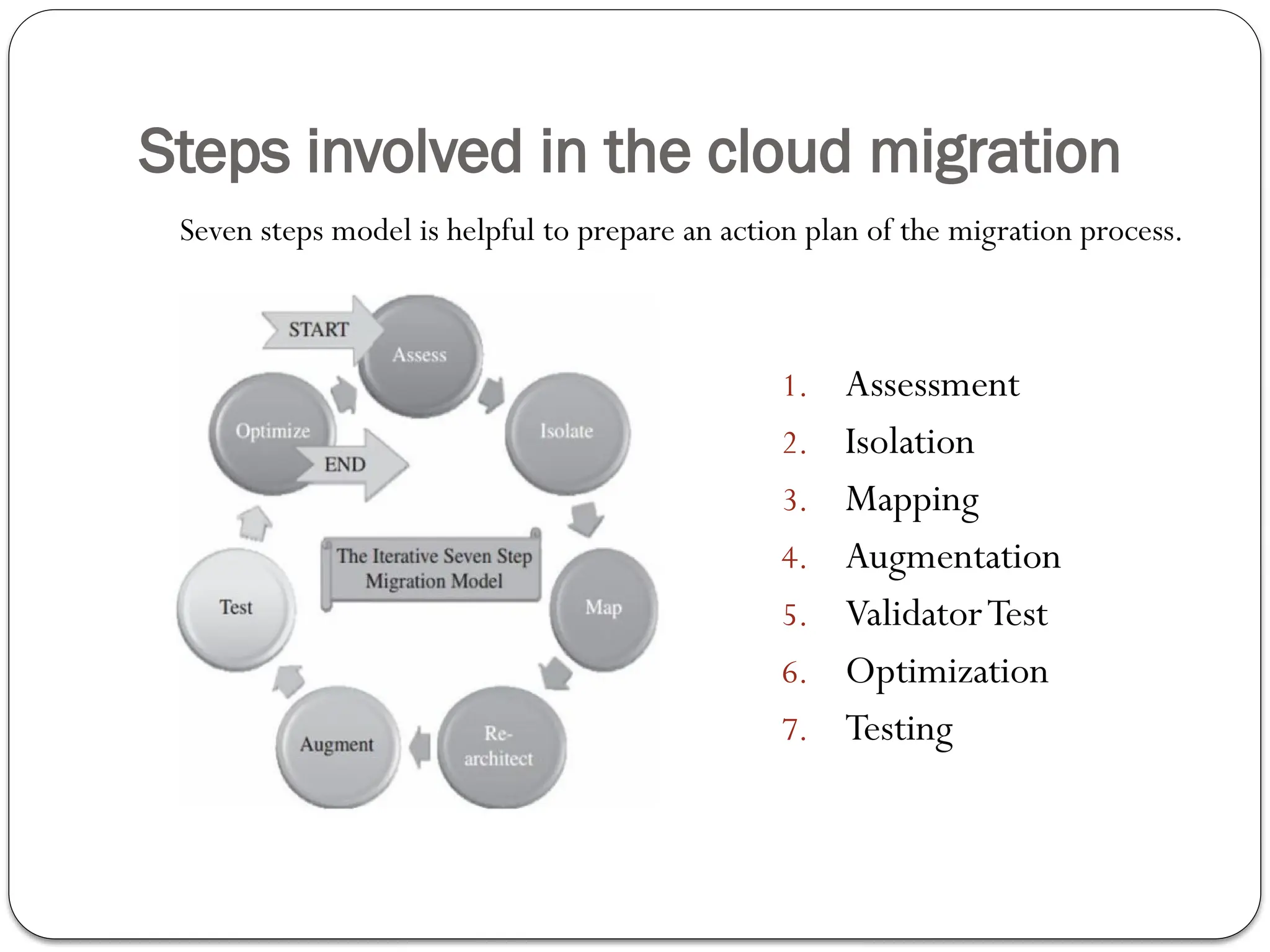
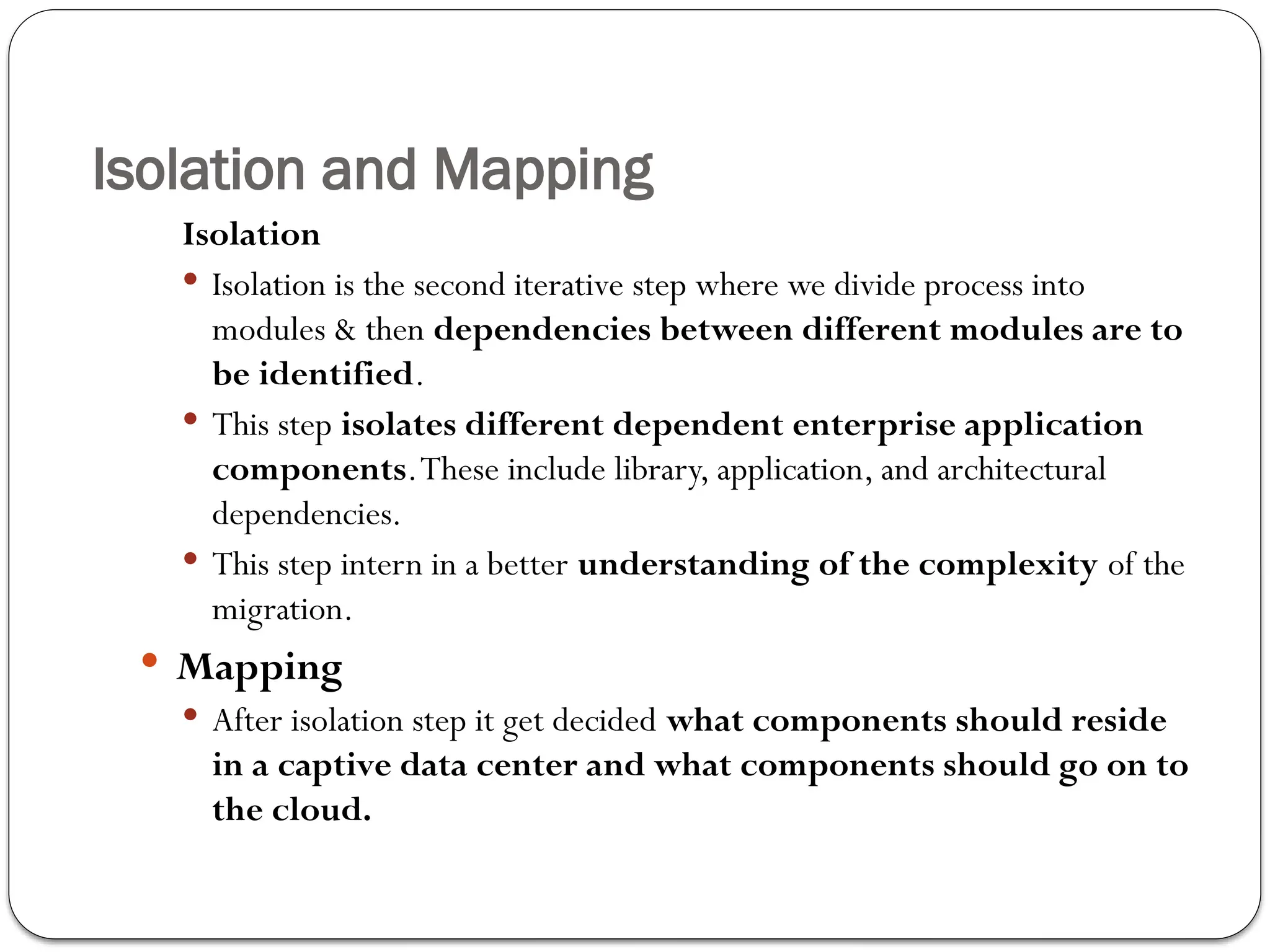
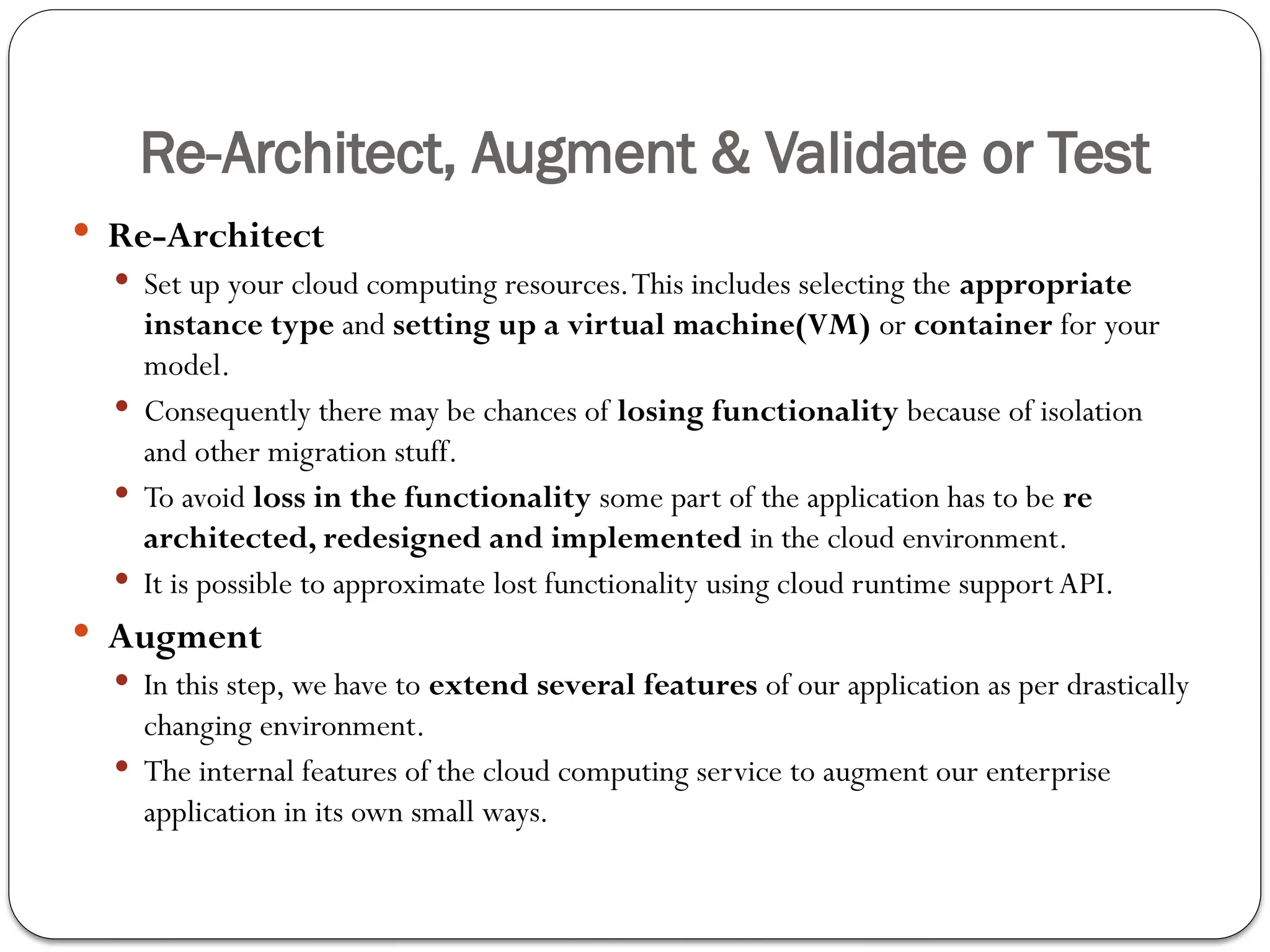
