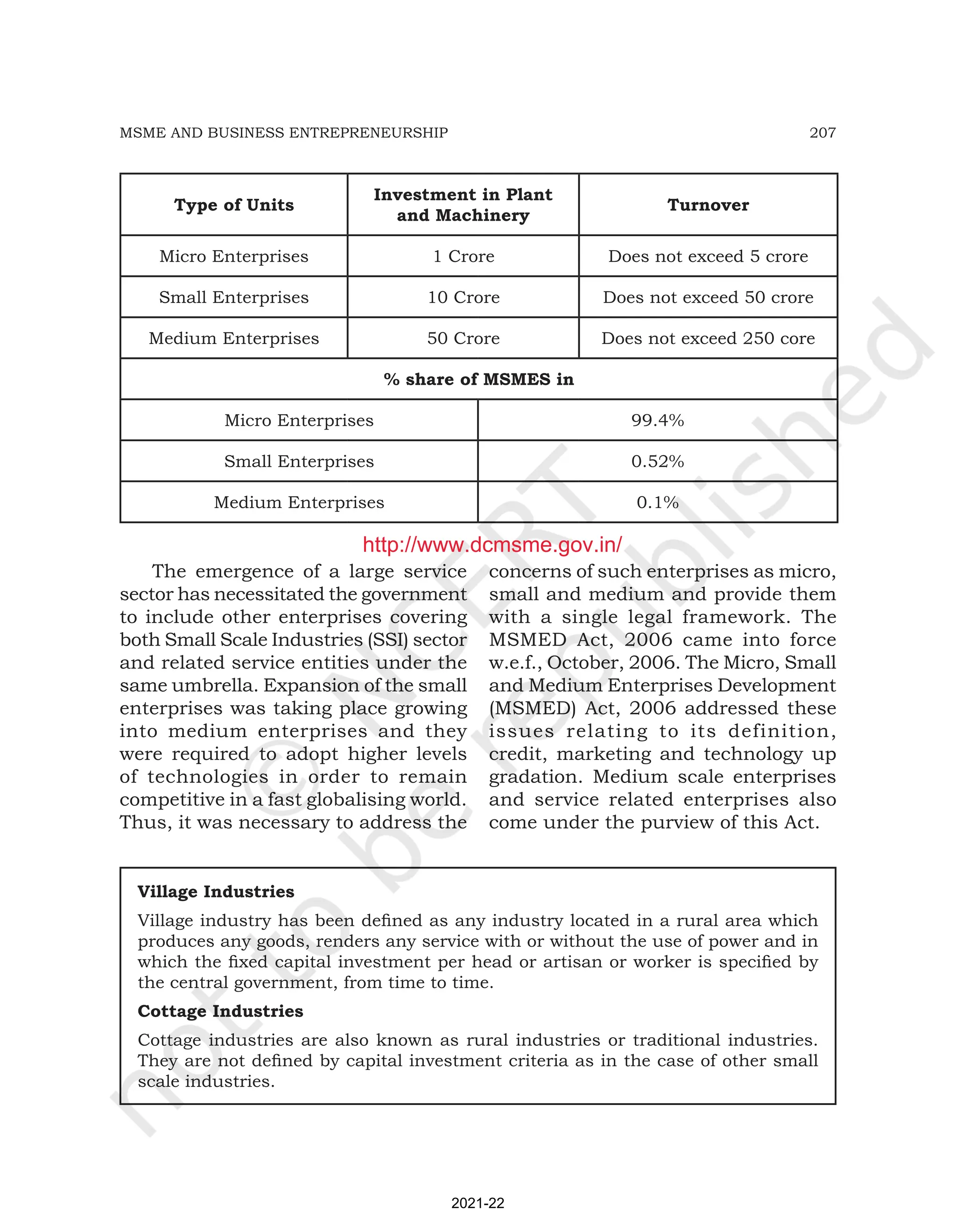
This document discusses Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in India. It covers the role and importance of MSMEs, defining their size based on investment and turnover, and some of the key problems they face. MSMEs are the largest employers in India after agriculture, and contribute significantly to GDP, exports, and balanced regional development. However, they struggle with issues like lack of access to adequate financing, raw materials, managerial skills, effective marketing, and global competition. Entrepreneurship and innovation are important for the growth and success of MSMEs.