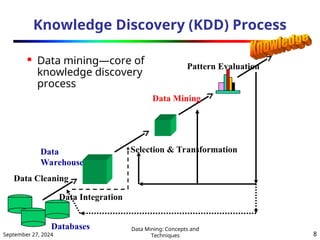
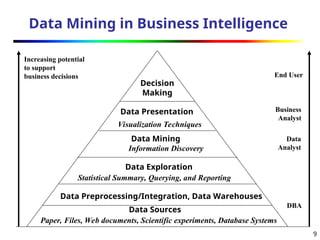
El capítulo 1 de 'Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques' introduce el concepto de minería de datos, justificando su necesidad debido al crecimiento explosivo de datos y la automatización en su recolección. Se describen las técnicas de minería de datos, funciones como la clasificación y análisis de patrones, y se destacan las aplicaciones en inteligencia empresarial, análisis de mercado y detección de fraudes. Se abordan también los desafíos del sector, como la metodología de minería y la evaluación de patrones interesantes.


















![Data Mining Function: (2) Association and
Correlation Analysis
Frequent patterns (or frequent itemsets)
What items are frequently purchased together in
your mart? Eg. Milk & bread
Association, correlation vs. causality
A typical association rule
Computer software [1%, 50%] (support,
→
confidence)
Confidence means that if one buys a computer there is a 50%
chance that she will buy software too. A 1% support means
that 1% of all transactions under analysis show that computer
& software are purchased together
Association rules are discarded as uninteresting if they
do not satisfy both a minimum support threshold
and a minimum confidence threshold
September 27, 2024
Data Mining: Concepts and
Techniques 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch1dm-240927082539-a7f9a7df/85/ch_1_dm-data-preprocessing-in-data-mining-21-320.jpg)