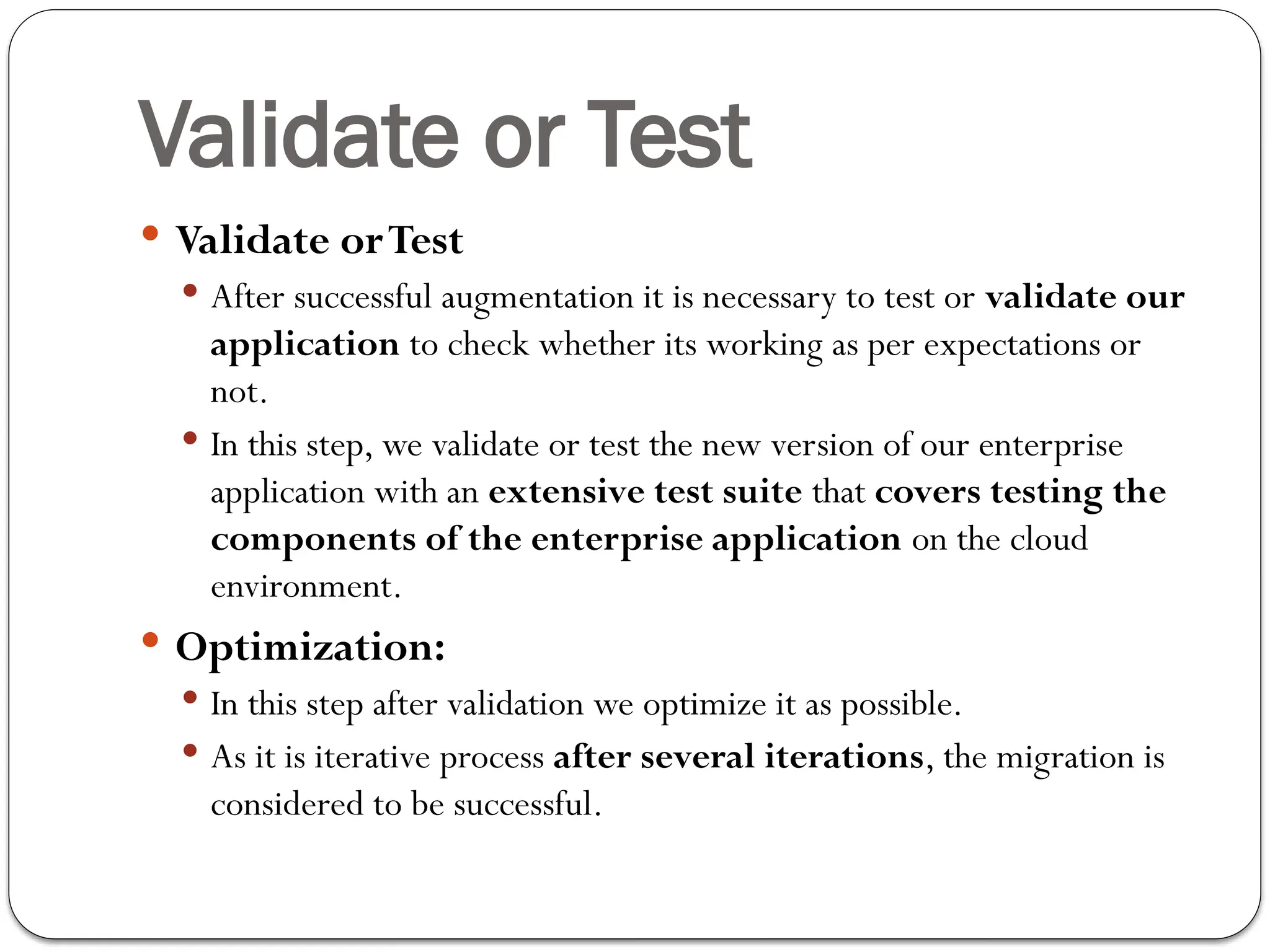
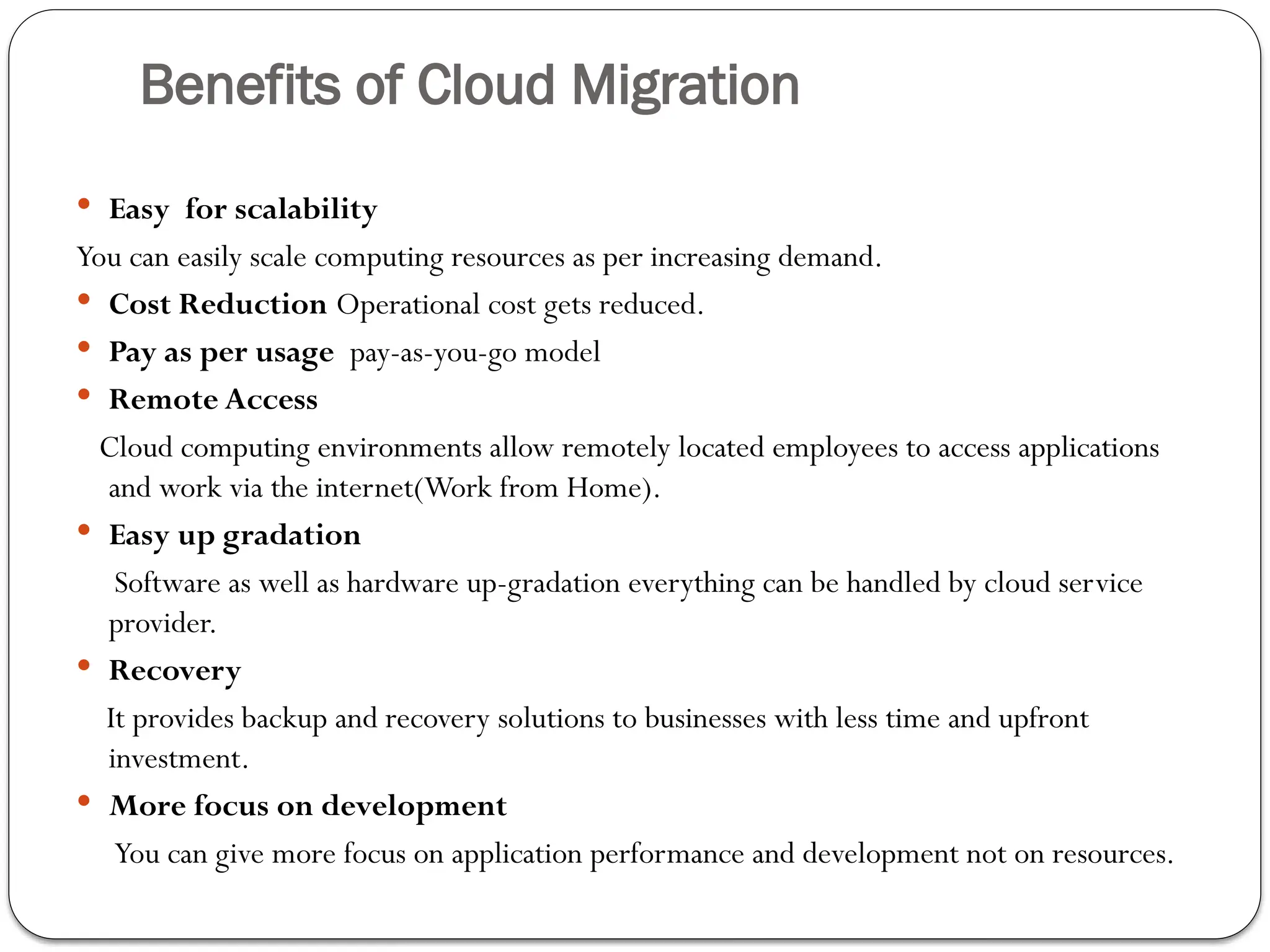
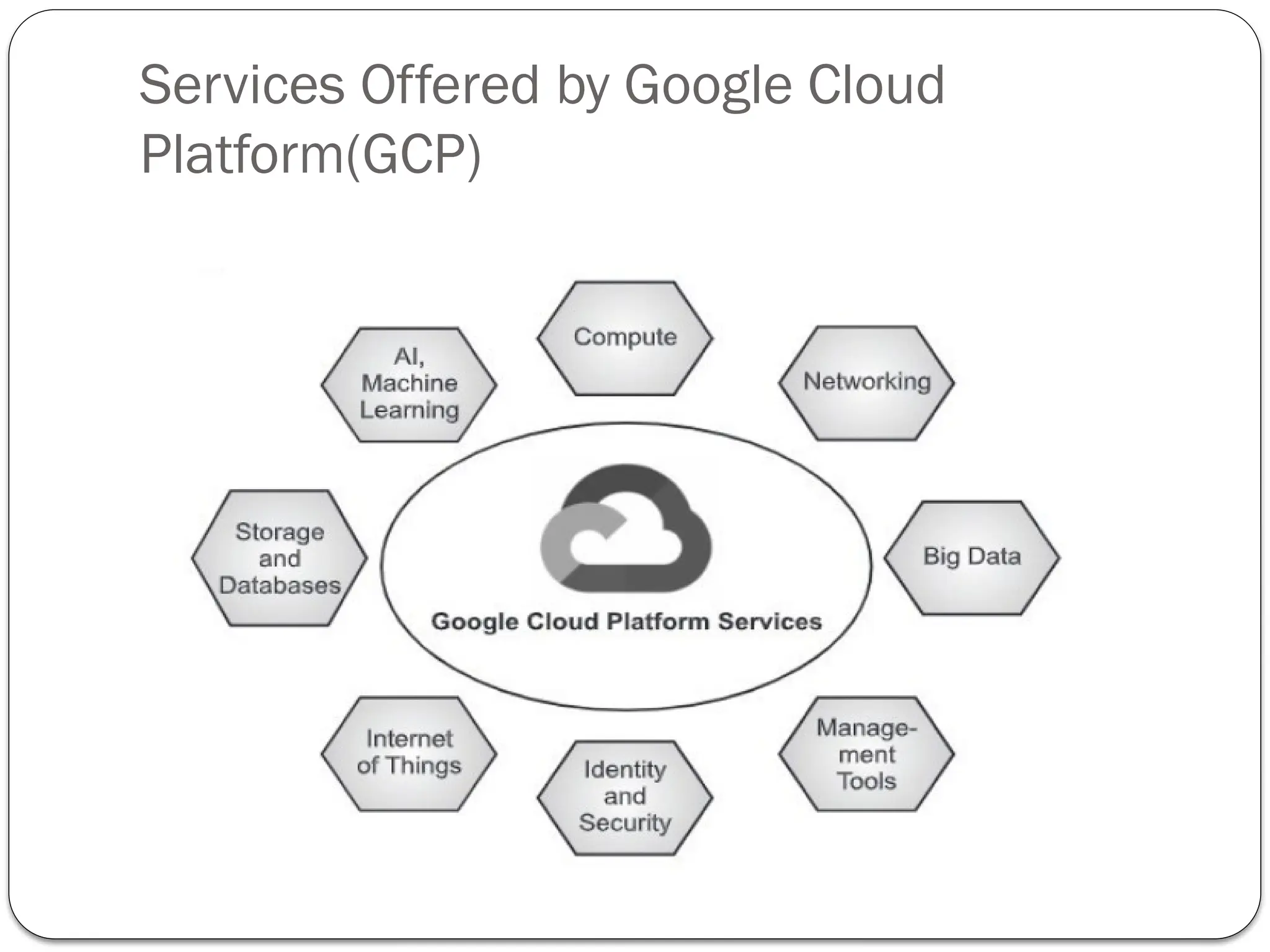
