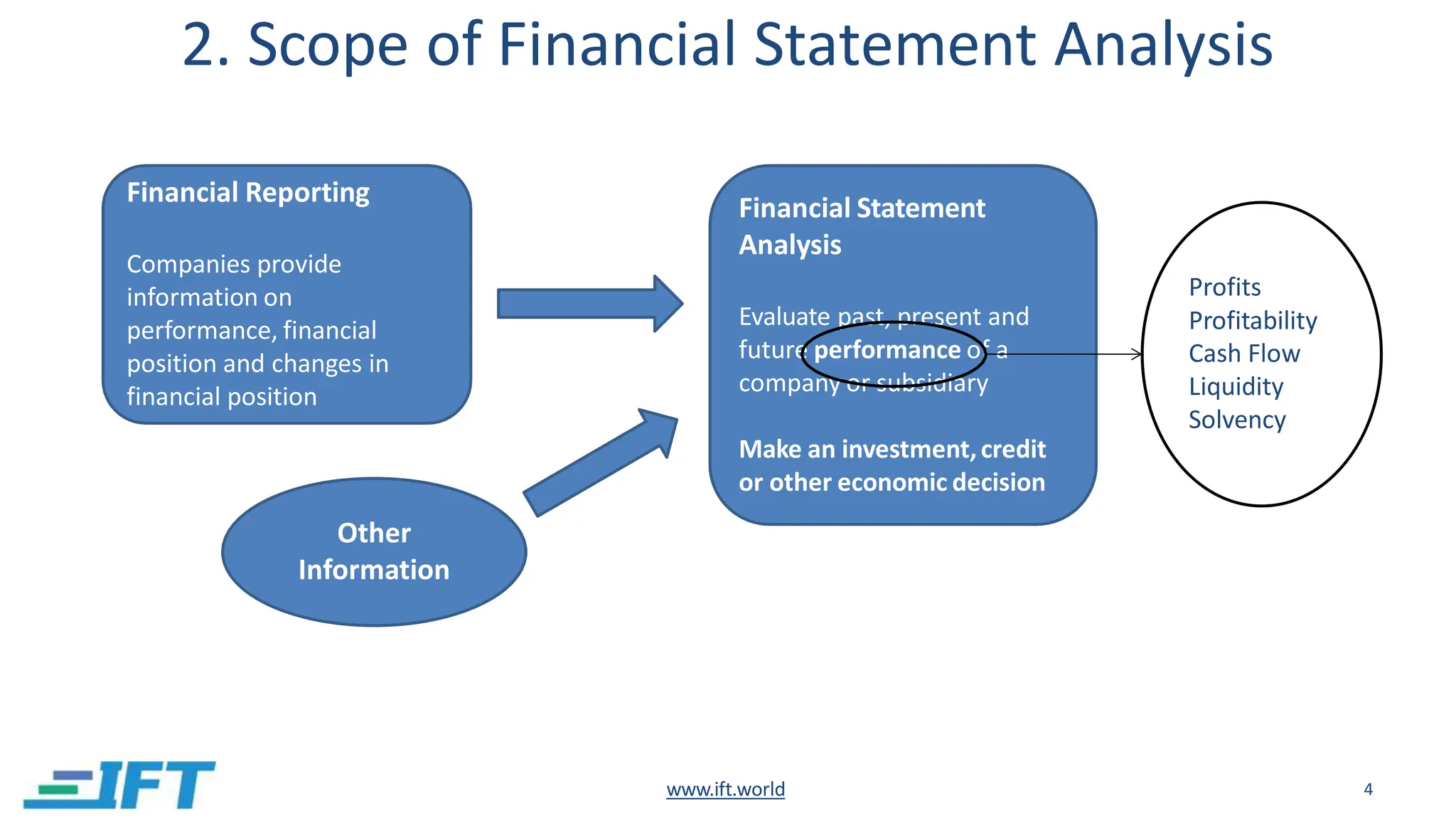
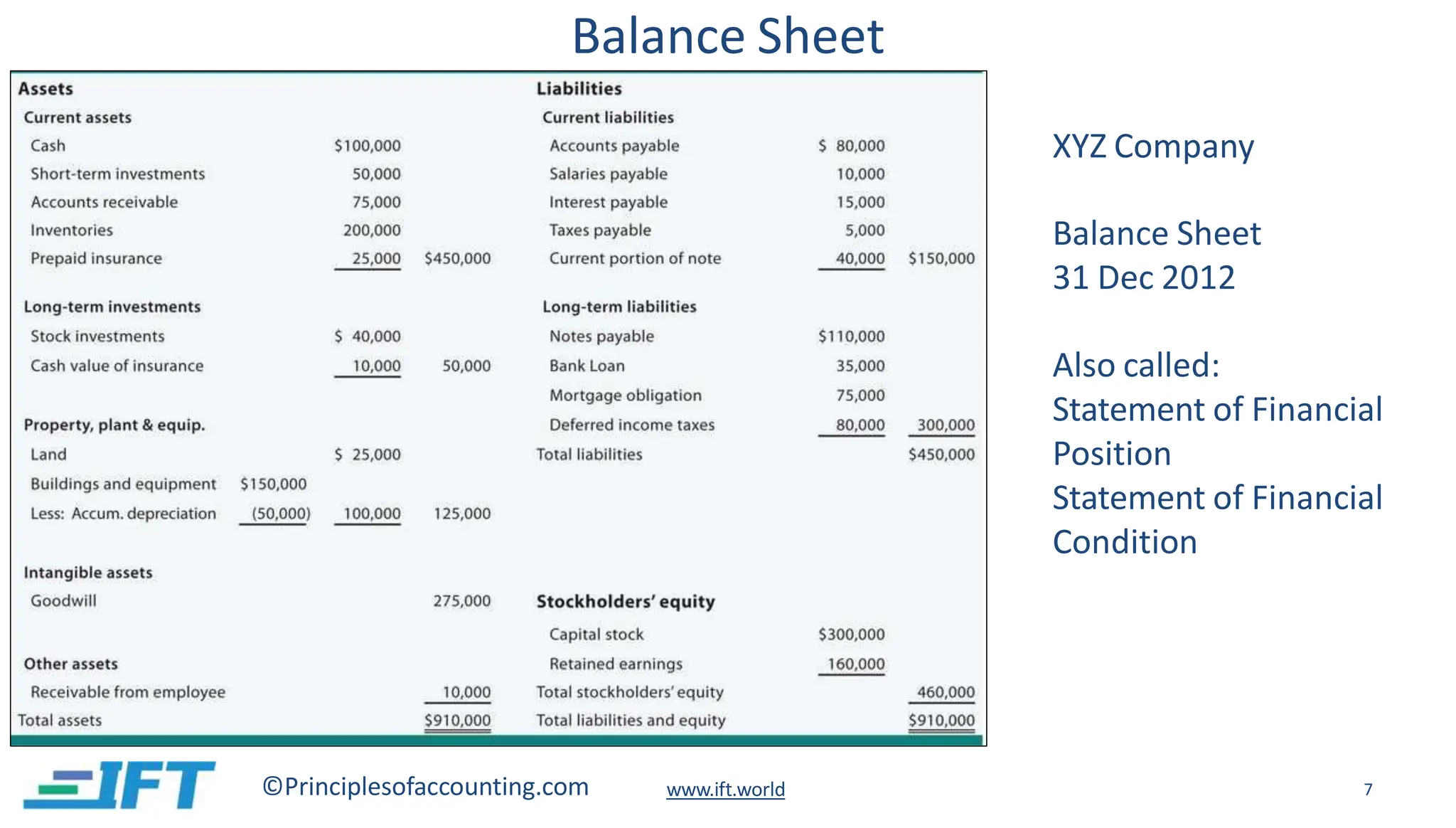
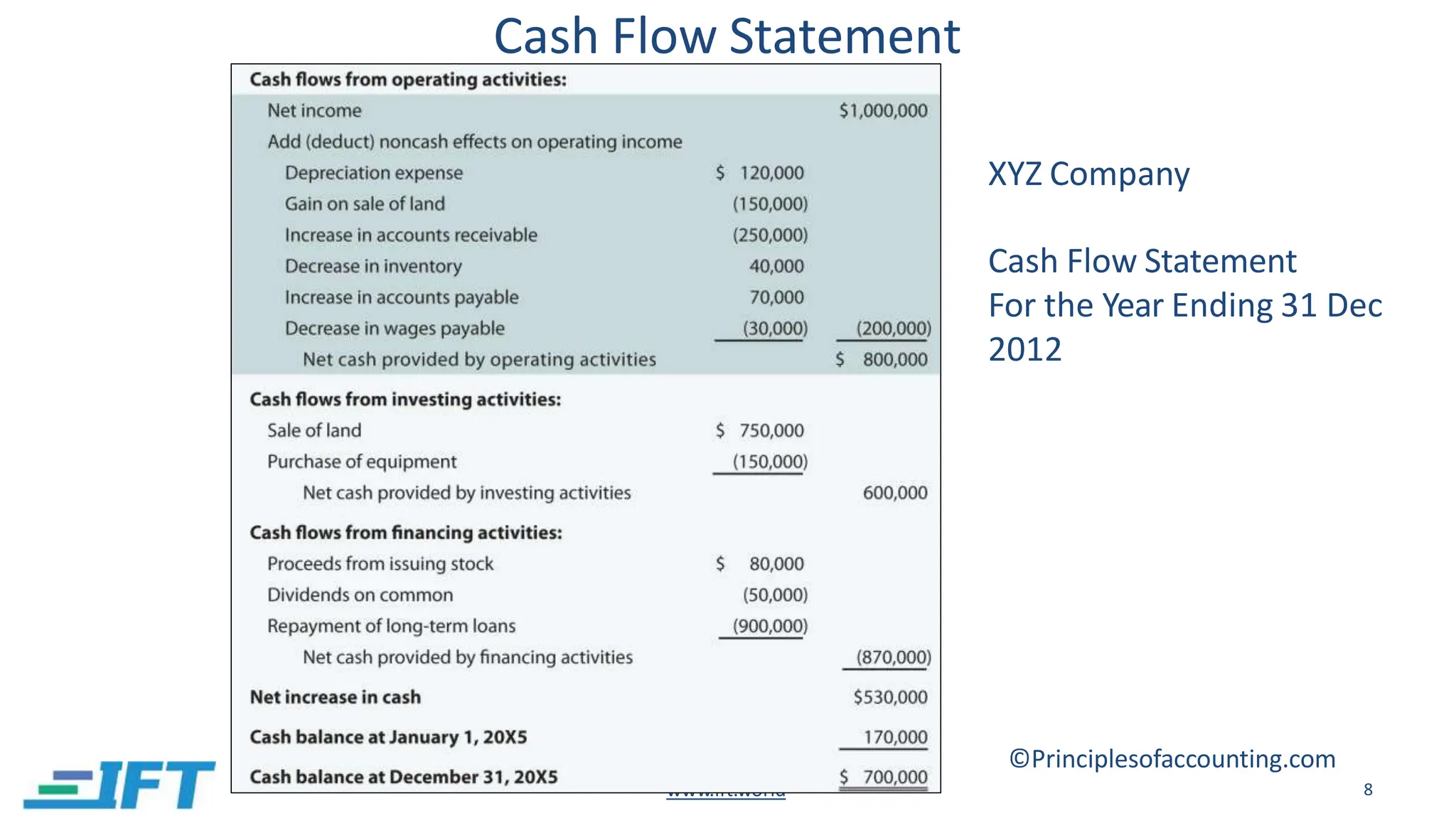
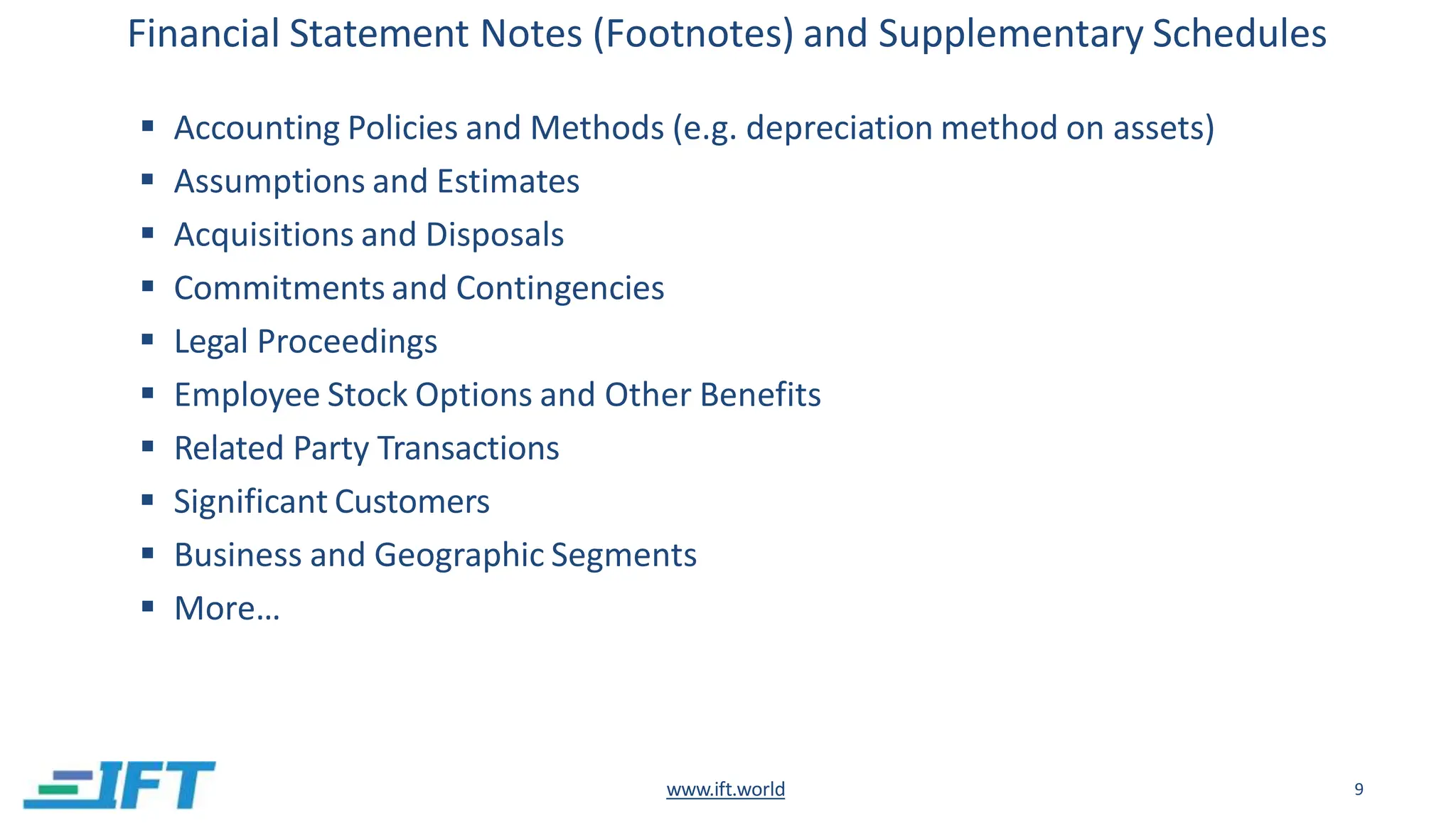
