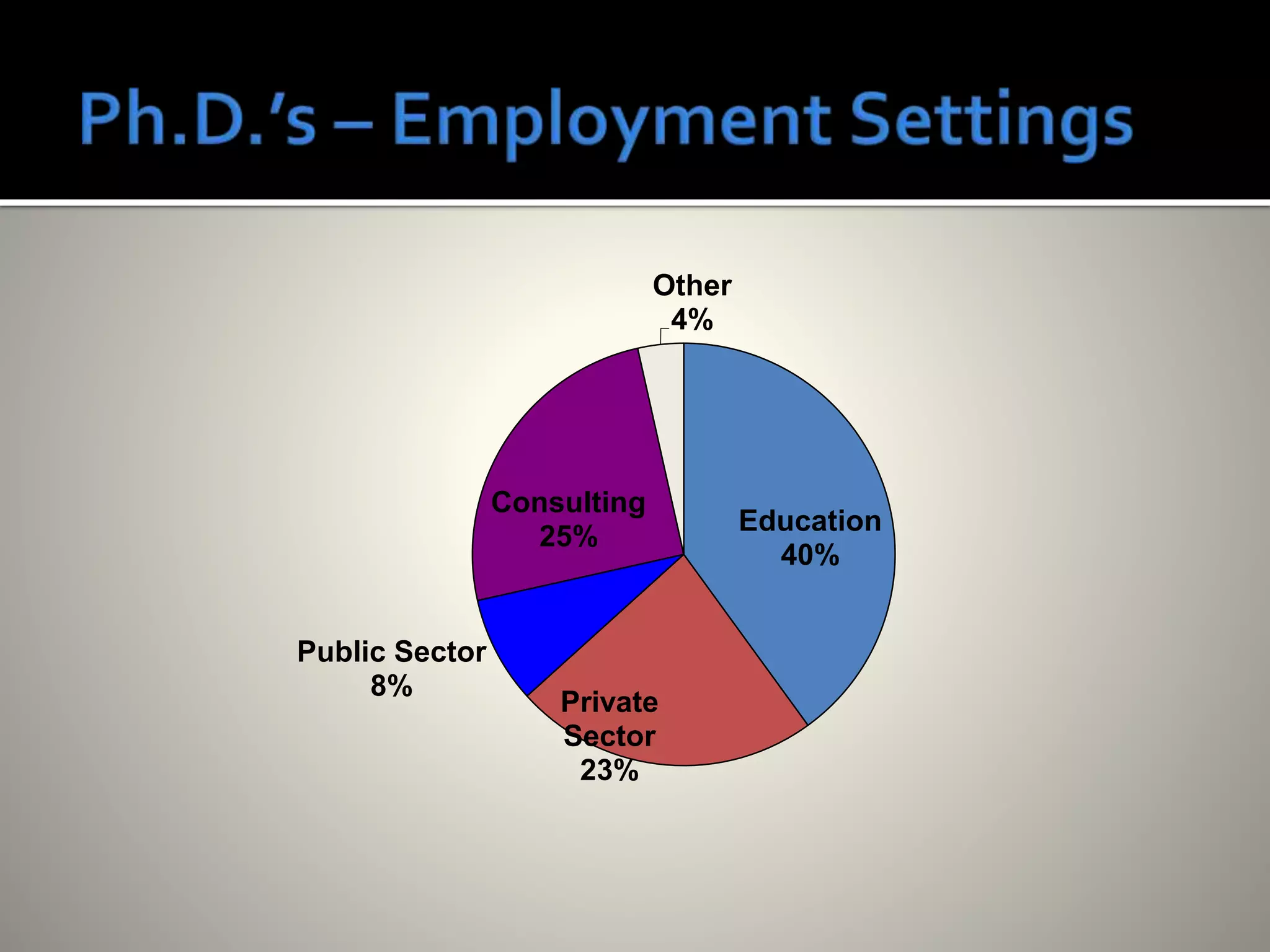
Industrial/Organizational (I/O) psychology applies psychological principles to workplace settings to enhance organizational efficiency and employee well-being. The field, which requires advanced degrees, focuses on personnel and organizational psychology, encompassing areas such as job analysis, employee performance, and organizational structure. I/O psychologists work across various sectors, employing research and quantitative methods to inform practices that optimize workplace environments.