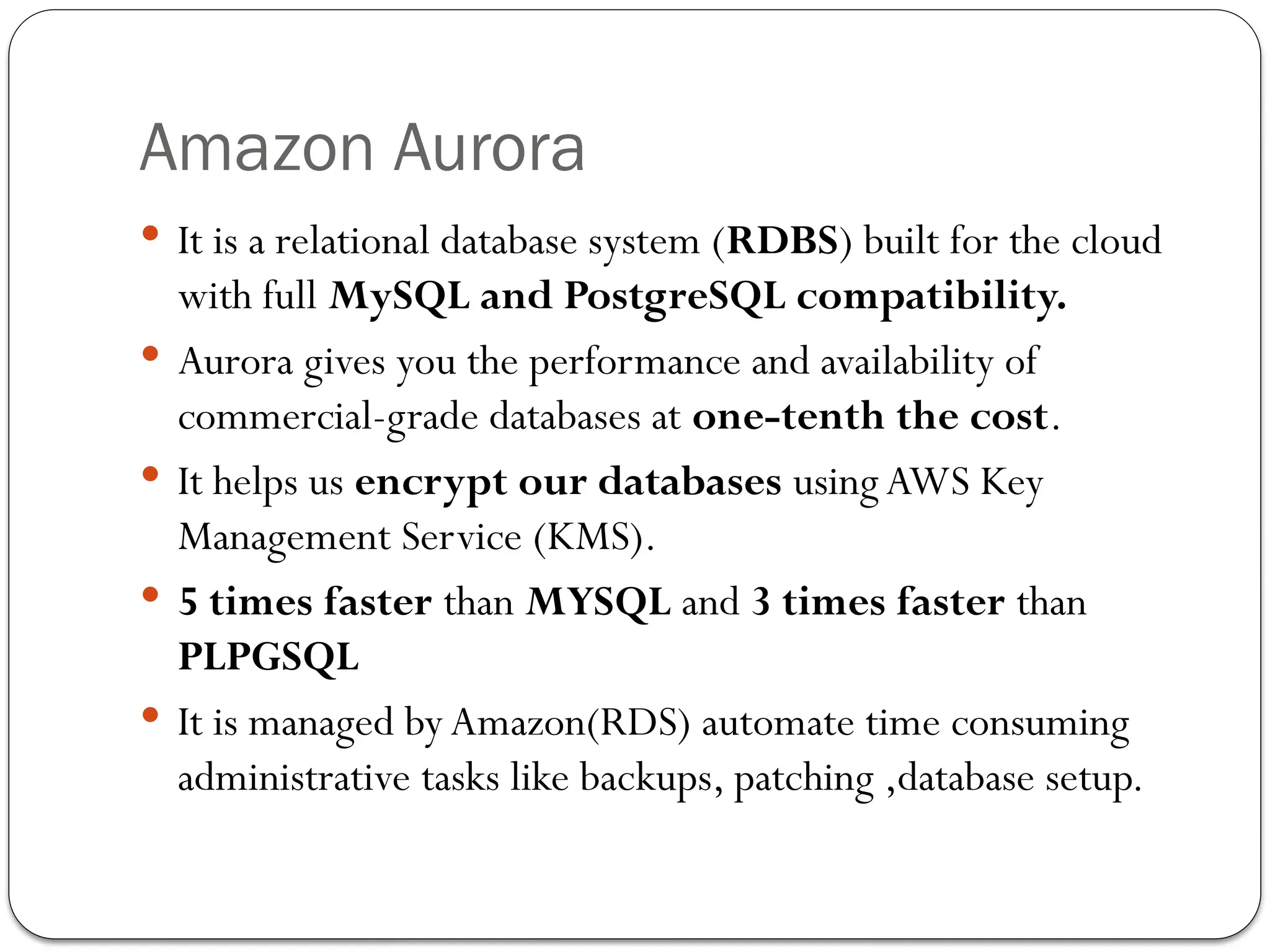
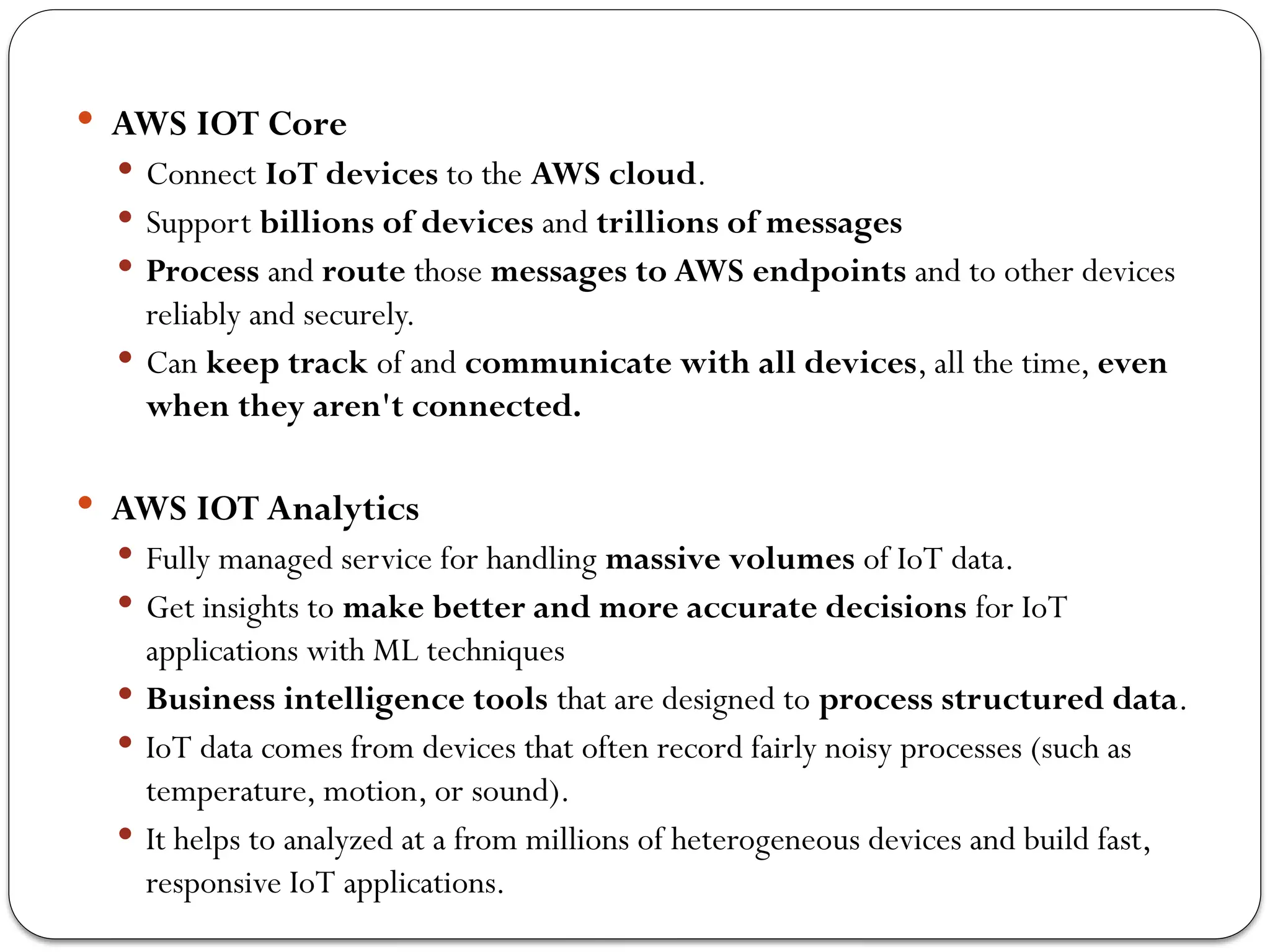
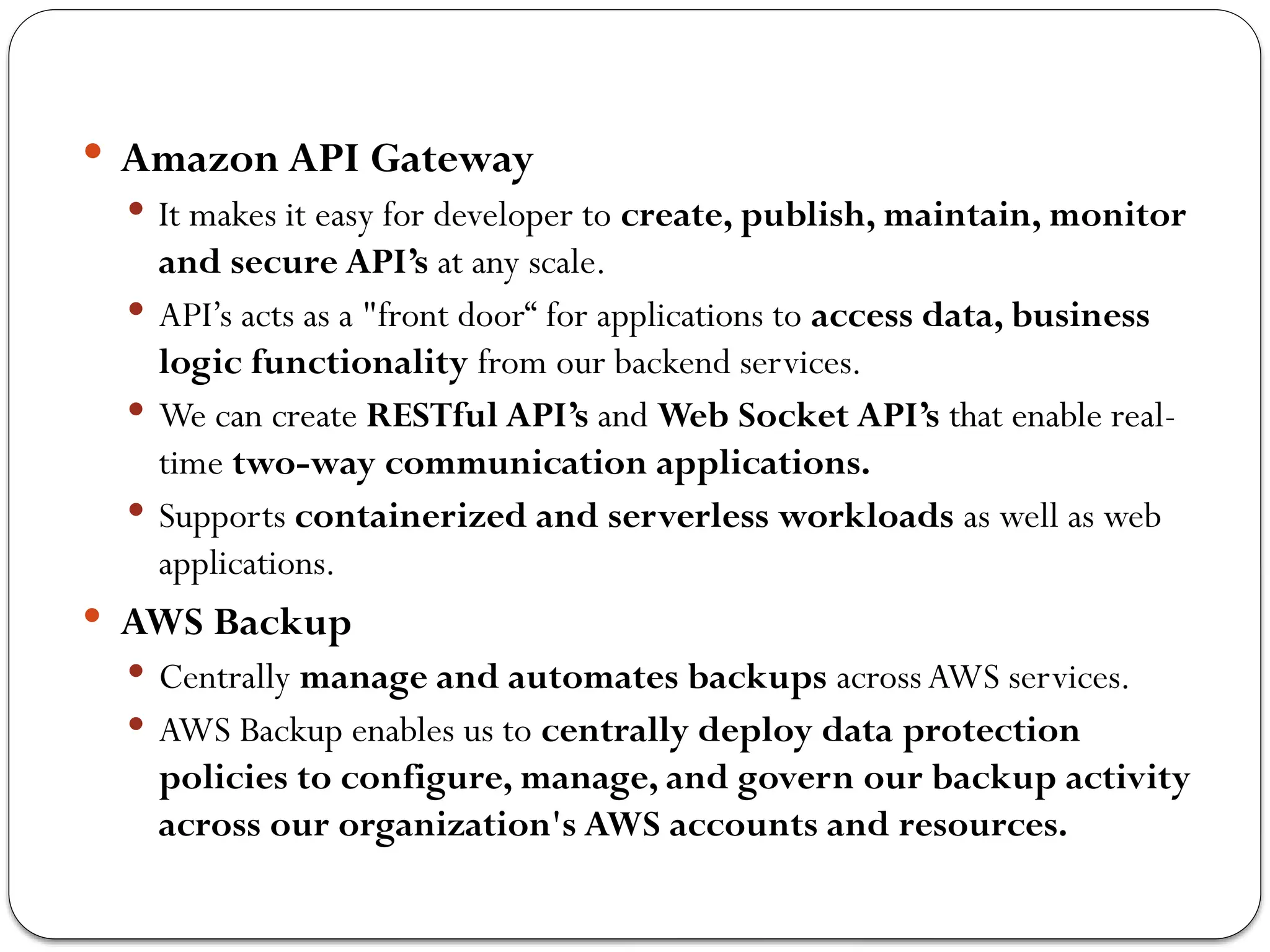
The document outlines the process of cloud migration, which involves moving applications and data from local environments to cloud platforms such as Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and Amazon Web Services. It details the steps in the migration process, including assessment, isolation, mapping, re-architecting, validation, and optimization, while also discussing the benefits and risks associated with cloud migration. Additionally, it provides an overview of cloud services offered by Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and Amazon Web Services, highlighting their features and capabilities in supporting business applications.