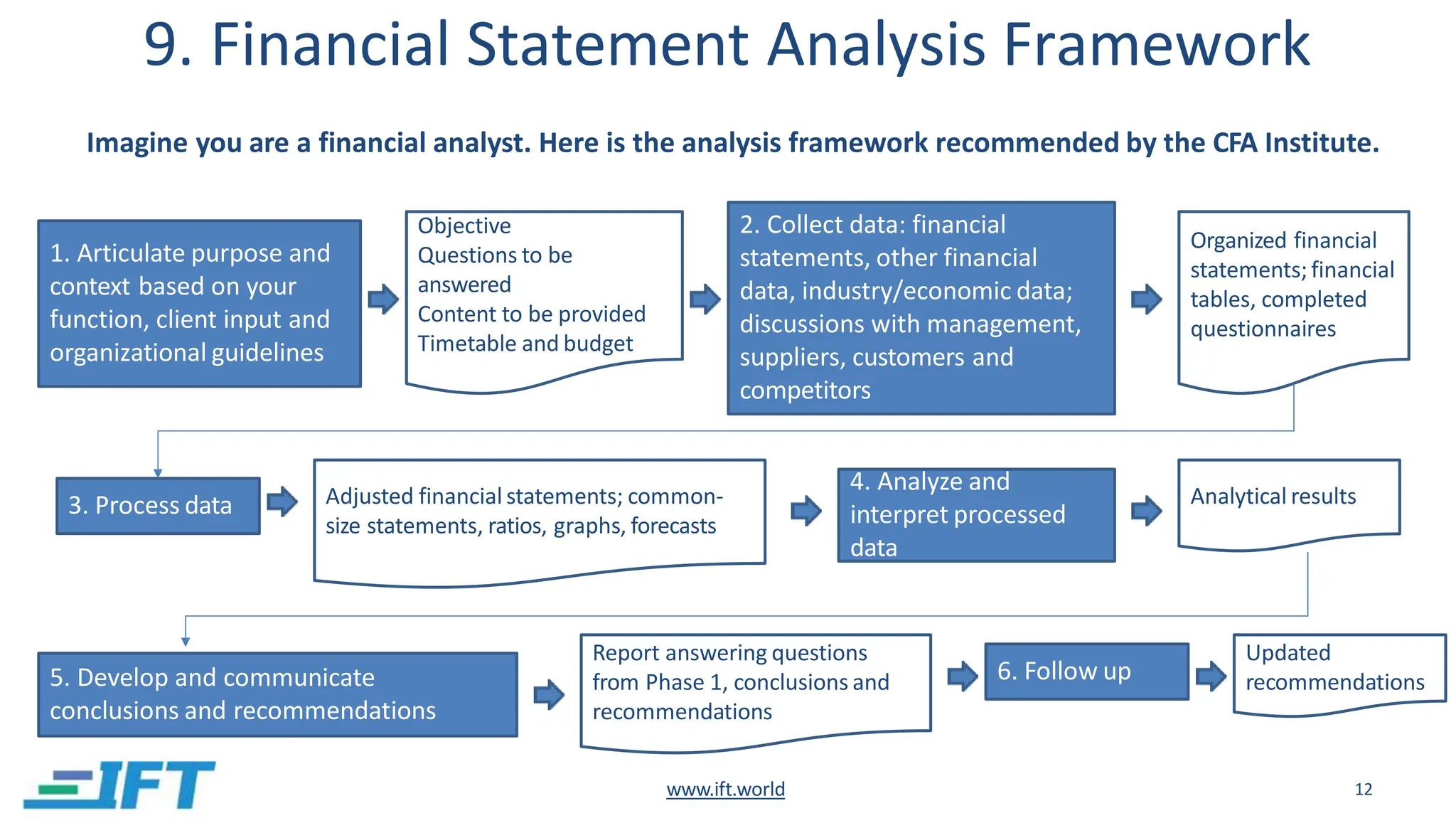
This document provides an introduction to financial statement analysis. It outlines the key components of financial statements, including the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. It also discusses other important sources of financial information for analysts, such as notes, management discussion and analysis, audit reports, and interim financial statements. Finally, it presents a six-step framework for conducting financial statement analysis to evaluate a company's performance, financial position, and changes in financial position.